Wegener's granulomatosis (WG) is characterised by granulomatous vasculitis of the airway and glomerulonephritis. Since its first description, important advances have occurred in diagnosis and treatment; however, the aetiology remains unknown. Involvement of the head and neck region can often occur as the first and only manifestation. The aim of this study was to determine the frequency of symptoms and signs in the region of the nose, ears and pharynx-larynx in a group of patients with WG.
Materials and methodsWe evaluated 17 patients with WG defined by clinical, laboratory and pathology criteria. Detailed histories were taken and an ENT physical examination, audiometry, tympanometry and nasofibrolaryngoscopy were performed in all the patients.
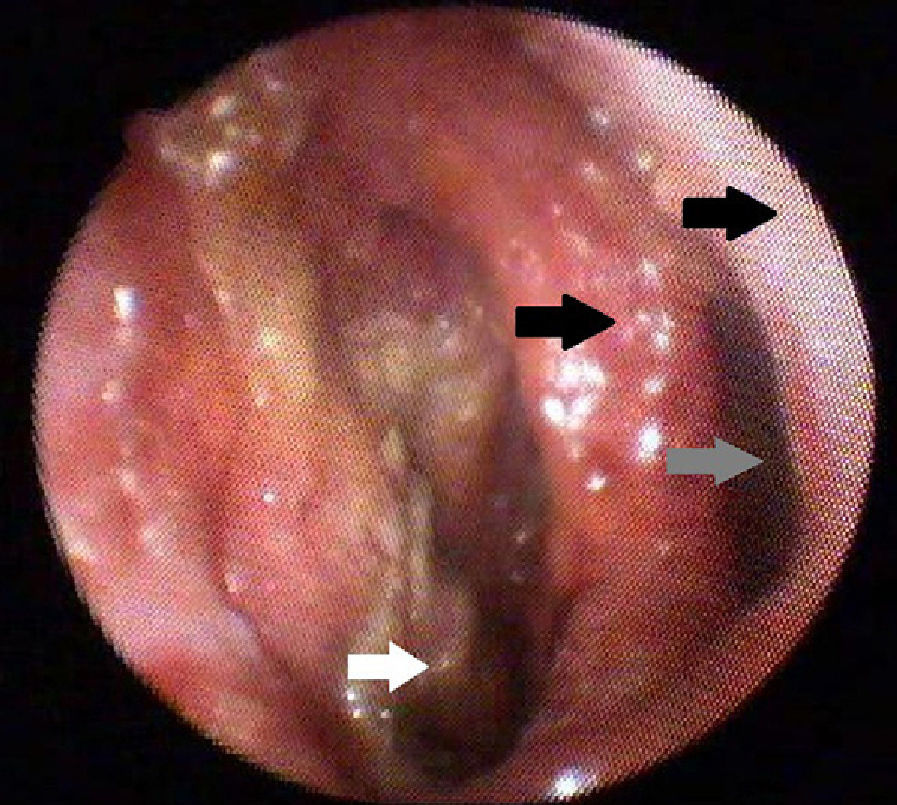
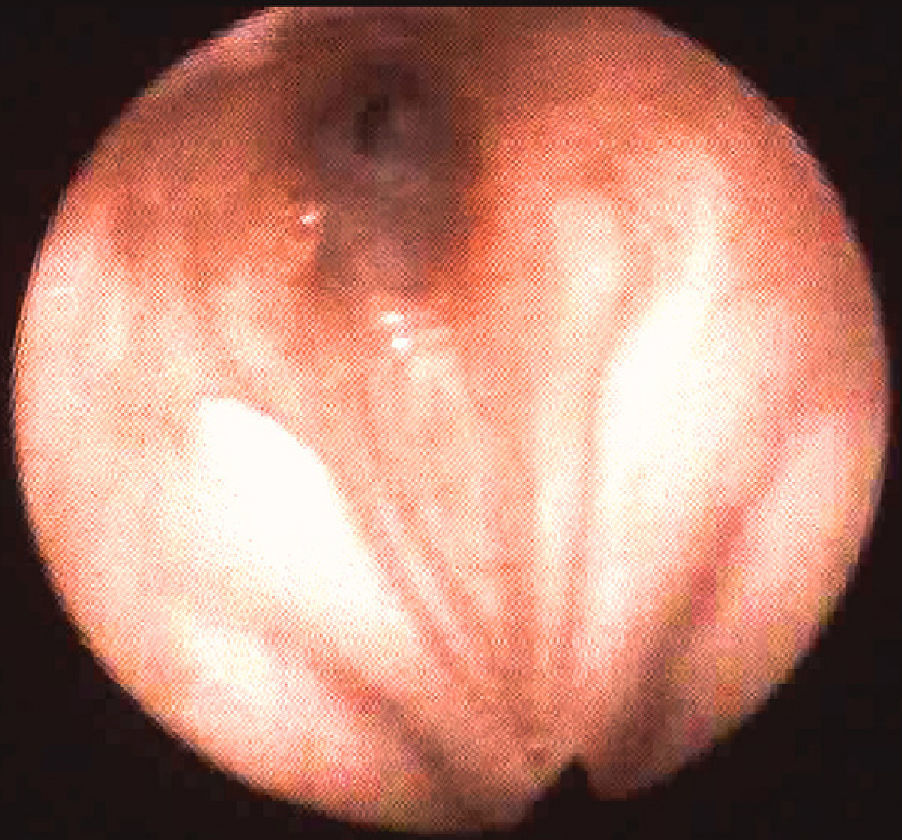
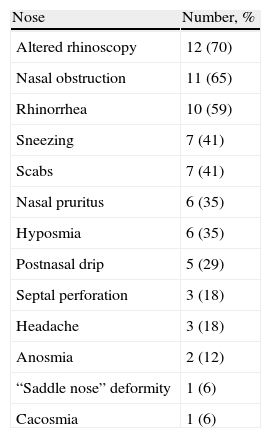
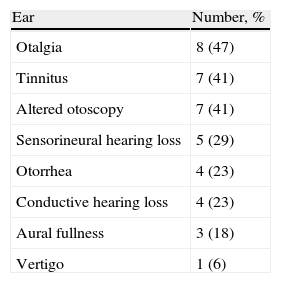
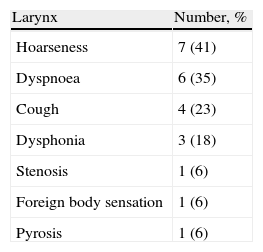
ResultsThe average age was 41.7 years and the average disease time was 9.12 years, ranging between 1 and 40. In these patients, 9 (53.1%) reported hearing loss and had altered audiometry, and 5 (55.6%) had bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. In the nose, nasal obstruction in 11 (64.8%) and rhinorrhoea in 10 (58.8%) were the most prevalent; there was altered endoscopy in 12 (70.2%). In the pharynx-larynx, dyspnoea in 6 (35%) and hoarseness in 7 (41.2%) were the most prevalent and 7 (41%) had an altered laryngoscopy.
ConclusionThe otolaryngologist plays an essential role in diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of these patients. Knowing common symptoms renders diagnosis and treatment easier and earlier.
