After surgical resection of papilloma, adjuvant therapy may be recommended for the control of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP). As the efficacy of adjuvant therapy remains unproven, the aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of cidofovir versus bevacizumab used as adjuvant therapies for the control of RRP.
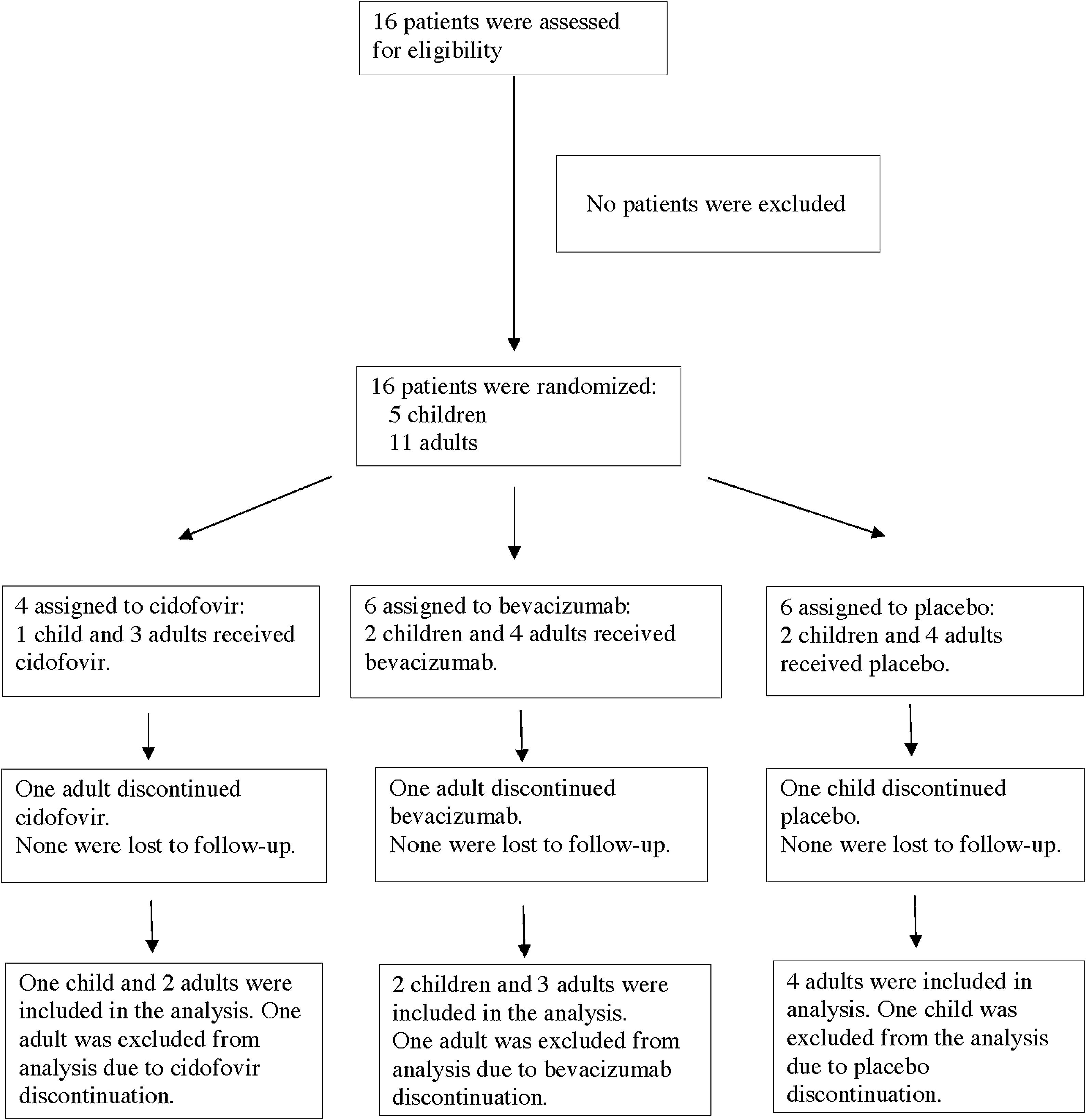
MethodsThis randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study was performed in a national respiratory disease referral centre. Patients with RRP were recruited prospectively and were divided into juvenile or adult RRP. Participants were randomly assigned to receive adjuvant therapy with cidofovir, bevacizumab or placebo. The study drug or placebo was administered after direct microlaryngoscopy with papilloma resection using cold instruments. The Derkay severity score and the Voice Handicap Index (VHI) were assessed at 3–6-week intervals, for a total of 3 visits. Follow-up included VHI and Derkay score assessments at 2-month intervals over the course of one year. Annual rates before and after surgical treatment were compared.
