Evaluar la persistencia terapéutica, el coste sanitario y las reacciones adversas en pacientes tratados con oxibutinina y mirabegrón para el tratamiento de la vejiga hiperactiva en condiciones de práctica médica habitual.
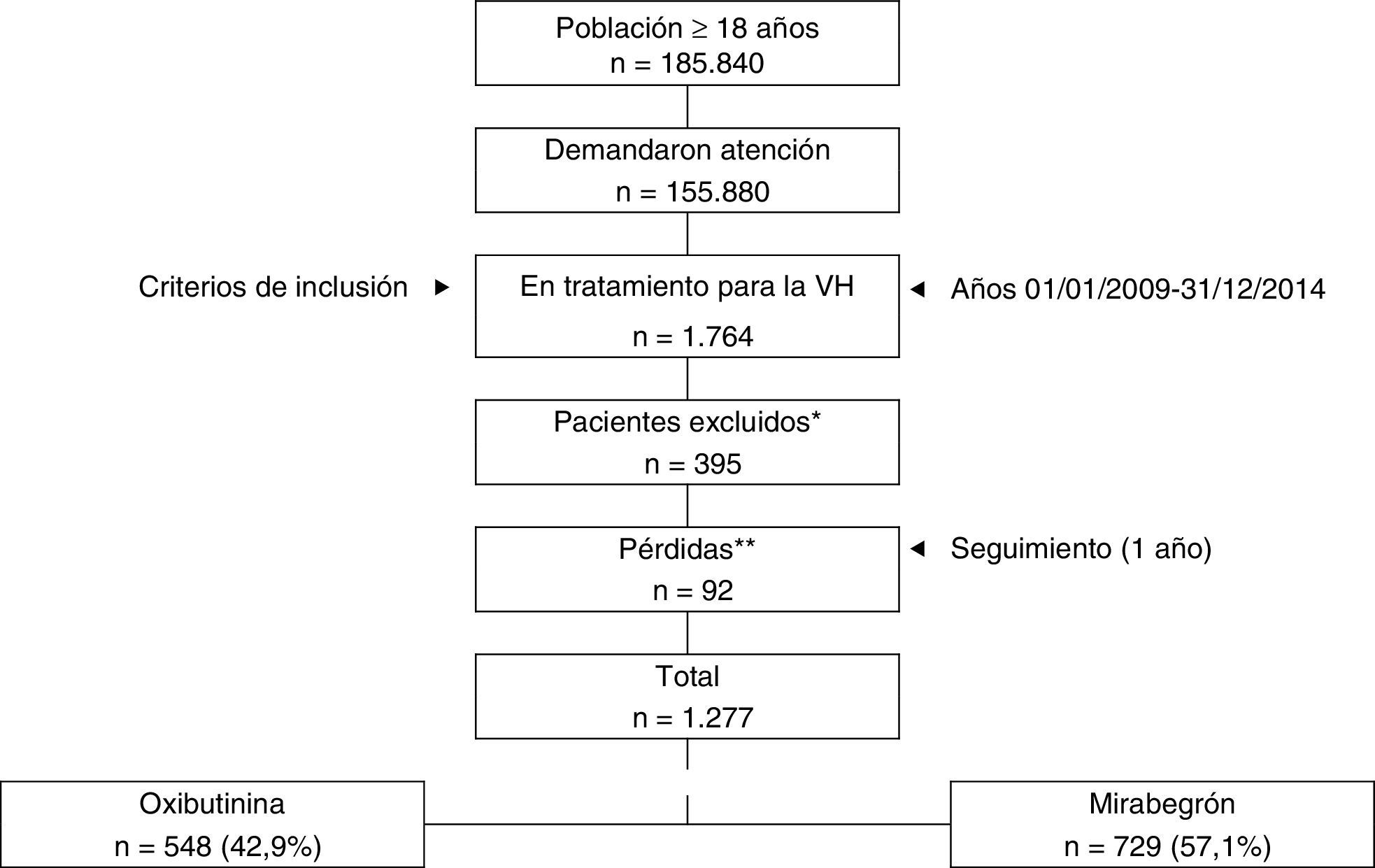
Pacientes y métodosSe diseñó un estudio observacional, multicéntrico, retrospectivo, realizado a partir de registros médicos de pacientes pertenecientes a 3 áreas geográficas distintas (Barcelona, Girona, Asturias). Se analizaron los 2 grupos de estudio (oxibutinina y mirabegrón). El seguimiento se realizó durante un año. La persistencia se definió como el tiempo (meses) sin abandono del tratamiento inicial o sin cambio a otra medicación al menos 60 días después de la prescripción inicial. Principales medidas: comorbilidad, uso de recursos sanitarios y reacciones adversas. Programa SPSSWIN; p<0,05.
