Parotid tumours, in addition to the wide variety of types, are histologically complex. Differentiating between benign and malignant tumours in preoperative diagnosis is important in deciding the type of surgery required. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple, quick, low-cost, low-invasive and well-tolerated tool used in the preoperative diagnosis of these tumours.
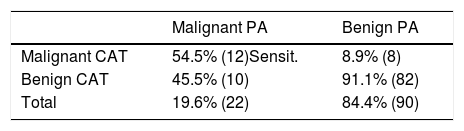
Material and methodswe calculated the sensitivity, specificity, predictive positive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of FNAC and computed tomography (CT) in the differentiation of benign and malignant parotid tumours operated between 2010 and 2014 in the oral and maxillofacial surgery department of the University Hospital Miguel Servet.
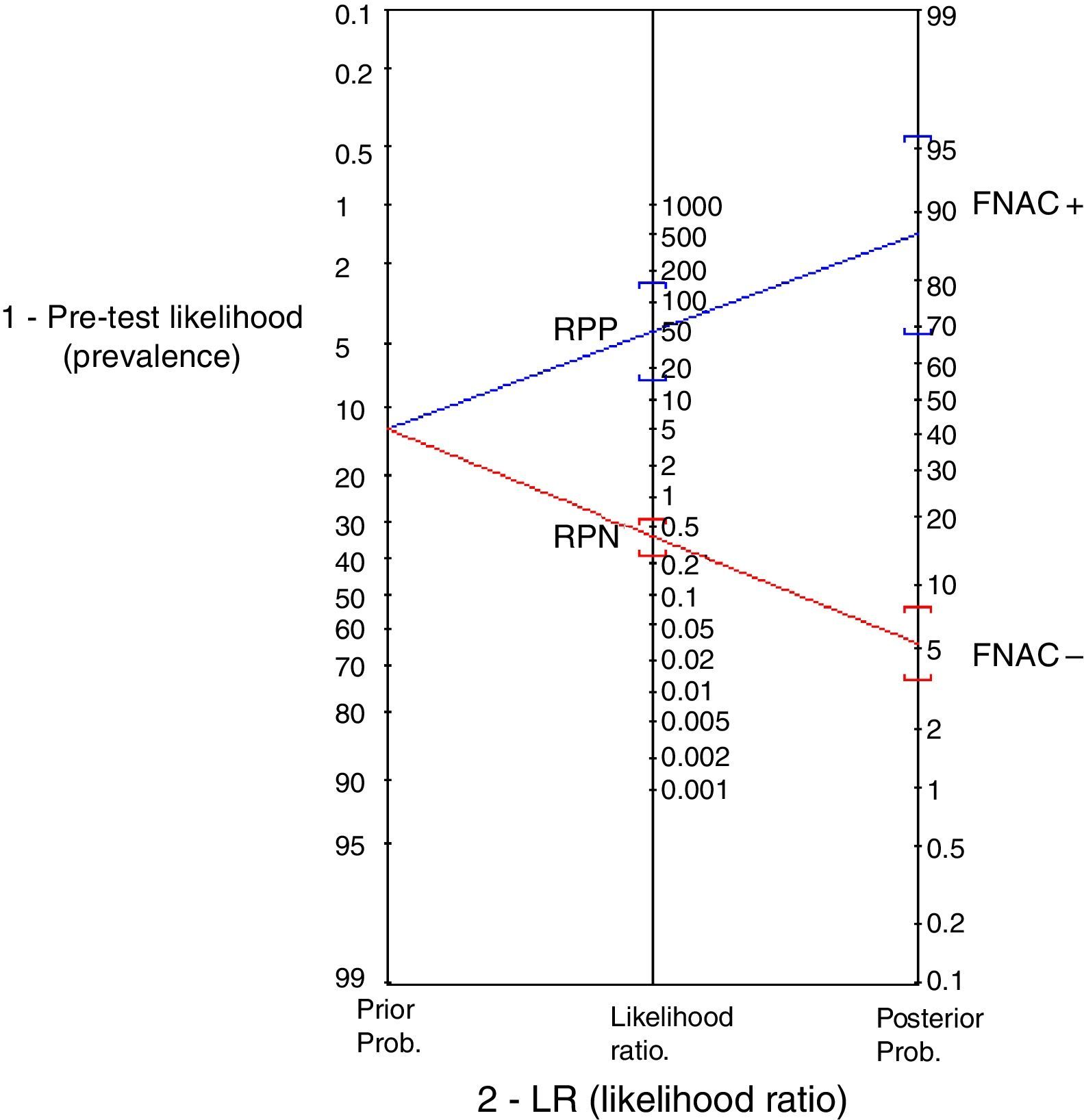
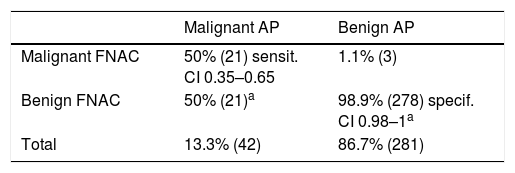
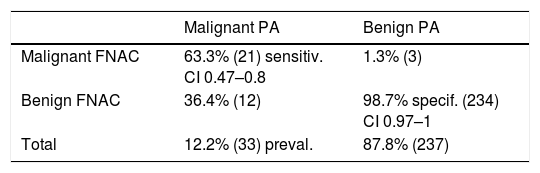
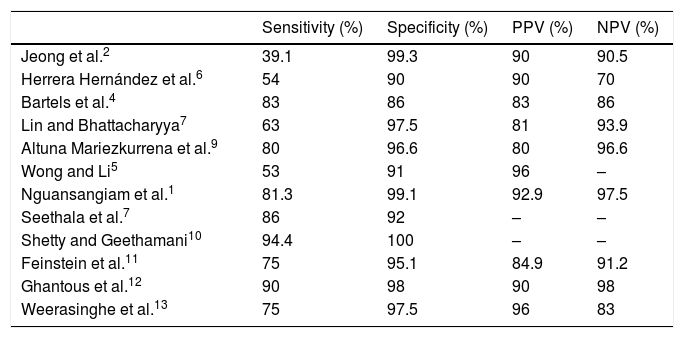
ResultsThe sensitivity of FNAC is 50%, while the specificity is high, at 98.7%. FNAC offers high reliability in the diagnosis of malignant tumours, despite its low sensitivity. However, when the diagnosis is indeterminate or benign, other than pleomorphic adenoma or Whartin tumour, the reliability to exclude malignancy decreases.
ConclusionThe low sensitivity of FNAC to differentiate malignant from benign parotid tumours, means that we cannot rule out other diagnostic tests, clinical symptoms and especially the intraoperative vision of each surgeon. Especially when the diagnosis is indeterminate. Nevertheless, it is a technique used in a systematised way and helps in pre-surgical decision-making.