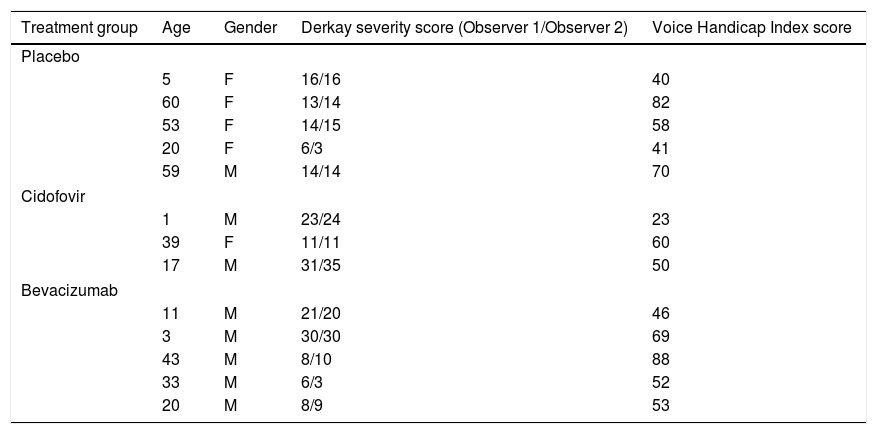
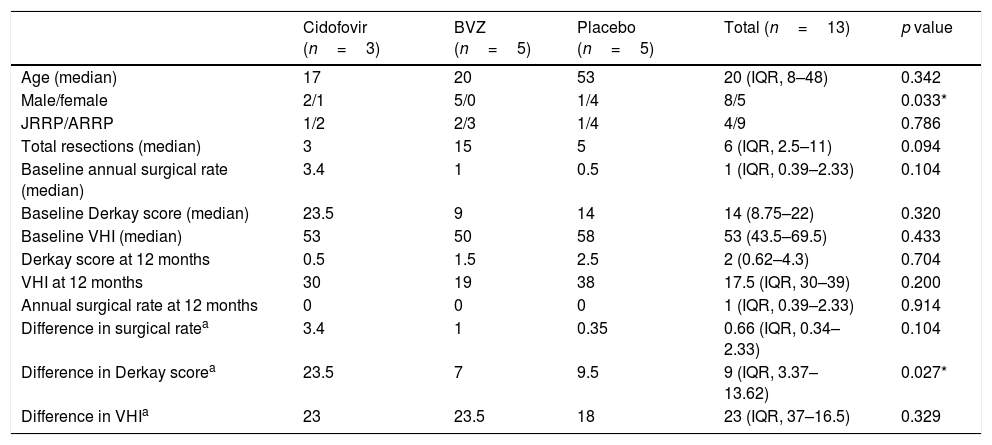
ResultsFive children and 11 adults were enrolled in the study. After one year, the group treated with cidofovir had a significant decrease in Derkay score (p=.027). No difference between treatment arms was observed in the annual surgery rate. There was a significant decrease in the VHI score in all treatment groups (p<.001), and no significant difference was observed between groups (p=.32).
ConclusionWhile we observed a significant decrease in RRP severity with intralesional cidofovir, we were unable to provide proof of efficacy of intralesional bevacizumab.
Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT02555800.
Tras la extirpación quirúrgica de los papilomas, puede recomendarse terapia adyuvante para el control de la papilomatosis respiratoria recurrente (PRR). Como la eficacia de la terapia adyuvante no está demostrada, el objetivo de este estudio fue comparar la eficacia de cidofovir frente a bevacizumab, utilizados como terapias adyuvantes para el control de PRR.
MétodosEstudio piloto aleatorizado, doble ciego y controlado por placebo, realizado en un centro nacional de referencia de enfermedades respiratorias. Se reclutó prospectivamente a los pacientes con PRR, y se dividieron en 2 grupos: PRR de jóvenes y PRR de adultos. A los participantes se les asignó aleatoriamente la administración de terapia adyuvante de cidofovir, bevacizumab o placebo. La administración de los fármacos de estudio o placebo se realizó tras practicar microlaringoscopia directa con extirpación de papilomas, utilizando instrumental frío. Se llevaron a cabo evaluaciones utilizando la puntuación de gravedad de Derkay y la escala VHI (Voice Handicap Index) a intervalos de 3 a 6 semanas, con un total de 3 visitas. El seguimiento incluyó evaluación de las escalas VHI y Derkay a intervalos de 2 meses, durante el curso de un año. Se compararon las tasas anuales pre- y postratamiento quirúrgico.
ResultadosEl estudio incluyó 5 niños y 11 adultos. Transcurrido un año, el grupo tratado con cidofovir reflejó una reducción significativa en la escala Derkay (p=0,027). No se observó diferencia alguna entre las ramas terapéuticas en la tasa quirúrgica anual. Se vio una reducción significativa en la puntuación VHI en todos los grupos terapéuticos (p<0,001), y no se observó diferencia significativa entre los grupos (p=0,32).
ConclusiónA pesar de verse una reducción significativa de la gravedad de PRR con la administración de cidofovir intralesional, no pudimos probar la eficacia de bevacizumab intralesional.