We have previously indicated that EGFR has a role in carcinogenesis in a subgroup of sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas (SNSCC). In addition, EGFR activates 2 of the most important intracellular signalling pathways: PI3K/pAKT/mTOR/pS6 and MAP pathway kinases. The objective of this study was to evaluate the involvement of the EGFR/PI3K/pAKT/mTOR/pS6 pathway and its relationship with clinical–pathological parameters and follow-up of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma.
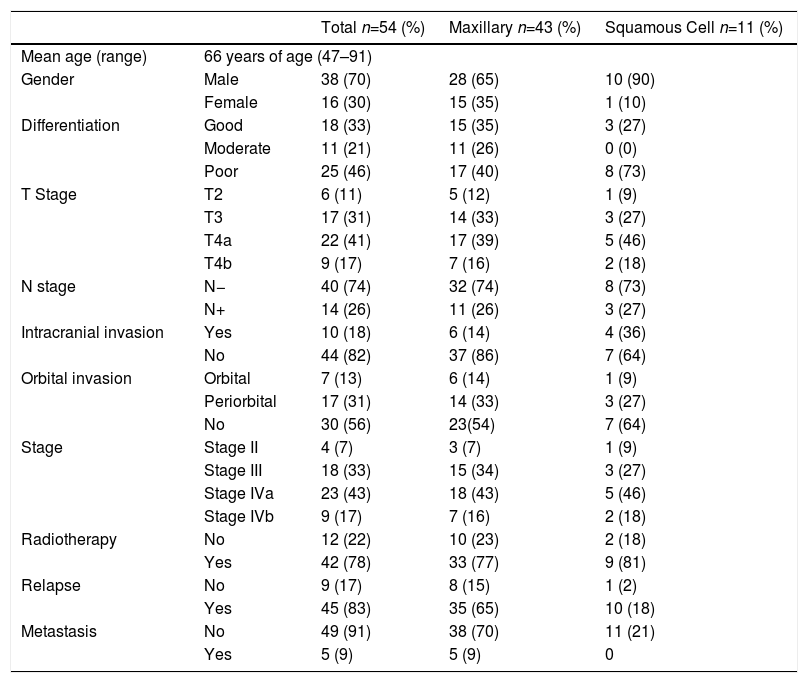
Material and methodsThe immunohistochemical expression of different components of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/pS6 pathway and its relationship with various clinical-pathological parameters was studied in a series of 54 patients with SNSCC.
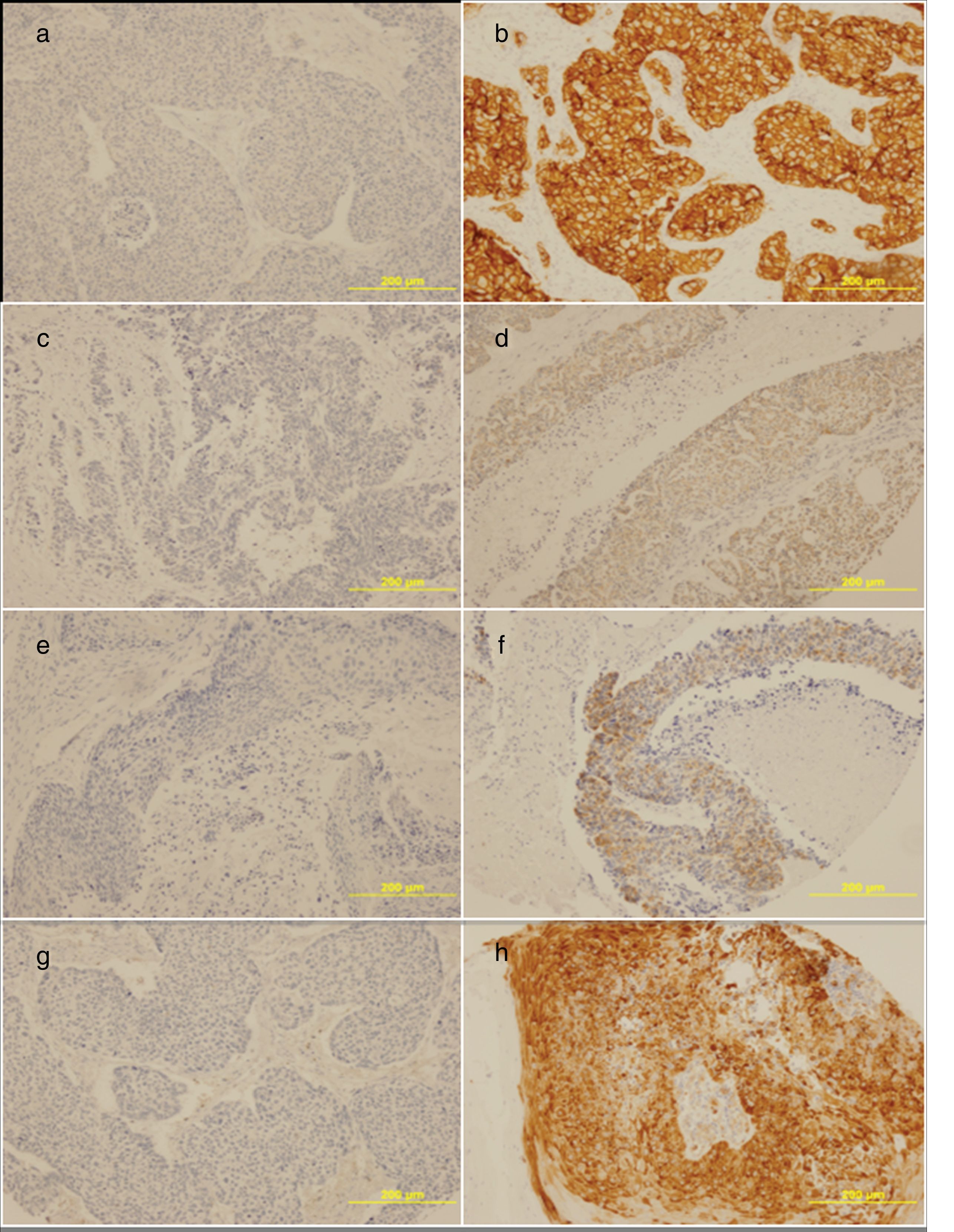
