Pediatric tympanoplasty is still a matter of controversy. Many factors have been associated with the surgical outcome of tympanoplasty in children, including age, size and location of the perforation, surgical technique and Eustachian tube dysfunction. The optimal approach and timing of this surgery remains controversial.
This study aims to evaluate the outcomes of pediatric tympanoplasty and analyze factors that may influence the success of this surgery.
Materials and methodsA retrospective review was conducted which included children from 5 to 15 years old that underwent tympanoplasty with or without ossiculoplasty for chronic tympanic perforation in a tertiary care university hospital over a 6-year period. Patients were divided in two age groups (5 to ≤10 years old and >10 to 15 years old). Children with cholesteatoma or that underwent simultaneous mastoidectomy were excluded.
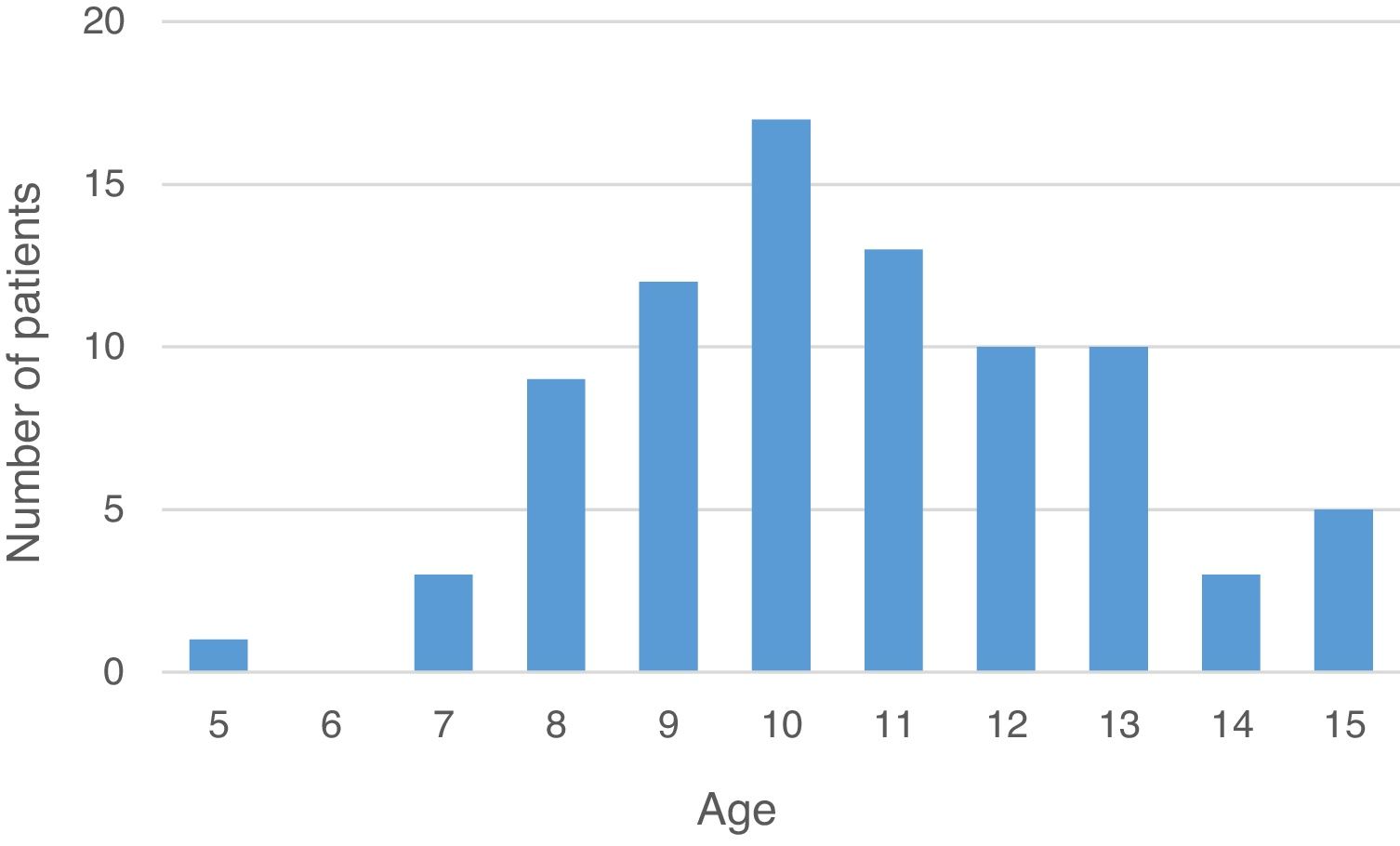
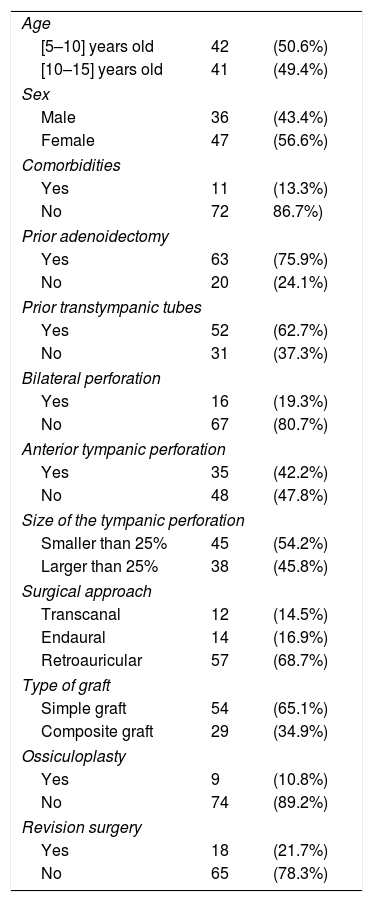
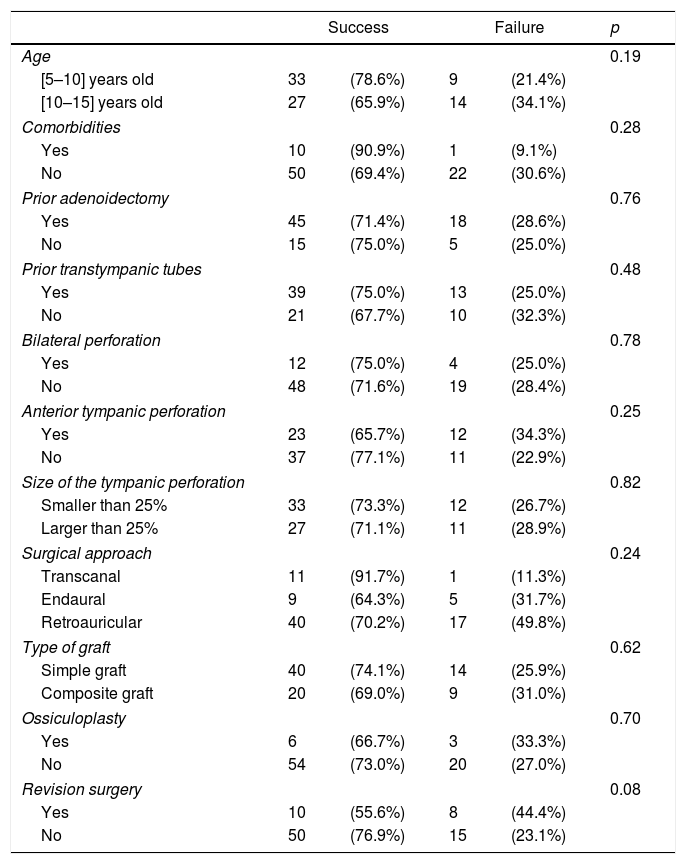
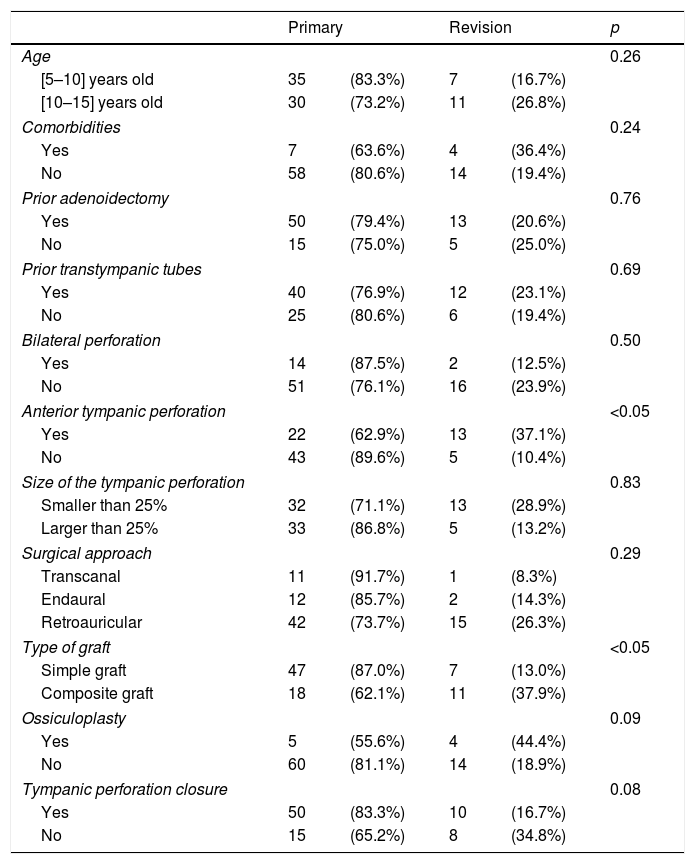
Results83 cases were included. Average age was 10.7±2.1 years and mean follow-up time was 9 months. Of the cases, 21.7% were revision surgeries. Successful closure of the tympanic membrane perforation was achieved in 76.9% of primary surgeries and 55.6% of revision surgeries. Most of the patients improved their conductive hearing-deficit. No statistical