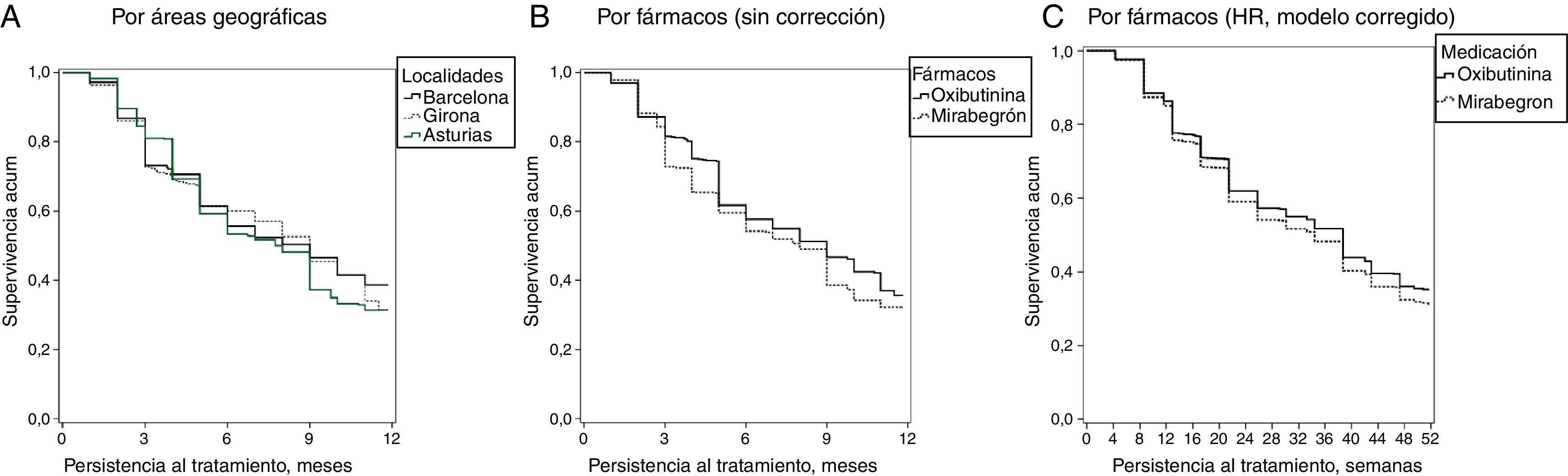
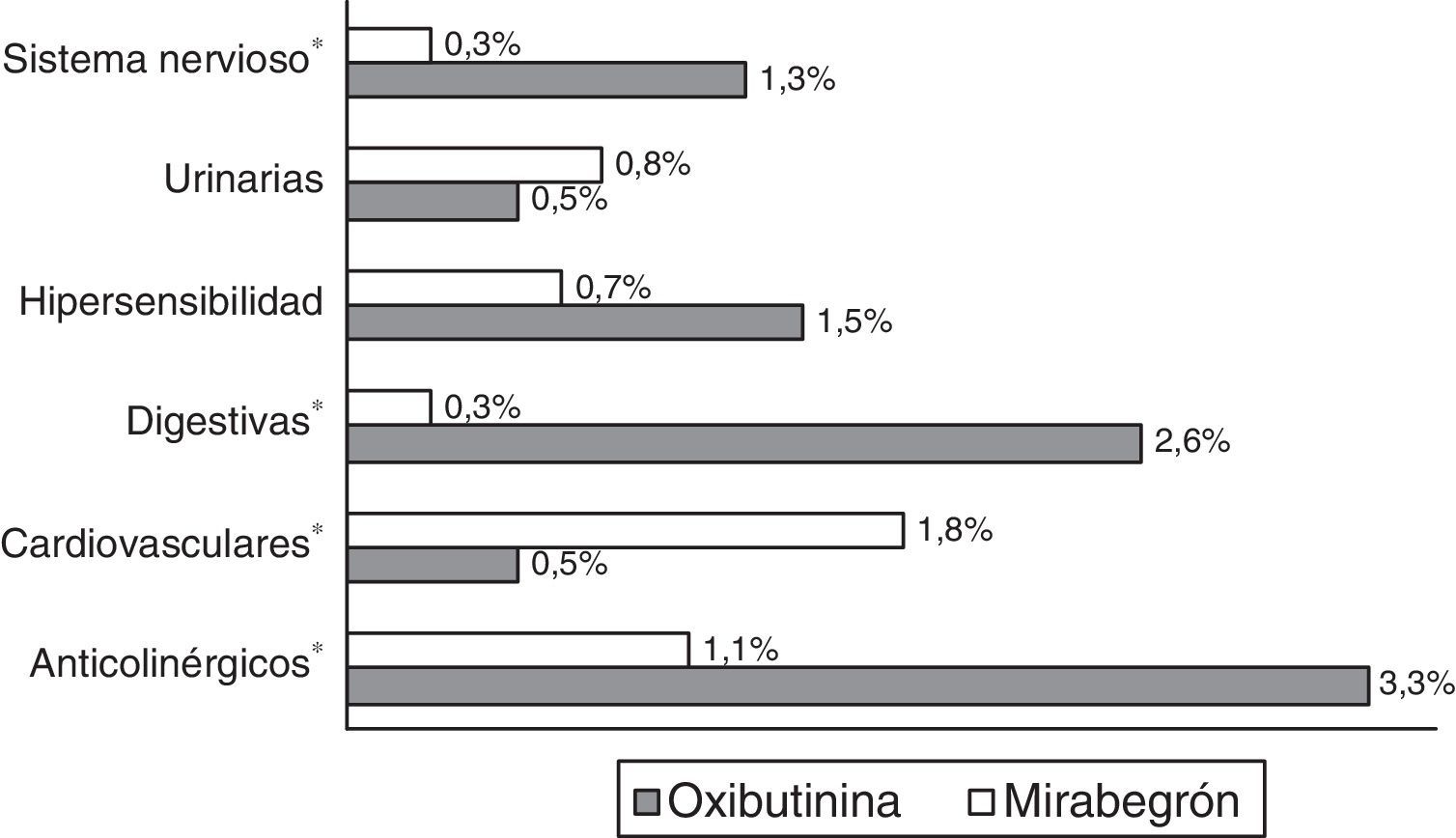
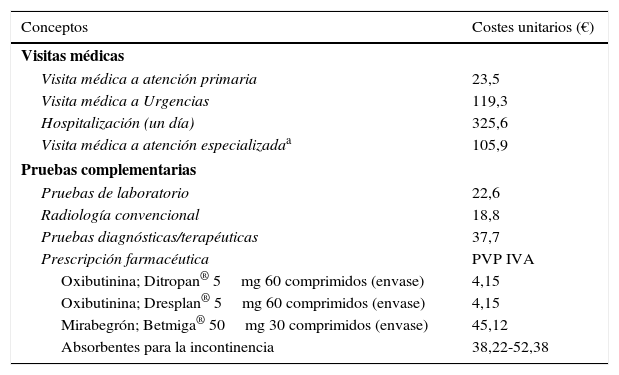
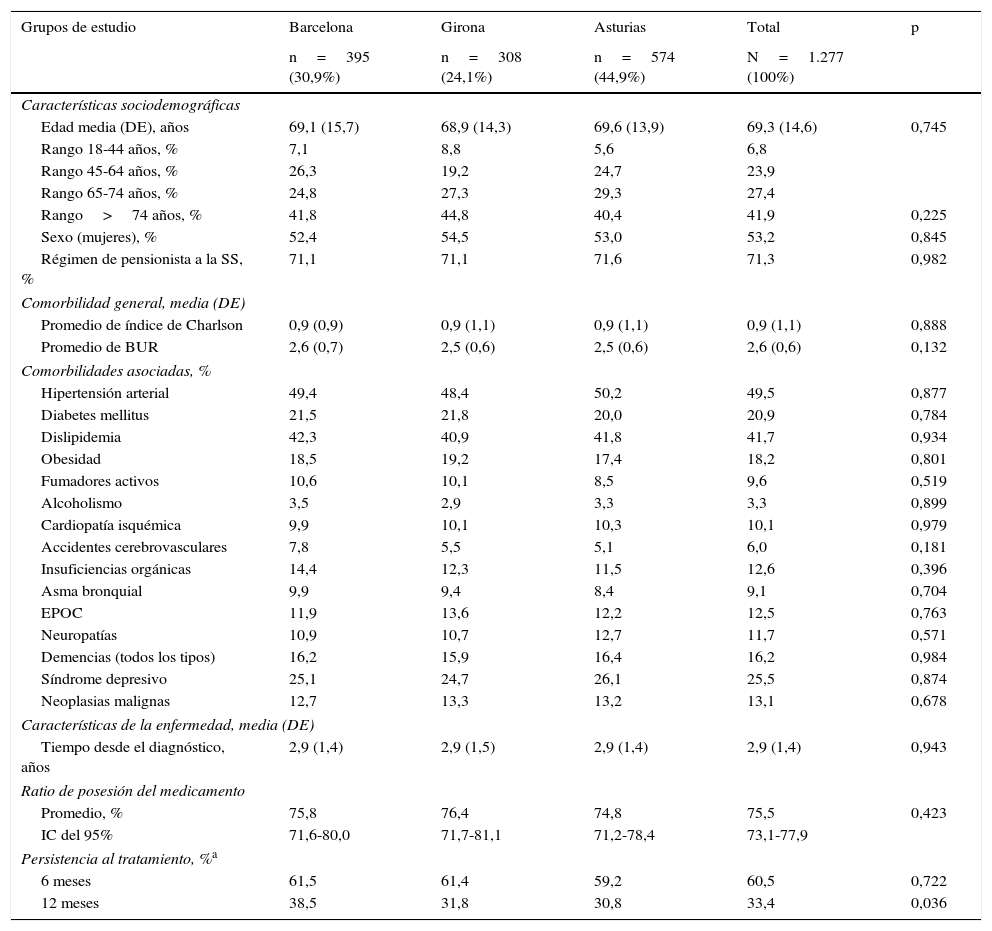
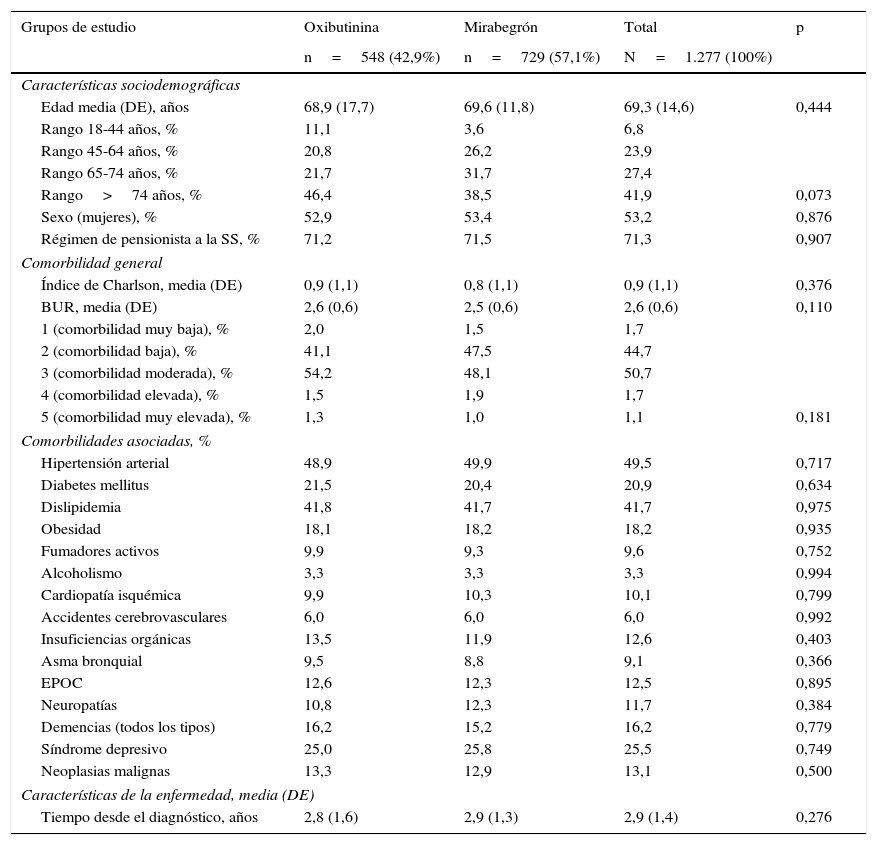
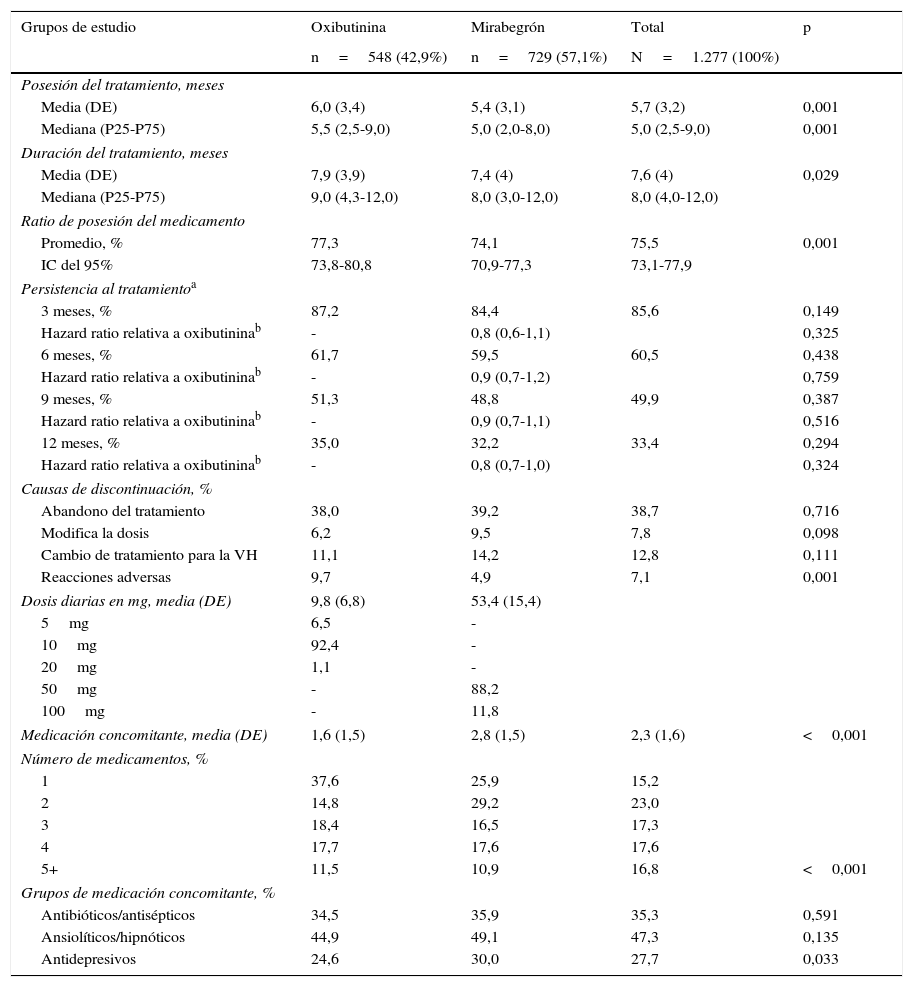
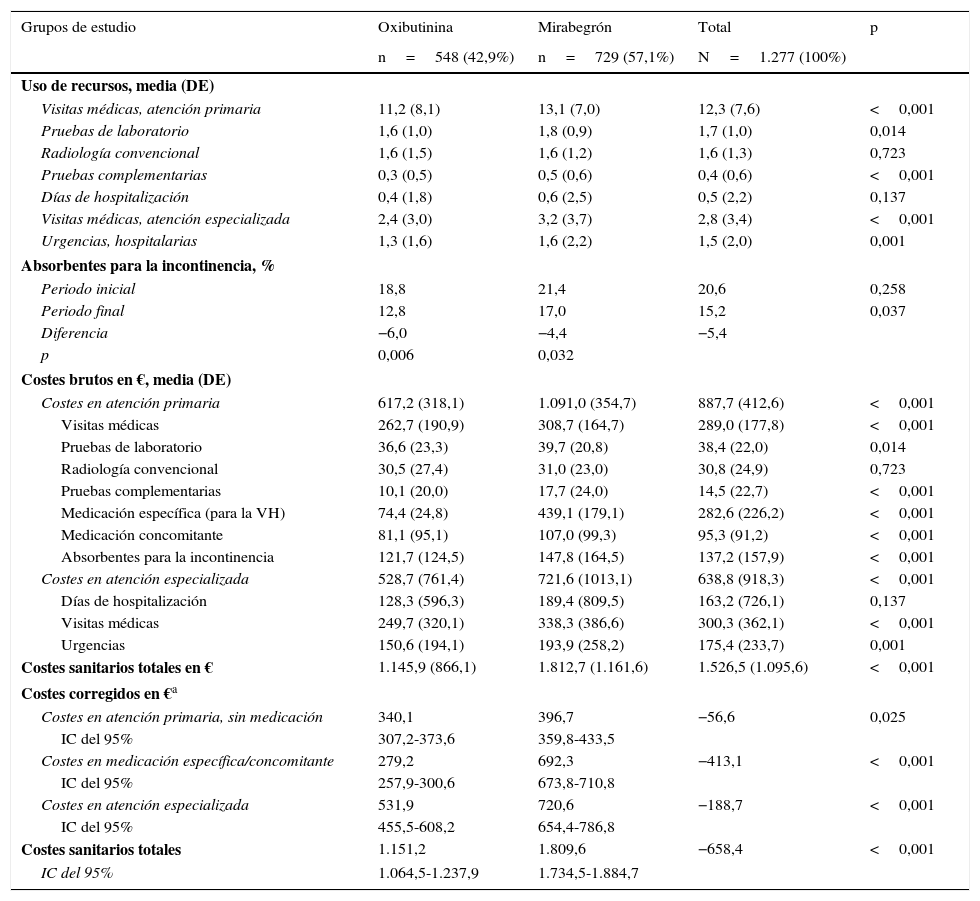
ResultadosSe analizaron 1.277 sujetos. La media de edad fue de 69,3 años y el 53,2% fueron mujeres. Por grupos: 42,9% oxibutinina y 57,1% mirabegrón. Las características demográficas y la morbilidad fueron parecidas. Los pacientes en tratamiento con oxibutinina en comparación con mirabegrón presentaron