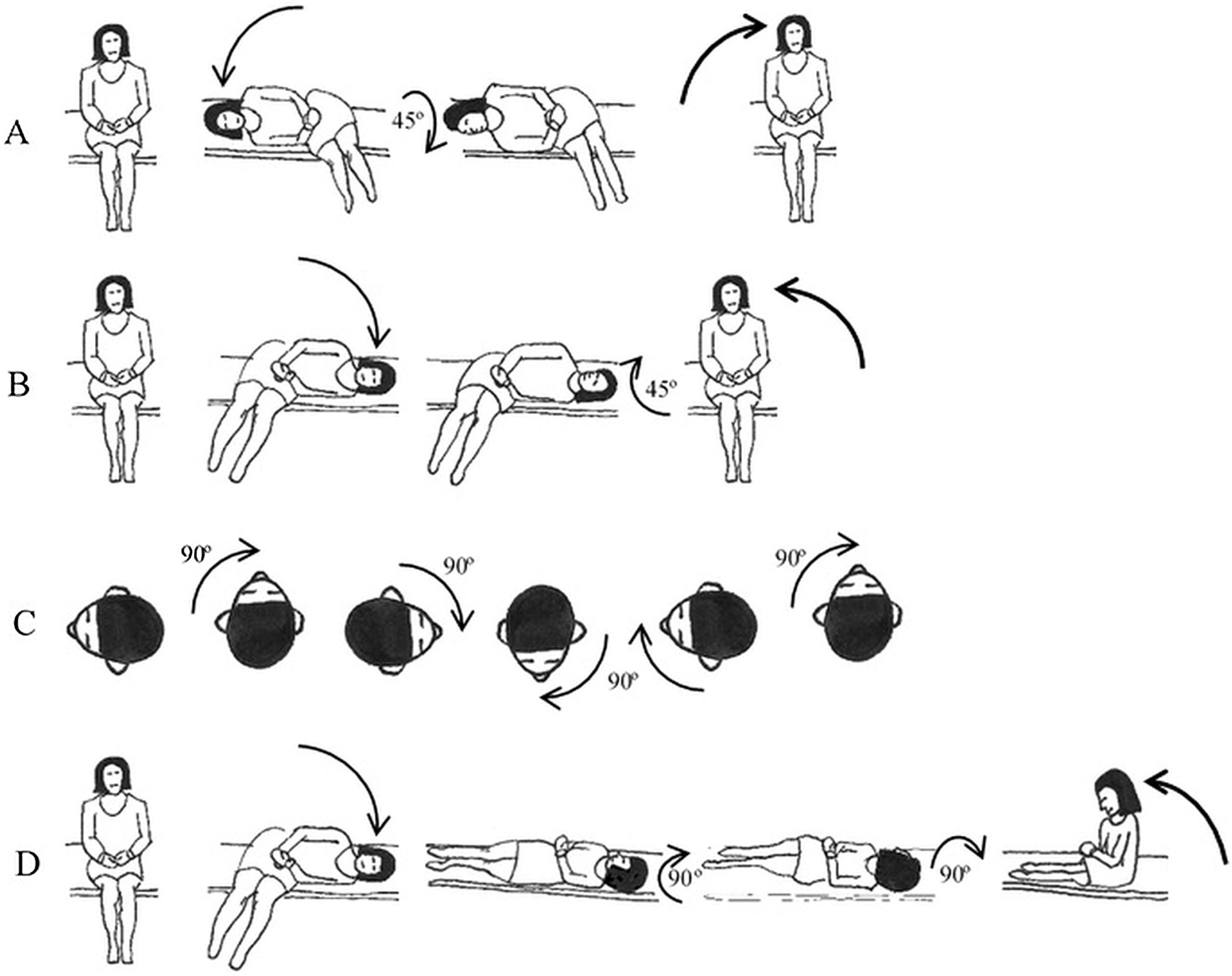
Multiple repositioning maneuvers have been described to treat lateral semi-circular canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (LC-BPPV) patients. In this study, we compare efficacy of four therapeutic repositioning maneuvers for LC-BPPV patients and aim to identify clinical variables associated with persistent disease.
Material and methodsA prospective study was conducted at a tertiary center, between January 2017 and September 2019. Patients diagnosed with LC-BPPV were randomly treated with Gufoni or barbecue-roll maneuvers (for the geotropic variant) and Gufoni-Appiani, barbecue-roll or Zuma-e-Maia maneuvers (for the apogeotropic form). Efficacy was compared and statistical analysis was performed to find clinical factors associated with no response.
