To evaluate the association between results from drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) and computed tomography with lateral cephalometry (CTLC) of the pharynx in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients, regarding the same anatomic level, in order to understand if CTLC could replace DISE in selected patients.
Study designCross-sectional.
SettingTertiary hospital.
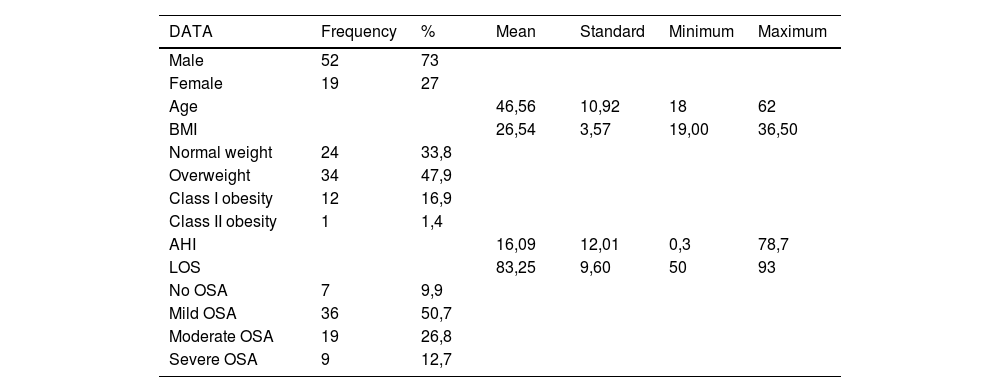
MethodsA total of 71 patients who attended the Sleep Medicine Consultation in the Otorhinolaryngology Department of Hospital CUF Tejo between 1.6.2019 and 30.9.2021, performed a polysomnographic sleep study and were elected to undergo DISE and CTLC of the pharynx for diagnostic purposes were selected. Obstructions at the same anatomic levels – tongue base, epiglottis and velum - were compared in both exams.
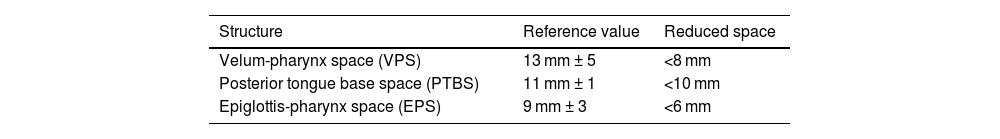
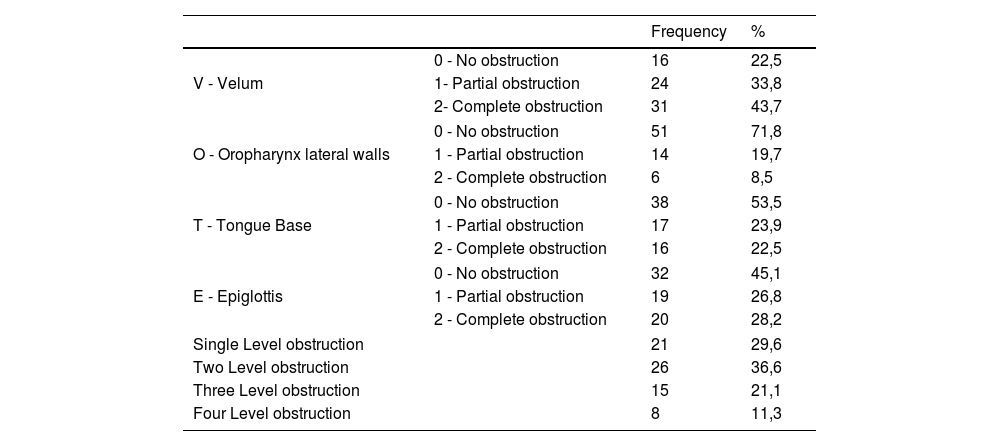
ResultsPatients with reduction of epiglottis-pharynx space on CTLC had also a complete obstruction at epiglottis level on the VOTE classification of DISE (p = 0,027). Reduction of velum-pharynx space or tongue base-pharynx space were not related to complete obstruction of the velum (P = 0,623) or the tongue base (p = 0,594) found in DISE. Those with two or more space reductions had a tendency to multilevel obstruction observed in DISE (p = 0.089).
ConclusionWhen evaluating the obstruction level(s) of an OSA patient, efforts should be made to perform DISE, since CTLC measures, though regarding at the same structures, don´t correlate completely with obstructions observed in DISE.
Evaluar la asociación entre los resultados de la endoscopia del sueño inducida por fármacos (DISE) y la tomografía computarizada con cefalometría lateral (TCCL) de faringe en pacientes con apnea obstructiva del sueño (AOS), en el mismo nivel anatómico, para comprender si la TCCL podría reemplazar DISE en pacientes seleccionados.
Diseño del estudioTransversal.
LugarHospital de tercer nivel.
MétodosUn total de 71 pacientes que acudieron a la Consulta de Medicina del Sueño en el Servicio de Otorrinolaringología del Hospital CUF Tejo entre el 1.6.2019 y el 30.9.2021, a los que se les había realizado un estudio polisomnográfico del sueño y fueron elegidos para realizar DISE y TCCL de faringe con fines diagnósticos, fueron seleccionados. Las obstrucciones en los mismos niveles anatómicos (base de la lengua, epiglotis y velo) se compararon en ambos exámenes.
ResultadosLos pacientes con reducción del espacio epiglotis-faringe en TCCL también tenían una obstrucción completa a nivel de epiglotis en la clasificación VOTE de DISE (p = 0,027). La reducción del espacio velo-faringe o base de la lengua-faringe no se relacionó con la obstrucción completa del velo (P = 0,623) o de la base de la lengua (p = 0,594) encontrada en DISE. Aquellos con dos o más reducciones de espacio presentaron tendencia a la obstrucción multinivel observada en DISE (p = 0,089).
ConclusiónAl evaluar el o los niveles de obstrucción de un paciente con AOS, se debe intentar realizar DISE, ya que las medidas de TCCL, aunque se refieren a las mismas estructuras, no se correlacionan completamente con las obstrucciones observadas en DISE.