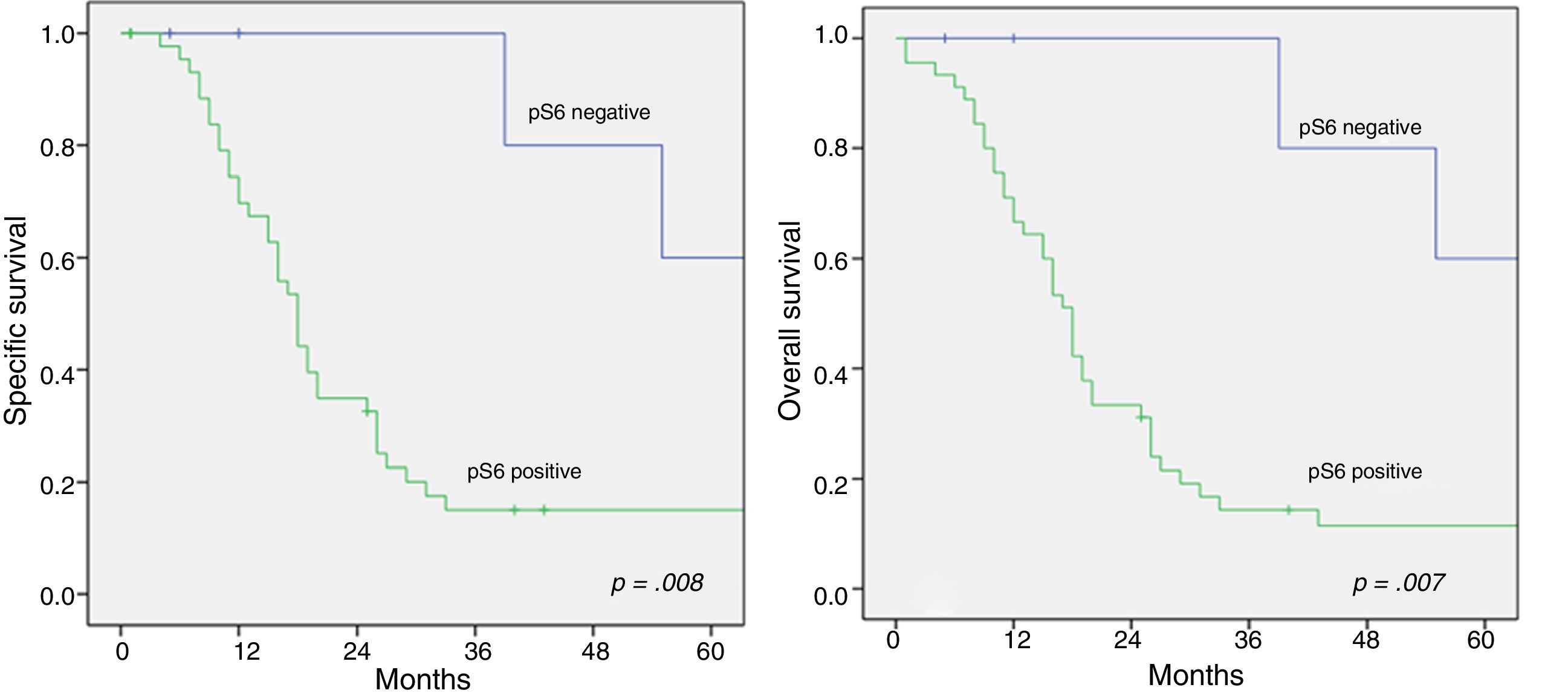
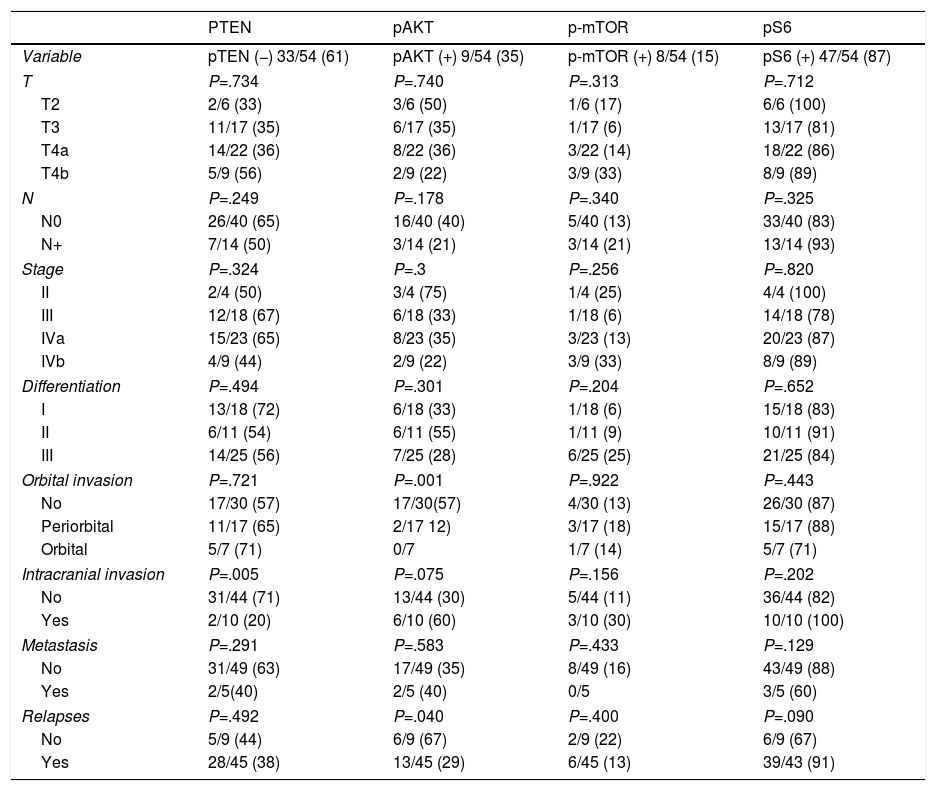
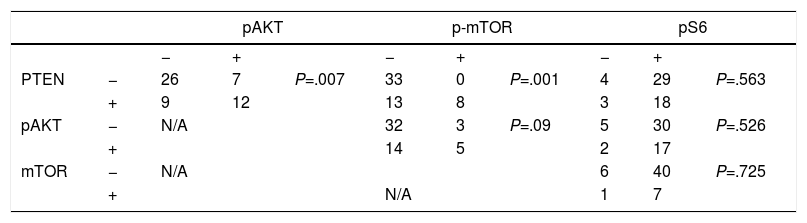
ResultsLoss of PTEN expression was observed in 33/54 cases (61%) and pAKT, mTOR and pS6 pre-expression was observed in 19/54 cases (35%), 8/54 cases (15%), and 47/54 cases (87%), respectively. Loss of PTEN expression was related to intracranial invasion and development of regional metastases (P=.005). Overexpression of pS6 was associated with a decrease in survival (P=.008), presence of local recurrences (P=.055), and worsening of overall prognosis (P=.007). No significant relationships were observed between pAKT and mTOR expression and the clinicopathological parameters studied.
ConclusionsAlterations in the expression of EGFR/PI3K/pAKT/mTOR/pS6 pathway components are common in a subgroup of SNSCC. This study reveals that the absence of pS6 overexpression is associated with better clinical outcomes. Therefore, pS6 expression could be considered as an unfavourable prognostic marker.