una similar persistencia al tratamiento (35,0 vs. 32,2%, p=0,294), aunque menores costes (1.151,2 vs. 1.809,6€, p<0,001). Las diferencias mayores se observaron en el precio de la medicación (279,2 vs. 692,3€, p<0,001; diferencia: −413,1€) y en las reacciones adversas (9,7 vs. 4,9%, p<0,001).
ConclusionesLos pacientes en tratamiento con oxibutinina frente a mirabegrón para la vejiga hiperactiva se asociaron a una parecida persistencia al tratamiento, menores costes sanitarios y mayores tasas de reacciones adversas de oxibutinina frente a mirabegrón.
To evaluate therapeutic persistence, healthcare resources, medical costs and adverse events of oxybutynin and mirabegron treatments in patients with overactive bladder in routine medical practice.
Patients and methodsAn observational, retrospective, multicentre study was carried out using the records of patients attended to in 3 different geographic locations (Barcelona, Girona, Asturias). An analysis was made on the 2 study groups (oxybutynin and mirabegron). Follow-up time was one year. Persistence was defined as the time (months), without discontinuation of the initial treatment, or without change of treatment at least 60 days after the initial prescription. Primary endpoints: comorbidity, healthcare resources used, and adverse events. The data was analysed using the SPSSWIN Program, with a significance of P<.05.
ResultsOf the total of1,277 patients included in the study, 42.9% were on oxybutynin and 57.1% mirabegron. The mean age was 69.3 years and 53.2% were female. Demographic characteristics and morbidity were similar between the drugs and had a similar persistence (35.0% oxybutynin vs. 32.2% mirabegron, P=.294), although their costs were lower (1,151.2 vs. €1,809.6, P<.001). The biggest differences were observed in the price of medication (279.2 vs. €692.3, P<.001; a variation of: −€413.1); and adverse events (9.7 vs. 4.9%, P<.001).
ConclusionsPatients treated with oxybutynin vs. mirabegron for overactive bladder had similar persistence with the treatment, lower healthcare costs, but with higher oxybutynin vs. mirabegron adverse reaction rates.
Artículo
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEMERGEN, (https://www.semergen.es/index.php?seccion=biblioteca&subSeccion=revistaSEMERGEN ) y autentifíquese.
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora