Impaired nasal breathing is a common condition among pediatric patients, being rhinitis the most common cause. In recent years, turbinate surgery, mainly turbinate radiofrequency ablation (TRA), has increased in popularity amongst pediatric otolaryngologists and rhinologists as a safe and useful technique to address turbinate hypertrophy in pediatric patients. The present paper is designed with the aim of assessing the current worldwide clinical practice regarding turbinate surgery in pediatric patients.
MethodsThe questionnaire was developed based on previous researches, by a group of 12 experts from the rhinology and pediatric otolaryngology research group belonging to the Young Otolaryngologists of the International Federation of Otorhinolaryngological societies (YO-IFOS). The survey was then translated to 7 languages and sent to 25 scientific otolaryngologic societies around the globe.
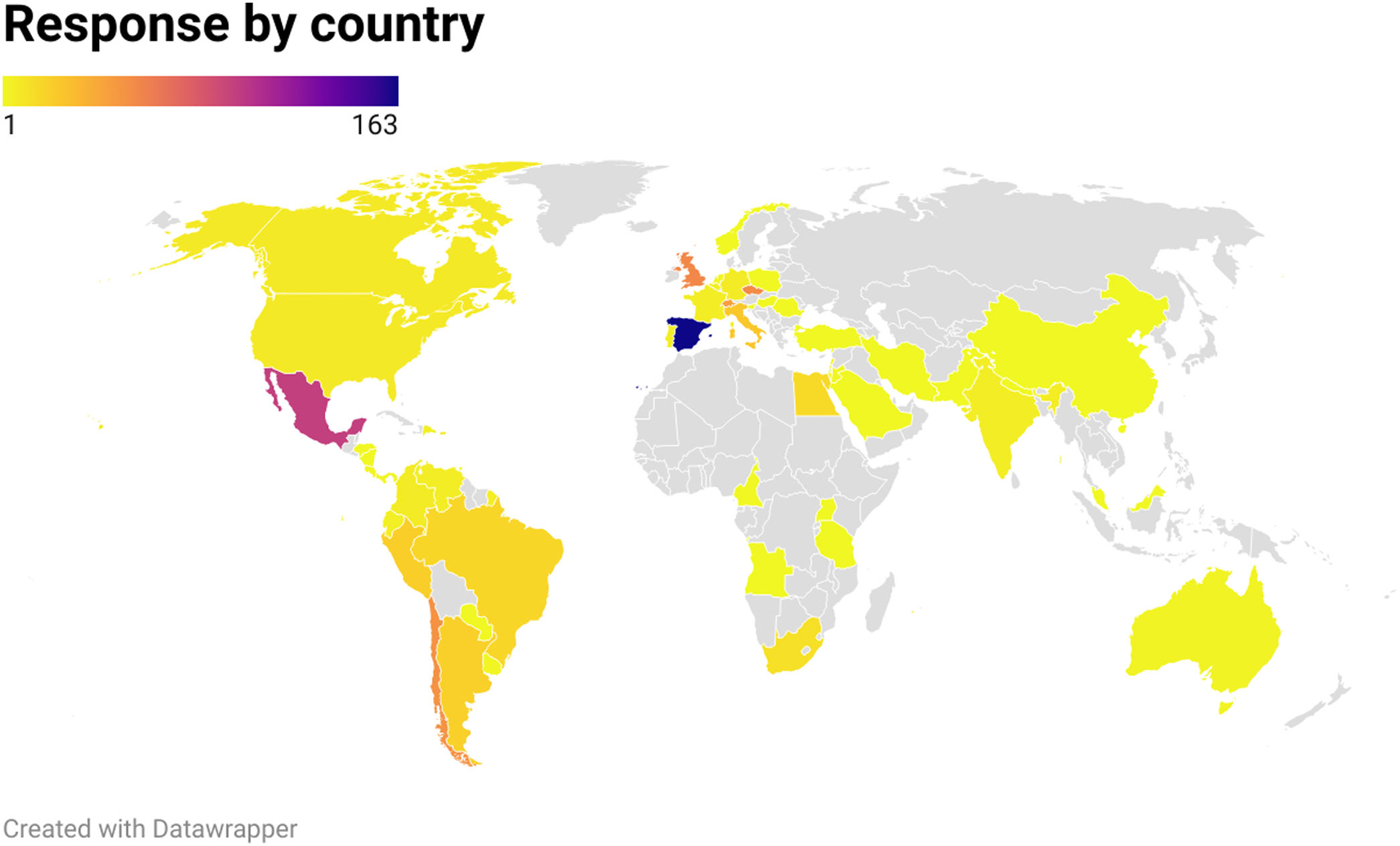
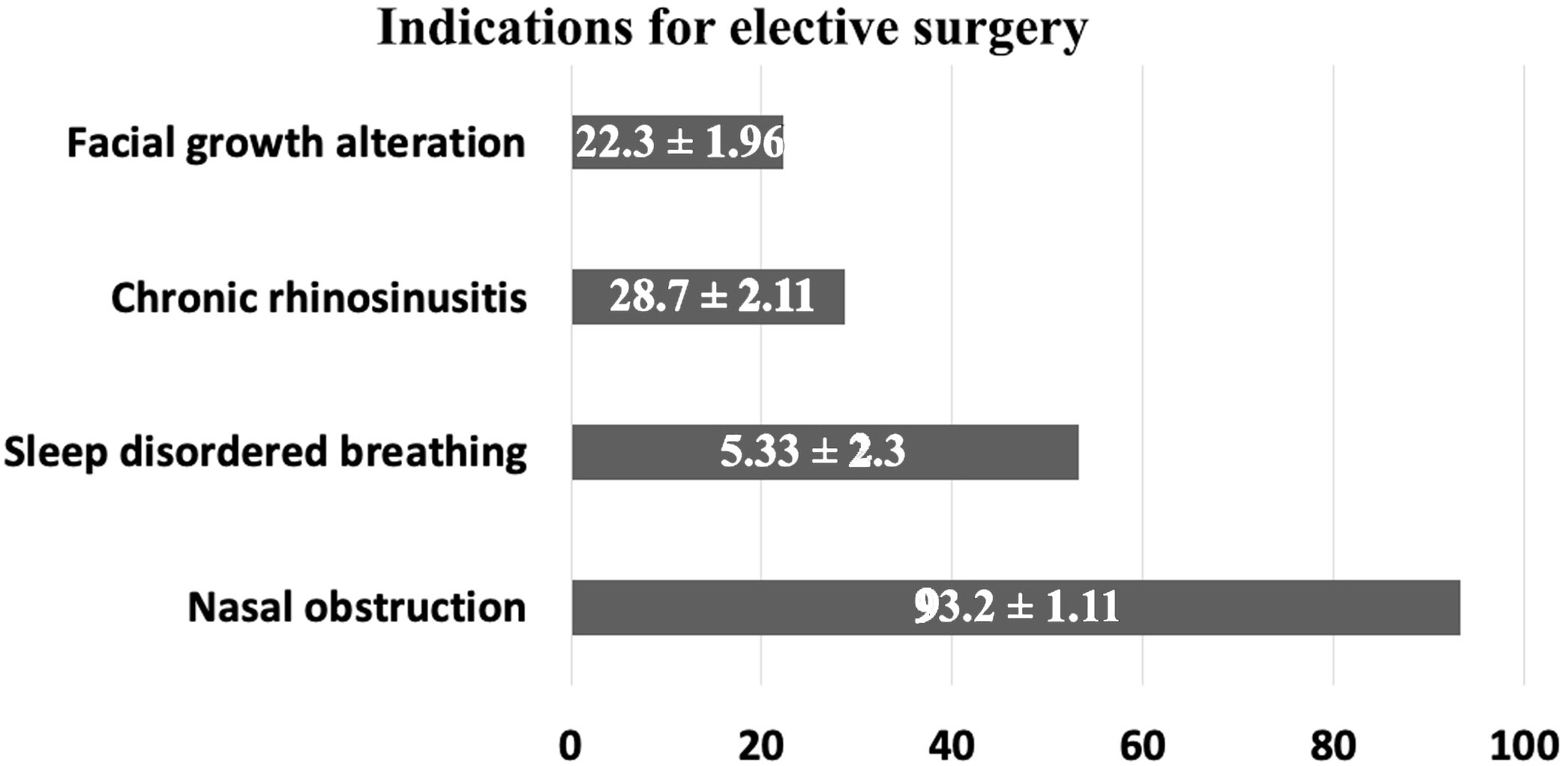
Results15 scientific societies agreed to distribute the survey to their members. There were 678 responses from 51 countries. From them, 65% reported to usually perform turbinate surgery in pediatric patients. There was a statistically significant increased likelihood of performing turbinate surgery for those practicing rhinology, sleep medicine, and/or pediatric otolaryngology compared to other subspecialties. The main indication to perform turbinate surgery was nasal obstruction (93.20%); followed by sleep disordered breathing (53.28%), chronic rhinosinusitis (28.70%) and facial growth alterations (22.30%).
