La lesión del nervio facial continúa siendo la complicación más grave de la cirugía de la glándula parótida. Debido a la creciente evidencia sobre las ventajas del uso de la monitorización intraoperatoria del nervio facial, se distribuyó una encuesta entre los miembros de la Sociedad Española de Otorrinolaringología y Cirugía de Cabeza y Cuello con el objetivo de determinar los patrones de uso en nuestro medio.
Material y métodosSe distribuyó un cuestionario que incluía 12 preguntas separadas en 3 secciones en formato e-mail a través del correo oficial de la Sociedad Española de Otorrinolaringología y Cirugía de Cabeza y Cuello. La primera sección de preguntas evaluaba las características demográficas, la segunda sección estaba relacionada con el patrón de uso de los sistemas de monitorización intraoperatoria del nervio facial y la tercera sección se refería a los litigios relacionados con la parálisis facial.
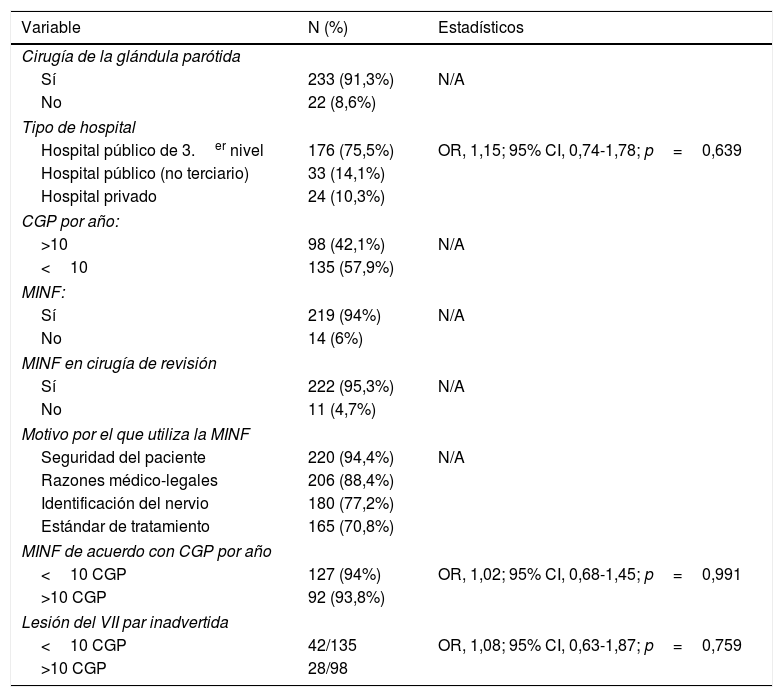
ResultadosSe enviaron un total 1.544 cuestionarios anónimos. Recibimos un total de 255 encuestas, para una tasa de respuesta global del 16,5%. De estos, 233 (91,3%) realizaban cirugía de glándula parótida y 94% usaban monitorización intraoperatoria del nervio facial. Un 94% de los encuestado usaba la monitorización intraoperatoria del nervio facial si realizaba menos de 10 parotidectomías por año y un 93,8% si realizaban más de 10 parotidectomías por año (OR, 1,02; IC del 95%, 0,68-1,45; p=0,991).
ConclusiónNuestros datos demuestran que la mayoría de los otorrinolaringólogos y cirujanos de cabeza y cuello en España están empleando la monitorización del nervio facial durante la cirugía de la glándula parótida. Casi todos coinciden en que esto busca mejorar las medidas de seguridad quirúrgica y consideran que la monitorización del nervio facial es útil para prevenir lesiones inadvertidas.
Facial nerve injury remains the most severe complication of parotid gland surgery. Due to the increasing evidence about the advantage of the use of intraoperative facial nerve monitoring, a survey was distributed among members of the Spanish Society of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery with the objective of determining patterns of its use.
Material and methodsA questionnaire which included 12 separate questions in 3 sections was distributed via email through the official email of the Spanish Society of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. The first section of questions was in relation to demographic characteristics, the second section was related to the pattern of monitoring use and the third section referred to litigation related to facial palsy.
Results1544 anonymous questionnaires were emailed. 255 surveys were returned, giving an overall response rate of 16.5%. From these, 233 (91.3%) respondents perform parotid gland surgery. Two-hundred nineteen (94%) respondents use intraoperative facial nerve monitoring. Of the respondents,94% used intraoperative facial nerve monitoring if in their current practice they performed fewer than 10 parotidectomies per year and 93.8% if they performed more than 10 (OR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.68-1.45; p=.991). With regard to lawsuits, just 3 (1.2%) of the respondents had a history of a parotid gland surgery–associated lawsuit and in just one case the facial nerve monitor was not used.
ConclusionOur data demonstrate that most otolaryngologists in Spain use intraoperative facial nerve monitoring during parotid gland surgery. Almost all of them use it to improve patient safety and consider that facial nerve monitoring should be helpful preventing inadvertent injury.