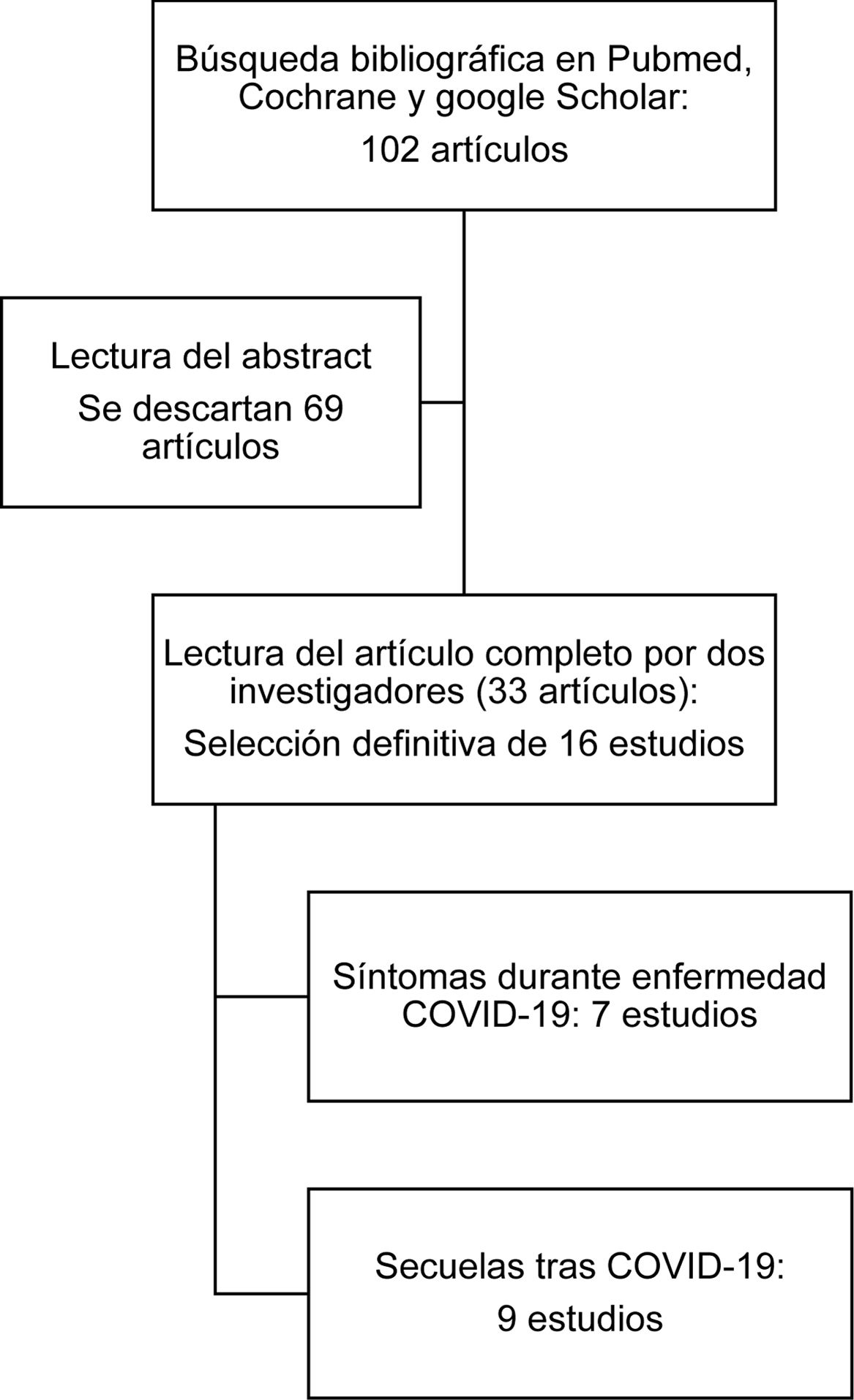
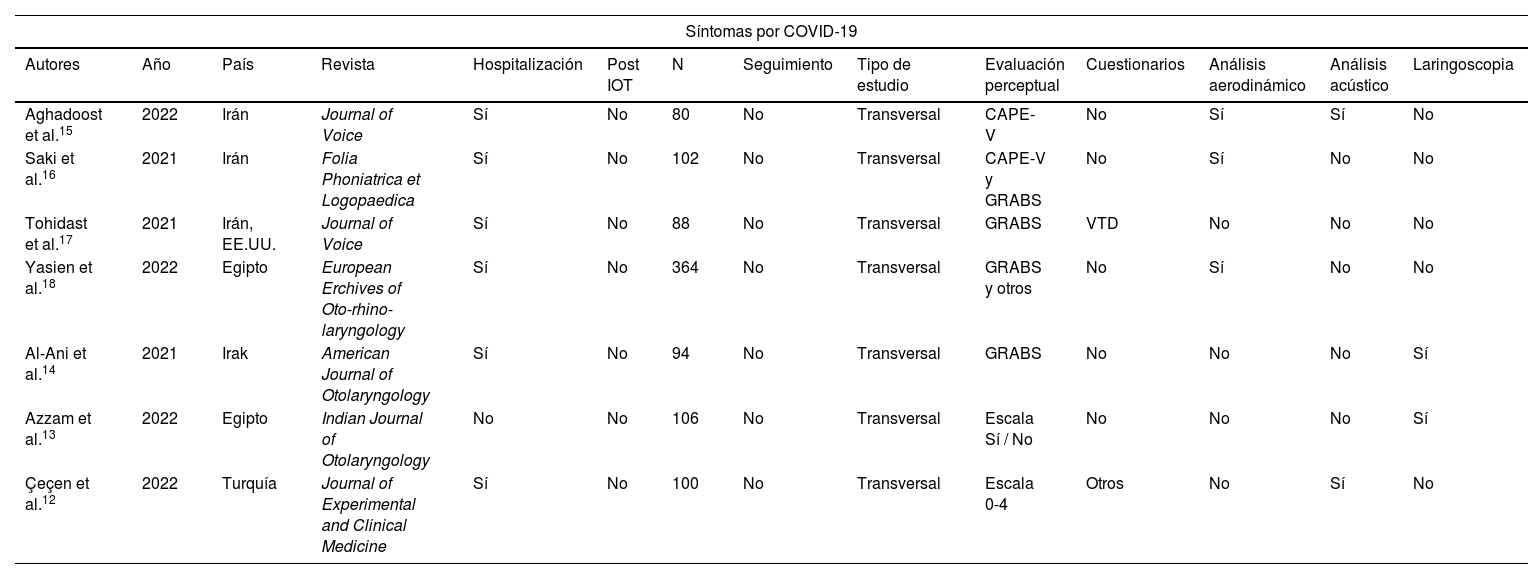
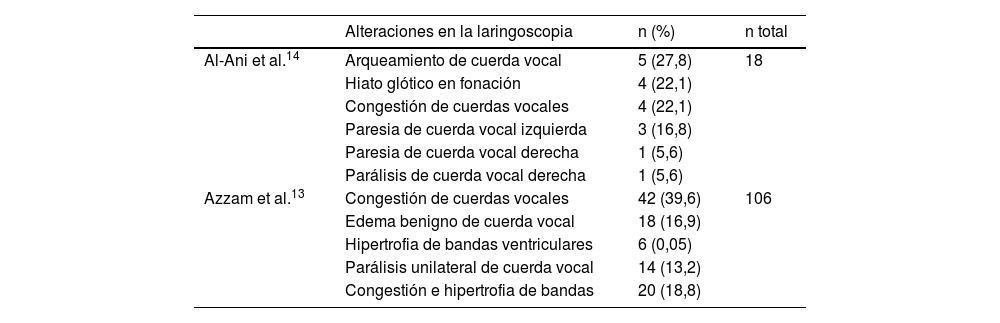
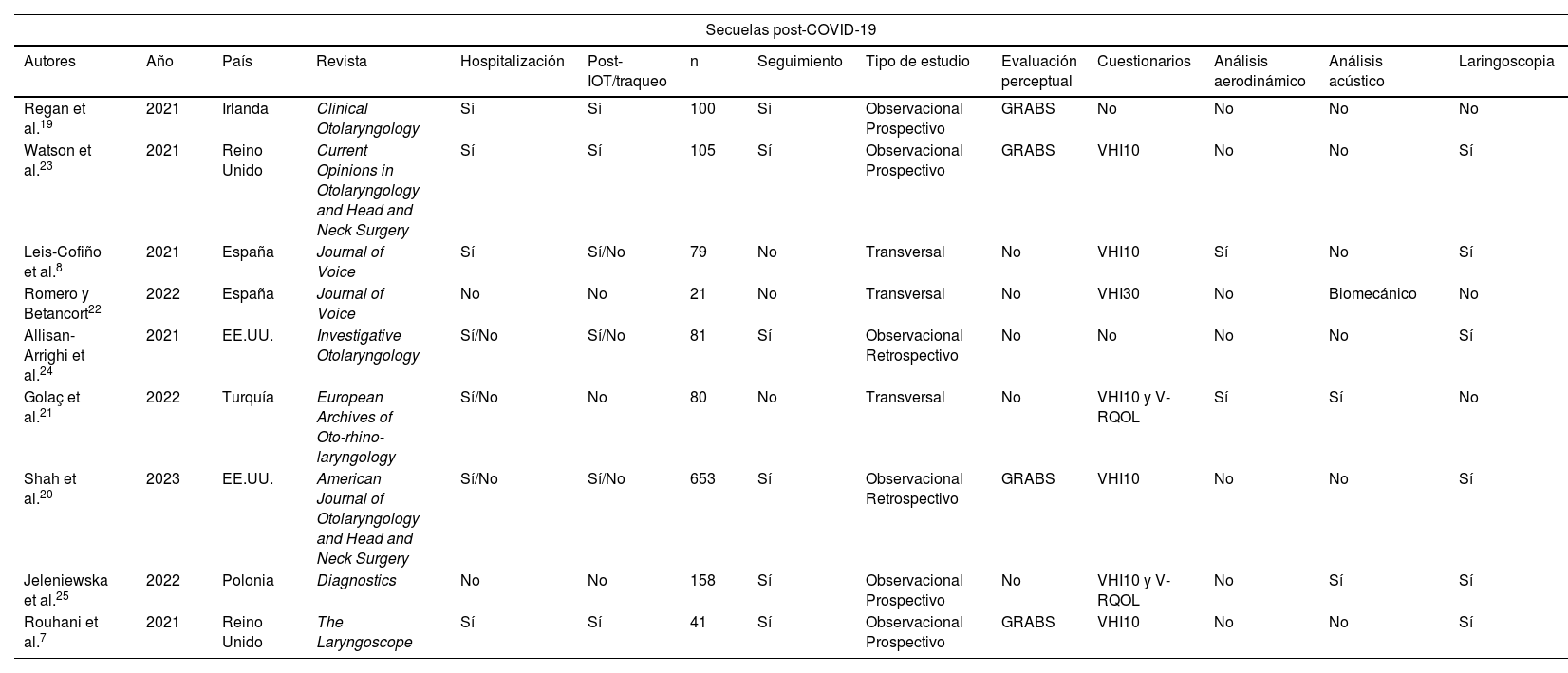
Entre los síntomas que presentan los pacientes con infección por SARS-CoV-2 podemos encontrar diversas alteraciones otorrinolaringológicas. La disfonía aparece en hasta el 79% de los pacientes infectados durante la fase aguda. La disfonía también puede presentarse como secuela, en muchas ocasiones infraestimada, posiblemente debido a su aparición junto con otros síntomas, también en pacientes tras intubación prolongada o traqueostomía. Presentamos una revisión sistemática de la literatura con búsqueda bibliográfica en PubMed, Cochrane y Google Scholar, con términos MESH incluyendo estudios en inglés y en español. Se analizan los resultados de los estudios encontrados y de las manifestaciones