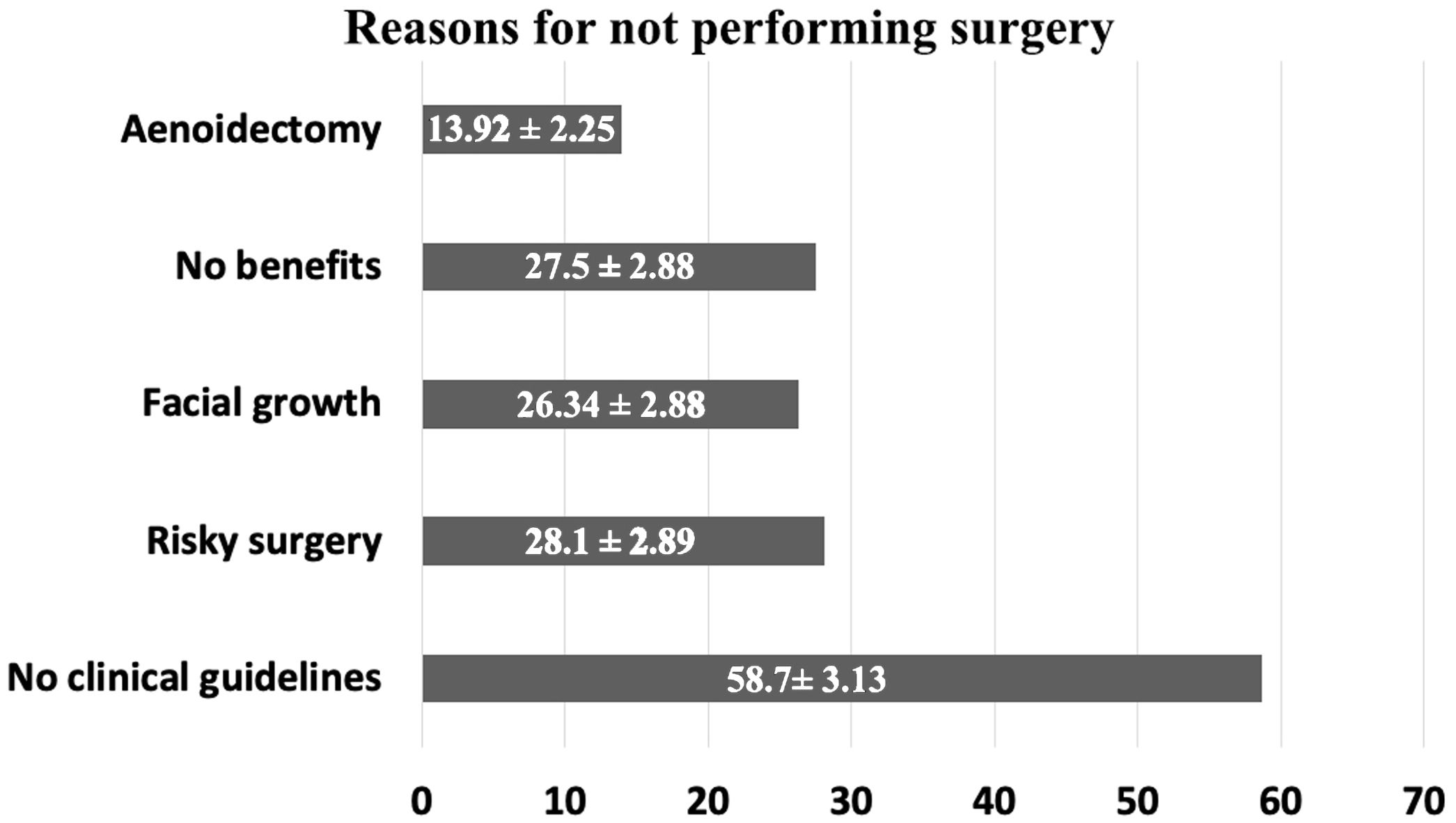
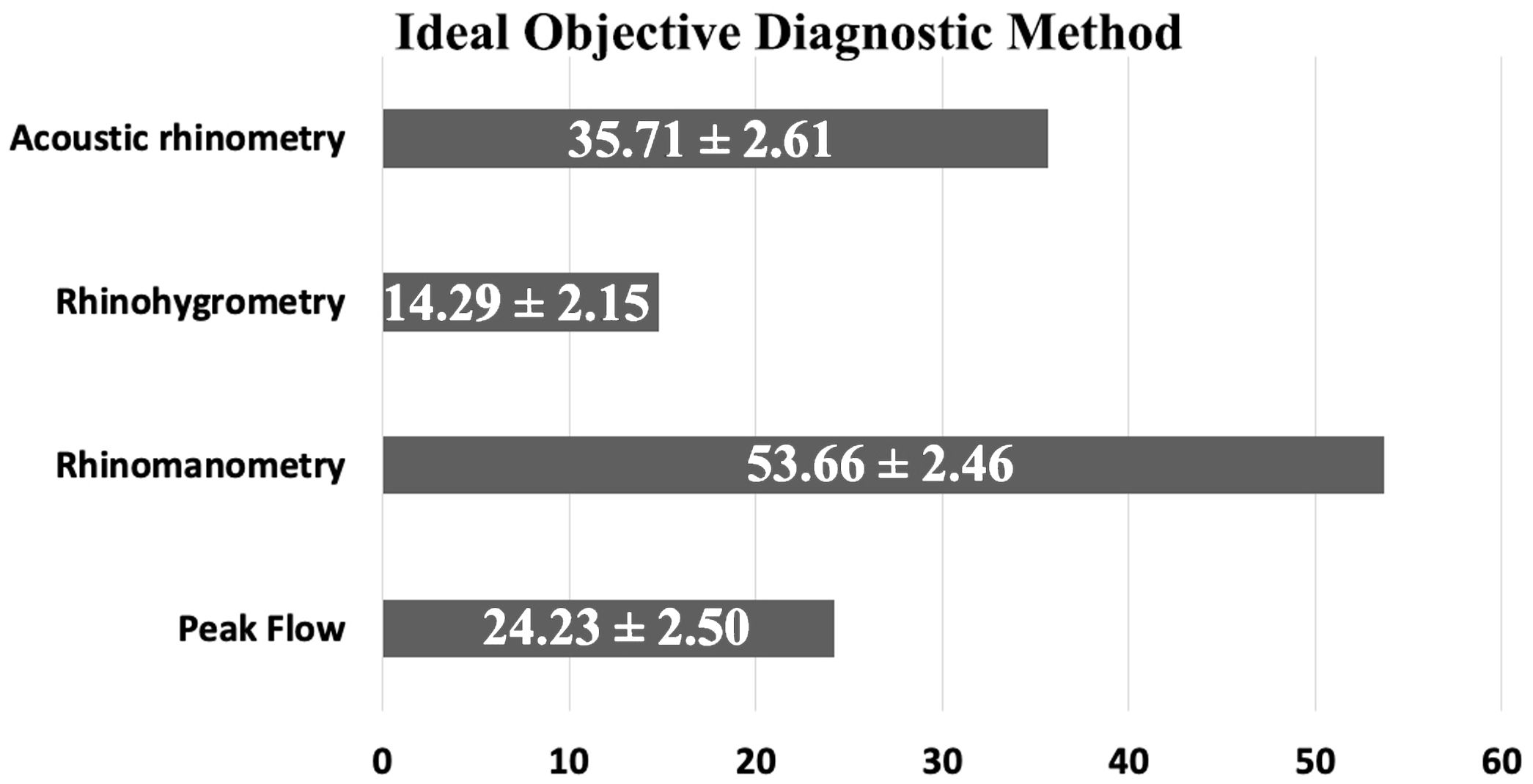
ConclusionsThere is no general consensus on the indications and ideal technique for turbinate reduction in children. This dissension arises mainly from the lack of scientific evidence. The points with highest agreement (>75%) between respondents is the use of nasal steroids prior to surgery; reintroducing nasal steroids in allergic patients; and performing turbinate surgery as day-case surgery.
La obstrucción nasal es una enfermedad habitual en pacientes pediátricos, siendo la rinitis la causa más frecuente. En los últimos años la cirugía de cornetes, especialmente la radiofrecuencia (RF), ha aumentado su popularidad entre los otorrinolaringólogos pediátricos y los rinólogos como una técnica segura y eficaz para tratar esta enfermedad en población pediátrica. Este artículo se diseña con el objetivo de evaluar la práctica clínica habitual a este respecto a nivel global.
MétodosEl cuestionario fue diseñado basado en trabajos previos por un grupo de 12 expertos del Grupo de Investigación en Rinología y en Otorrinolaringología Pediátrica de la Young Otolaryngologists of the International Federation of Otorhinolaryngological societies (YO-IFOS). La encuesta fue traducida a 7 idiomas y enviada a 25 sociedades científicas.
ResultadosQuince sociedades científicas aceptaron distribuir la encuesta entre sus miembros. Hubo 678 respuestas de 51 países. De ellos, el 65% comunicó realizar de manera habitual cirugía de cornetes en población pediátrica. Se observó una mayor probabilidad de realizar la intervención entre especialistas en Rinología, Medicina del sueño u Otorrinolaringología pediátrica comparado con el resto de las subespecialidades. La indicación más habitual para realizar la cirugía fue obstrucción nasal (93,20%), seguida por trastorno respiratorio del sueño (53,28%), rinosinusitis crónica (28,70%) y alteraciones del desarrollo facial (22,30%).
ConclusionesNo existe un consenso general en las indicaciones ni en la técnica quirúrgica de elección para esta cirugía en pacientes pediátricos. La desavenencia nace principalmente de la falta de evidencia científica. Los puntos con mayor acuerdo (> 75%) entre los respondedores fueron el uso de corticoide tópico nasal previo a la cirugía; reintroducir la medicación tópica en pacientes alérgicos, y realizar la cirugía de manera ambulatoria.