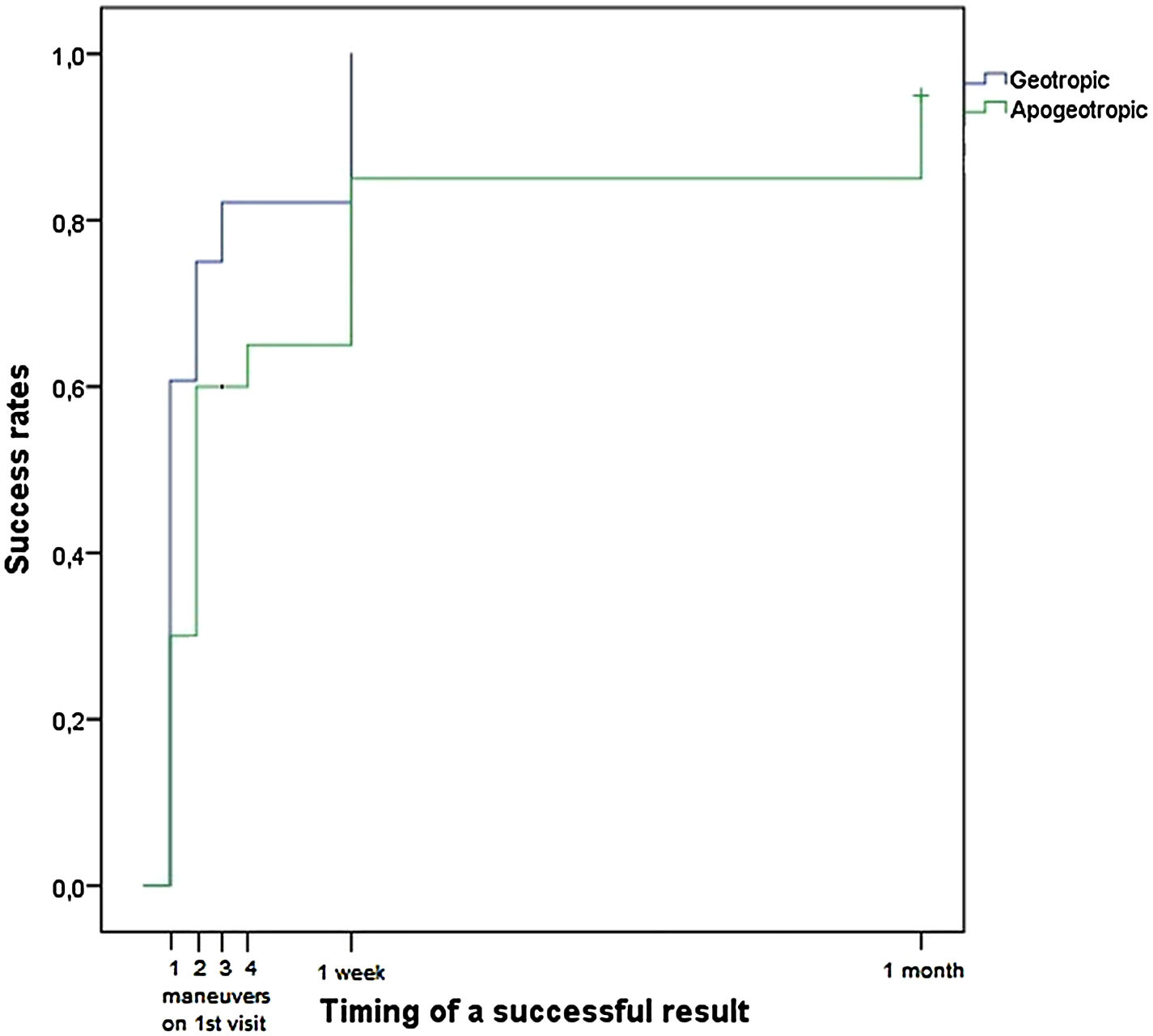
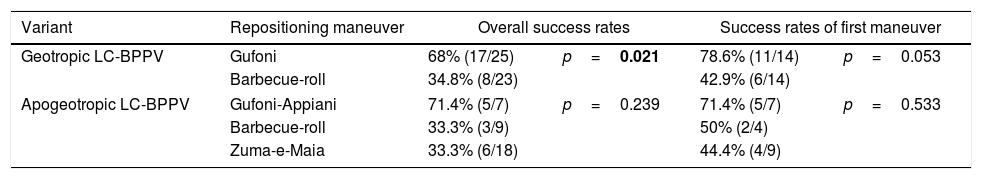
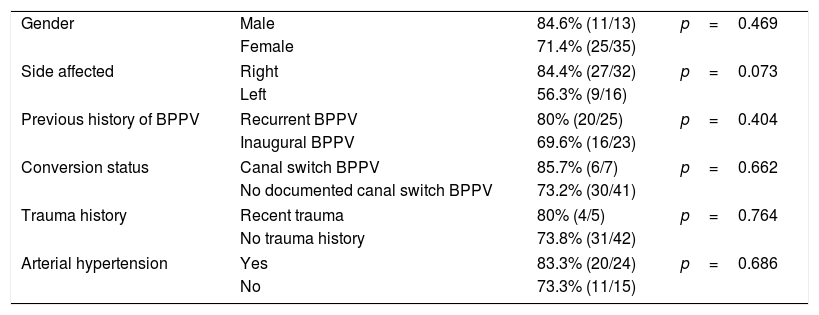
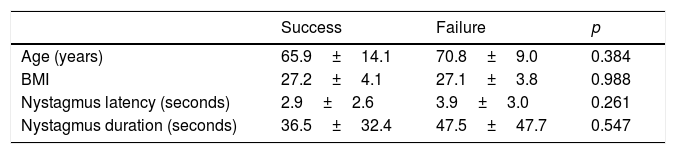
ResultsForty-eight patients and 82 maneuvers were included. Female patients and right side were more commonly affected. The mean age was 67 years. Seven cases (14.6%) resulted from a canal-switch. One single maneuver resolved 23 cases (47.9%) and the success rate rose to 75% at the end of the first visit (after up to 4 maneuvers) and to 93.8% after a-week of follow-up. Success rates were significantly better with Gufoni (68%) than with barbecue roll (34.8%; p=0.021) in geotropic LC-BPPV and better with Gufoni-Appiani (71.4%) than barbecue roll and Zuma-e-Maia maneuvers (33.3%; p=0.239) in apogeotropic LC-BPPV. Higher rates of persistent disease after first visit were found with older patients, left side and apogeotropic LC-BPPV and with longer latency and duration diagnostic nystagmus.
ConclusionOur study suggests that Gufoni and Gufoni-Appiani maneuvers may be the most efficacious treatment for geotropic and apogeotropic LC-BPPV, respectively, compared to barbecue-roll and Zuma-e-Maia maneuvers.
Se han descrito múltiples maniobras de reposicionamiento para tratar a los pacientes con vértigo postural paroxístico benigno del canal semicircular lateral (VPPB-CSL). En este estudio comparamos la eficacia de 4 maniobras de reposicionamiento terapéutico para pacientes de BPPV-CSL, con el objetivo de identificar las variables clínicas asociadas a la persistencia de la enfermedad.