Los tumores de parótida, además de la gran diversidad de tipos que existen, son histológicamente complejos. Su diagnóstico preoperatorio, principalmente en cuanto a diferenciar tumores benignos de malignos es importante a la hora realizar un tipo de cirugía u otra. La punción-aspiración con aguja fina (PAAF) es una herramienta simple, rápida, y de bajo coste, poco invasiva y bien tolerada, que se usa en el diagnóstico preoperatorio de estos tumores.
Material y métodosSensibilidad, especificidad, valour predictivo positivo y valour predictivo negativo de la PAAF y la tomografía computadorizada (TAC) en la diferenciación de tumores benignos y malignos de parótida operados durante los años 2010 a 2014 por el Servicio de Cirugía Oral y Maxilofacial.
ResultadosLa sensibilidad de la PAAF es de un 50%, baja, similar a los artículos publicados, mientras que la especificidad es alta, de un 98,7%. La PAAF ofrece una fiabilidad alta en el diagnóstico de tumores malignos, a pesar de su baja sensibilidad. Sin embargo, cuando el diagnóstico es no concluyente, o benigno que no sea adenoma pleomorfo o tumour de Whartin, la fiabilidad para excluir malignidad disminuye.
ConclusiónLa baja sensibilidad de la PAAF para diferenciar tumores malignos de benignos en la parótida hace que no podamos dejar de lado otras pruebas diagnósticas, la clínica y sobre todo la visión intraoperatoria de cada cirujano. Sobre todo cuando el diagnóstico es no concluyente. A pesar de esto, es una técnica utilizada de forma sistematizada y que ayuda a tomar decisiones prequirúrgicas.