vocales en pacientes durante la enfermedad por COVID-19 y las secuelas producidas. La disfonía es una manifestación aguda de la COVID-19 con alteraciones en análisis aerodinámico y acústico y en la fibrolaringoscopia. La disfonía post-COVID puede ser un síntoma persistente que es a menudo infraestimado, requiriendo manejo multidisciplinar e intervención logopédica. Las secuelas laríngeas son frecuentes en pacientes post-intubación o post-traqueostomía y se relacionan con el tiempo de intubación, el número de tubo, la pronación y las secuelas respiratorias.
Among the symptoms presented by patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, we can find various otorhinolaryngological alterations. Dysphonia appears in up to 79% of infected patients during the acute phase. Dysphonia can also occur as a sequelae, often underestimated, possibly due to its appearance along with other symptoms, also in patients after prolonged intubation or tracheostomy. We present a systematic review of the literature with a bibliographic search in PubMed, Cochrane and Google Scholar, with MESH terms including studies in English and Spanish. The results of the studies found and the vocal manifestations in patients during COVID-19 disease and the consequences produced are analysed. Dysphonia is an acute manifestation of COVID-19 with alterations in aerodynamic and acoustic analysis and in fibrolaryngoscopy. Post-COVID dysphonia can be a persistent symptom that is often underestimated, requiring multidisciplinary management and speech therapy intervention. Laryngeal sequelae are common in post-intubation or post-tracheostomy patients and are related to intubation time, tube number, pronation and respiratory sequelae.