La granulomatosis de Wegener (GW) se caracteriza por una vasculitis granulomatosa de vías aéreas y glomerulonefritis. Desde su primera descripción han surgido importantes avances para su diagnóstico y tratamiento, sin embargo su etiología aún es desconocida. La afectación de la región de cabeza y cuello muchas veces puede ocurrir como su primera y única manifestación. El objetivo del estudio es determinar la frecuencia de los síntomas y signos en la región de nariz, oídos y faringe-laringe en un grupo de pacientes con GW.
Materiales y métodosSe evaluaron 17 pacientes con diagnóstico de GW definido por criterios clínicos, de laboratorios y anatomopatológico. Fueron realizadas anamnesis detallada, un examen físico otorrinolaringológico minucioso, audiometría, impedanciometría y nasofibrolaringoscopia en todos los pacientes estudiados.
ResultadosLa edad media de los pacientes al diagnóstico fue de 41,7 años, y el tiempo promedio con la enfermedad fue de 9,12 años, variando entre uno y 40 años. De los pacientes estudiados, 9 (53,1%) tenían hipoacusia y presentaron audiometría alterada, y 5 (55,6%) presentaron hipoacusia neurosensorial bilateral. A nivel nasal, los síntomas más frecuentes fueron obstrucción en 11 (64,8%) y rinorrea en 10 (58,8%), con endoscopia alterada en 12 (70,2%). A nivel faringo-laríngeo, la disnea en 6 (35,2%) y la carraspera en 7 (41,2%), con laringoscopia alterada en 7 (41,2%).
ConclusiónEl otorrinolaringólogo desempeña un papel esencial para el diagnóstico, seguimiento y tratamiento de estos pacientes. Conocer sus síntomas más comunes facilita su diagnóstico y tratamiento precoces.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora