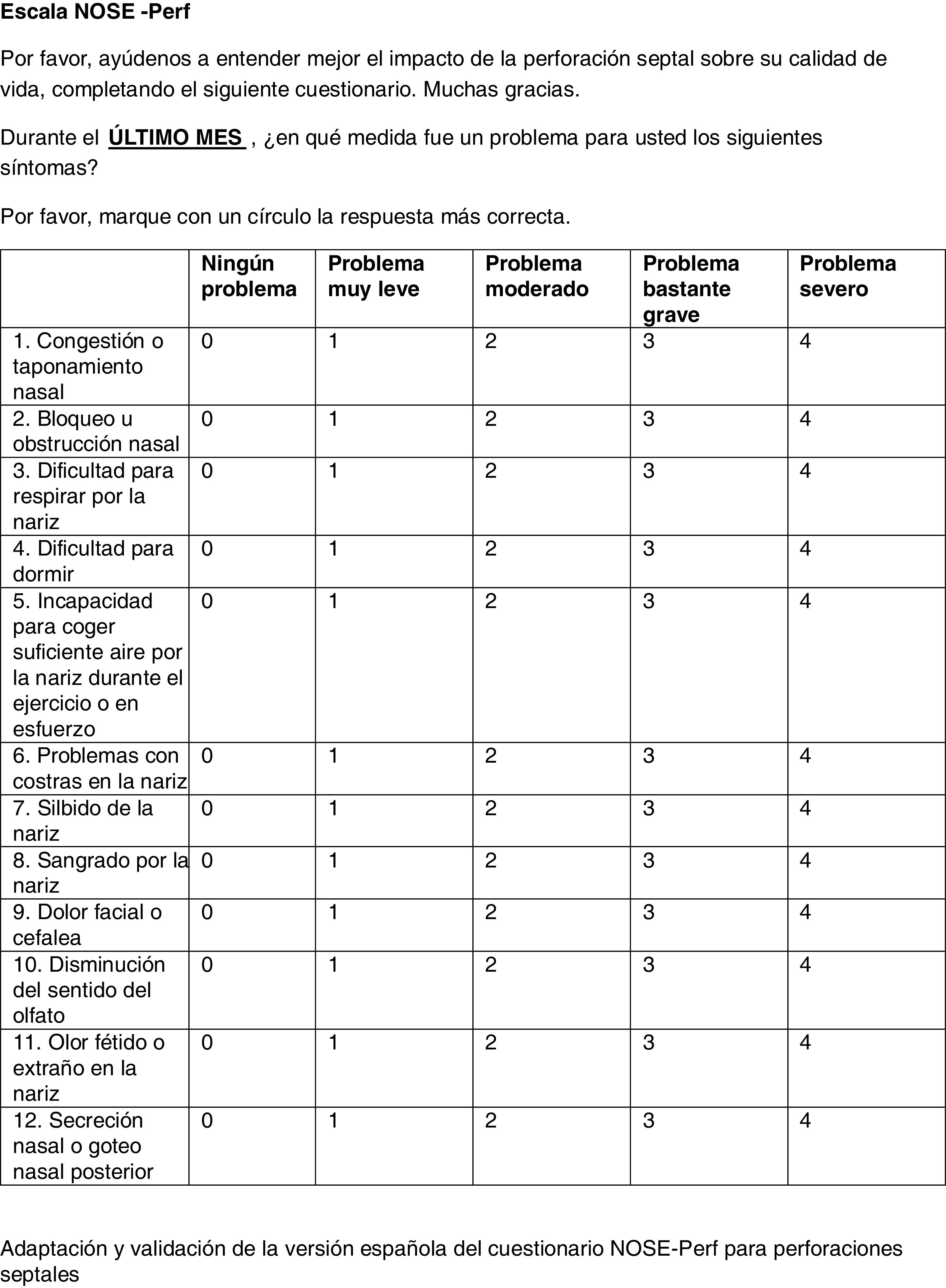
Septal perforation (SP) cause heterogeneous symptoms depending on the anatomical location, highlighting scabs, nasal obstruction and/or epistaxis. The use of questionnaires to determine the quality of life in different pathologies is increasing in sinonasal pathologies and in patients with SP the NOSE-Perf questionnaire was constructed, currently validated in English. The aim of this study is the translation, cross-cultural adaptation, and validation of the NOSE-Perf questionnaire into Spanish.
