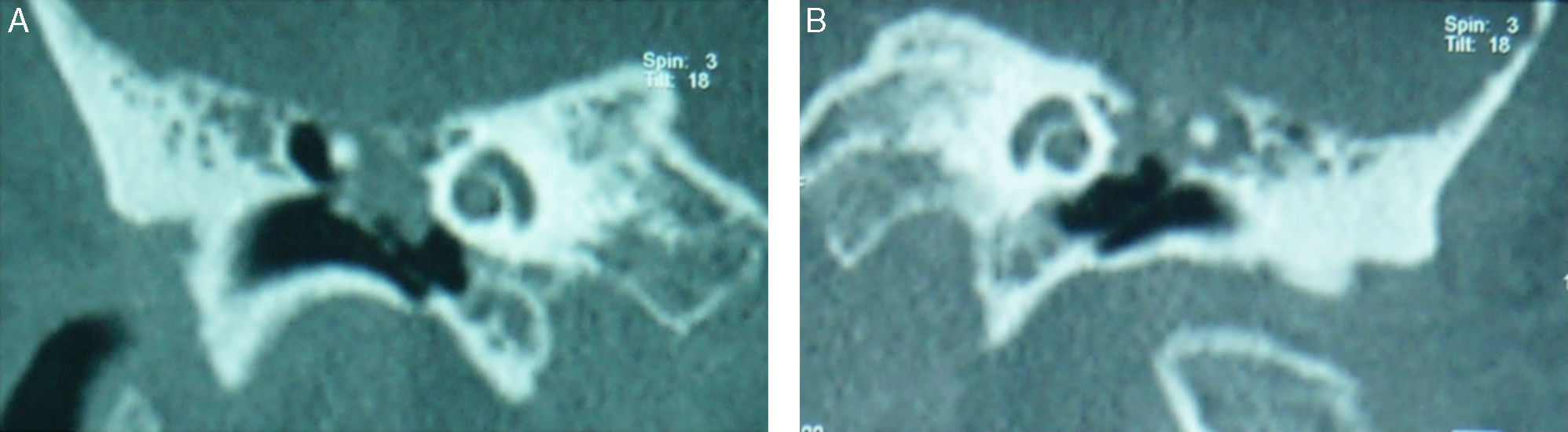
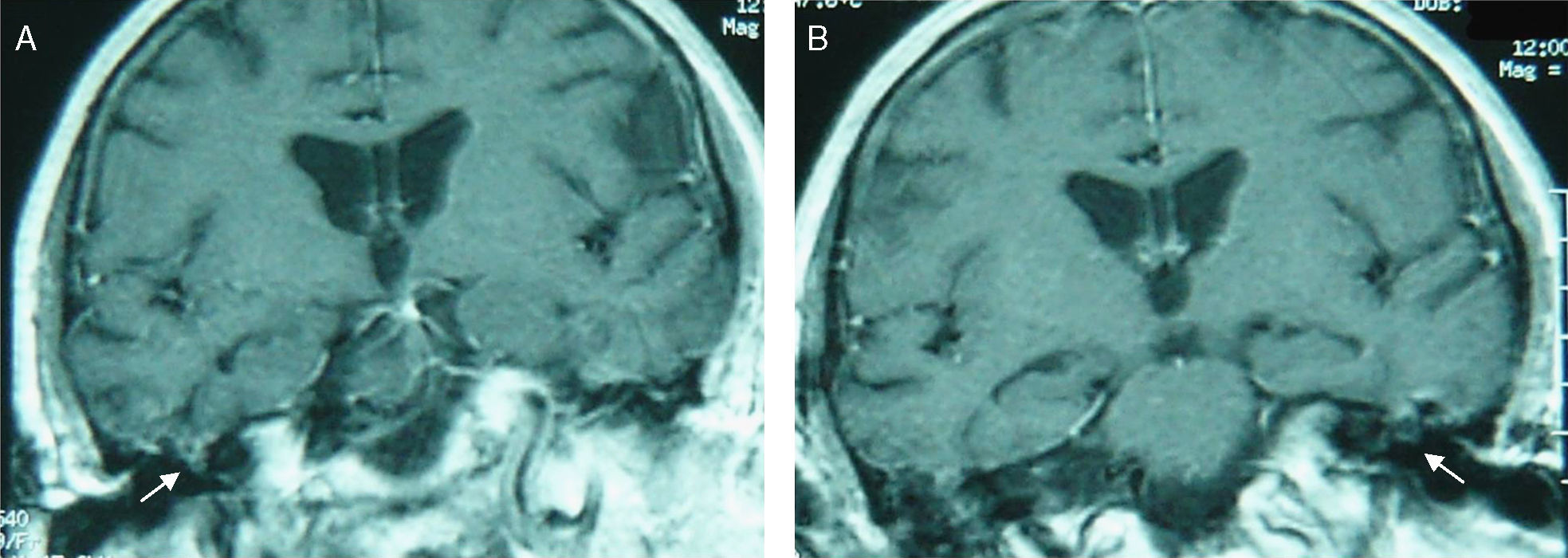
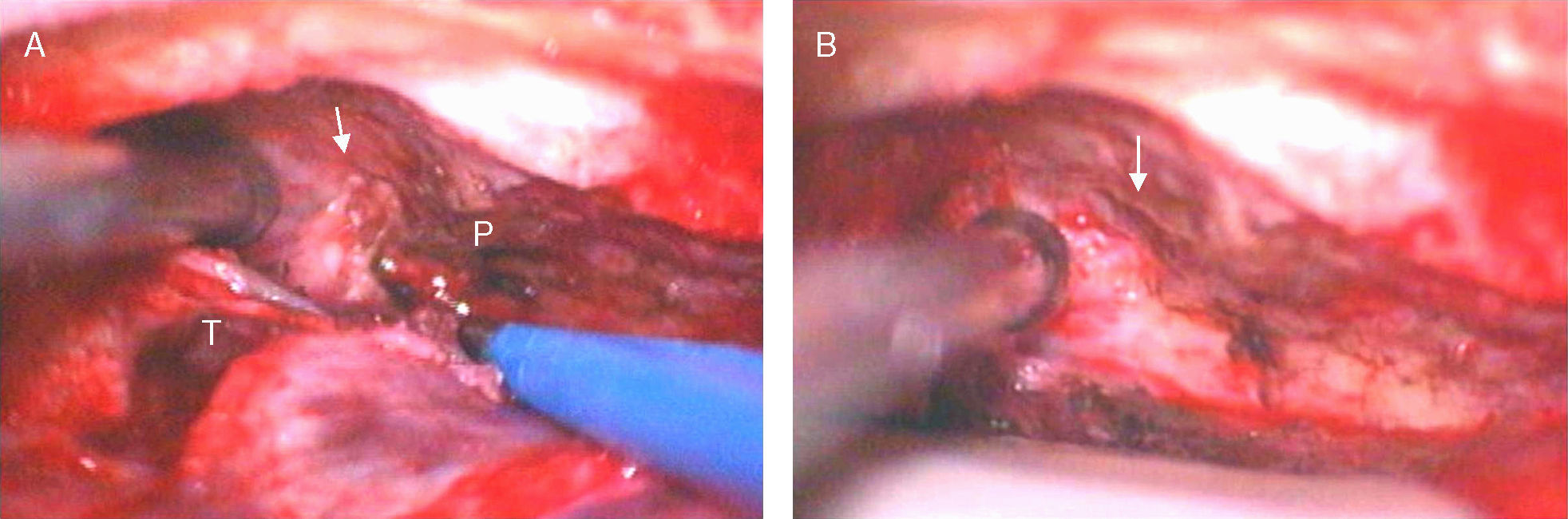
La herniación espontánea de tejido cerebral a través de un defecto óseo y dural a nivel temporal es una rara entidad, siendo todavía más infrecuente que esta circunstancia se produzca de forma bilateral. La presentación suele ser en forma de otorrea intermitente y persistente en el tiempo. La manifestación como rinolicuorraquia es muy poco habitual. El objetivo es presentar este inusual caso de un encefalocele espontáneo bilateral por defecto bilateral del tegmen tympani.
Spontaneous herniation of brain parenchyma through a dural and osseous defect in the temporal bone is a rare entity and a bilateral form is even more infrequent. It usually presents as an intermittent but persistent otorrhea. Manifestation as nose cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is very uncommon. Our objective is presenting this unusual case report of a spontaneous bilateral encephalocele with a bilateral tegmen tympani defect.