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo en un centro terciario, entre enero de 2017 y septiembre de 2019. Se trató aleatoriamente a los pacientes diagnosticados de VPPB-CSL con las maniobras de Gufoni o Barbecue-Roll (para la variante geotrópica) y las maniobras de Gufoni-Appiani, Barbecue-Roll o Zuma-e-Maia (para la forma apogeotrópica), comparándose su eficacia y realizándose un análisis estadístico para encontrar los factores clínicos asociados a la falta de respuesta.
ResultadosEl estudio incluyó 48 pacientes y 82 maniobras. Las mujeres y el lado derecho fueron los más comúnmente afectados. La edad media fue de 67 años. Siete casos (14,6%) fueron resultado de un fenómeno de reentrada. Una única maniobra resolvió 23 casos (47,9%), elevándose la tasa de éxito al 75% al finalizar la primera visita (tras un máximo de 4 maniobras) y al 93,8% tras una semana de seguimiento. Las tasas de éxito fueron significativamente más altas con la maniobra de Gufoni (68%) en comparación con la de Barbecue-Roll (34,8%; p=0,021) en VPPB-CSL geotrópico, y también fueron más altas con las maniobras de Gufoni-Appiani (71,4%) en comparación con las de Barbecue-Roll y Zuma-e-Maia (33,3%; p=0,239) en VPPB-CSL apogeotrópico. Las tasas más altas de persistencia de la enfermedad tras la primera visita se encontraron en pacientes mayores, lado izquierdo y VPPB-CSL apogeotrópica, con mayor latencia y duración del nistagmo diagnóstico.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio sugiere que las maniobras de Gufoni y Gufoni-Appiani pueden ser el tratamiento más eficaz para VPPB-CSL geotrópico y apogeotrópico, respectivamente, en comparación con las maniobras de Barbecue-Roll y Zuma-e-Maia.