En estudios previos hemos indicado que EGFR tiene un papel en la carcinogénesis en un subgrupo de carcinomas epidermoides nasosinusales (CENS). Además, EGFR activa a 2 de las más importantes vías de señalización intracelular como son la PI3K/pAKT/mTOR/pS6 y la vía MAP-cinasas. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la participación de la ruta de EGFR/PI3K/pAKT/mTOR/pS6 y su relación con parámetros clínico-patológicos y de seguimiento de los CENS.
Material y métodosLa expresión proteica de PTEN, pAKT, mTOR y pS6 fue analizada mediante inmunohistoquímica en 54 CENS. Los resultados fueron relacionados con diversos parámetros clínico-patológicos y la supervivencia.
ResultadosLa pérdida de expresión de PTEN se observó en 33/54 casos (61%) y la sobreexpresión de pAKT, mTOR y pS6 se observó en 19/54 casos (35%), 8/54 casos (15%) y 47/54 casos (87%), respectivamente. La pérdida de expresión de PTEN se relacionó con la invasión intracraneal y el desarrollo de metástasis regionales (p=0,005). La ausencia de sobreexpresión de pS6 se relacionó con una supervivencia específica (p=0,008) y global (p=0,007) más favorables y la ausencia de recidivas locales (p=0,055). No se observaron relaciones significativas entre la expresión de pAKT y mTOR y los parámetros clínico-patológicos estudiados.
ConclusionesLas alteraciones en la expresión de los componentes de la vía EGFR/PI3K/pAKT/mTOR/pS6 son frecuentes en un subgrupo de CENS. Este estudio revela que la ausencia de sobreexpresión de pS6 se relaciona con mejores resultados clínicos, por lo que la expresión pS6 podría considerarse como un marcador pronóstico.