difference in graft failure was noted regarding age, presence of craniofacial dysmorphism and surgical approach. The use of simple graft (temporal muscle fascia or tragus perichondrium) was significantly superior in primary surgery (p<0.05). We also found a significant difference between the location of the perforation and revision surgery, with anterior perforations showing a higher risk (p<0.05).
ConclusionsPediatric tympanoplasty is effective in repairing chronic tympanic perforations. In our study, accepted predictors of surgical outcome such as age and surgical approach were not associated with graft failure.
La timpanoplastia pediátrica continúa siendo una cuestión controvertida. Se han asociado muchos factores al resultado quirúrgico de la timpanoplastia en niños, incluyendo la edad, el tamaño y la localización de la perforación, la técnica quirúrgica y la disfunción de la trompa de Eustaquio. El enfoque óptimo y la elección del momento de esta cirugía continúan siendo controvertidos. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar los resultados de la timpanoplastia pediátrica y analizar los factores que pueden influir en el éxito de esta cirugía.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó una revisión retrospectiva, que incluyó a niños de 5 a 15 años de edad sometidos a timpanoplastia con o sin osiculoplastia para perforación timpánica crónica en un hospital universitario terciario a lo largo de un periodo de 6 años. Se dividió a los pacientes en 2 grupos de edad (de 5 a ≤10 años, y >10 a 15 años). Se excluyó a los niños con colesteatoma o a los que se sometió simultáneamente a mastoidectomía.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 83 casos. La edad media fue de 10,7±2,1 años, y el tiempo medio de seguimiento fue de 9 meses. El 21,7% de los casos fueron cirugías de revisión. El cierre exitoso de la perforación de la membrana timpánica se logró en el 76,9% de las cirugías primarias, y el 55,6% de las cirugías de revisión. La mayoría de los pacientes mejoró su pérdida auditiva conductiva. No se apreció diferencia estadística en cuanto a fracaso del injerto en términos de edad, presencia de dismorfismo craneofacial y abordaje quirúrgico. El uso de injerto simple (fascia de músculo temporal o pericondrio tragal) fue significativamente superior en la cirugía primaria (p<0,05). Encontramos también una diferencia significativa entre la localización de la perforación y la cirugía de revisión, presentando las perforaciones anteriores un riesgo más alto (p<0,05).
ConclusionesLa timpanoplastia pediátrica es efectiva para reparar las perforaciones timpánicas crónicas. En nuestro estudio, los factores predictivos aceptados del resultado quirúrgico, tales como la edad y el abordaje quirúrgico, no estuvieron asociados al fracaso del injerto.