Material and methodsProspective single-centre study of 81 patients (38 with SP and 43 controls), visited in the rhinology section of a tertiary hospital. Adaptation and translation NOSE-Perf into Spanish and validation using the NOSE and NOSE-Perf questionnaire in Spanish.
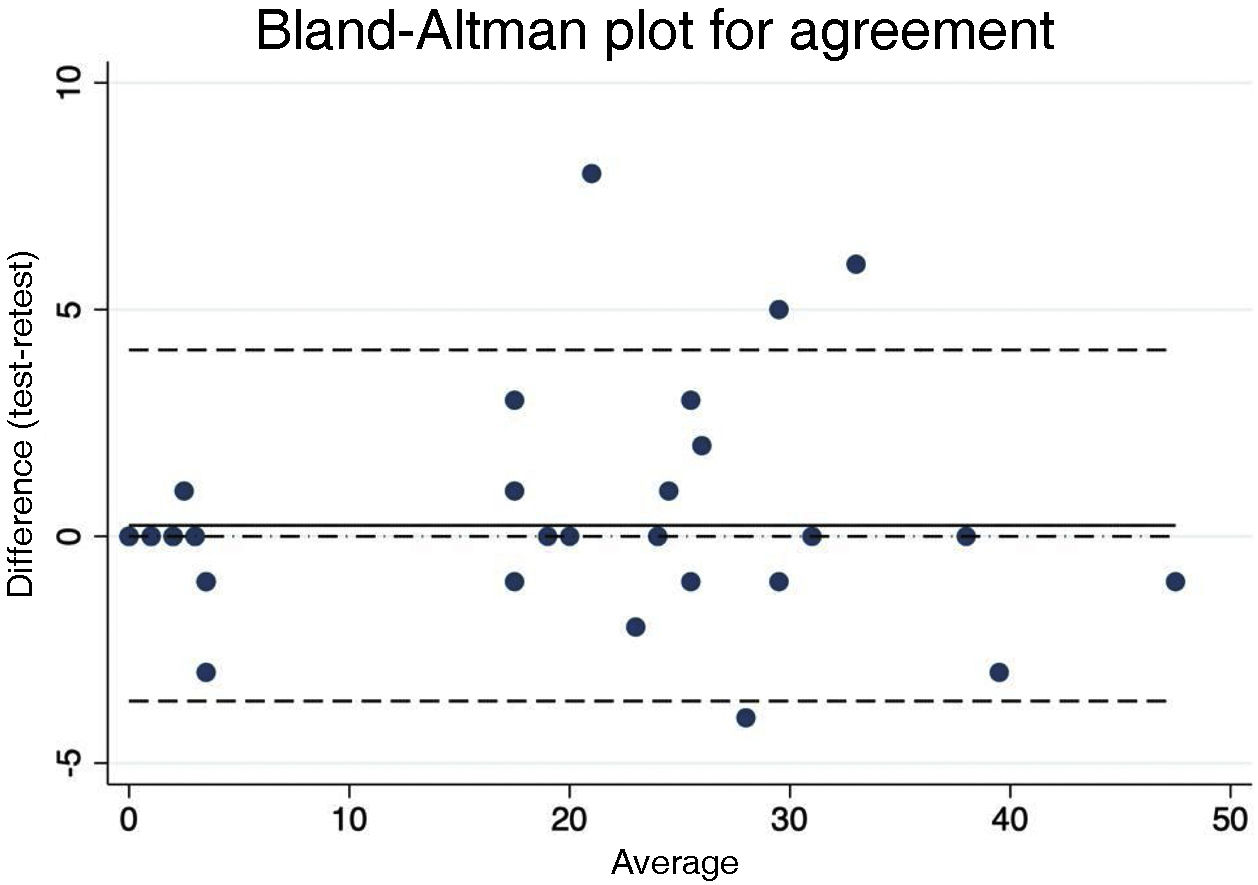
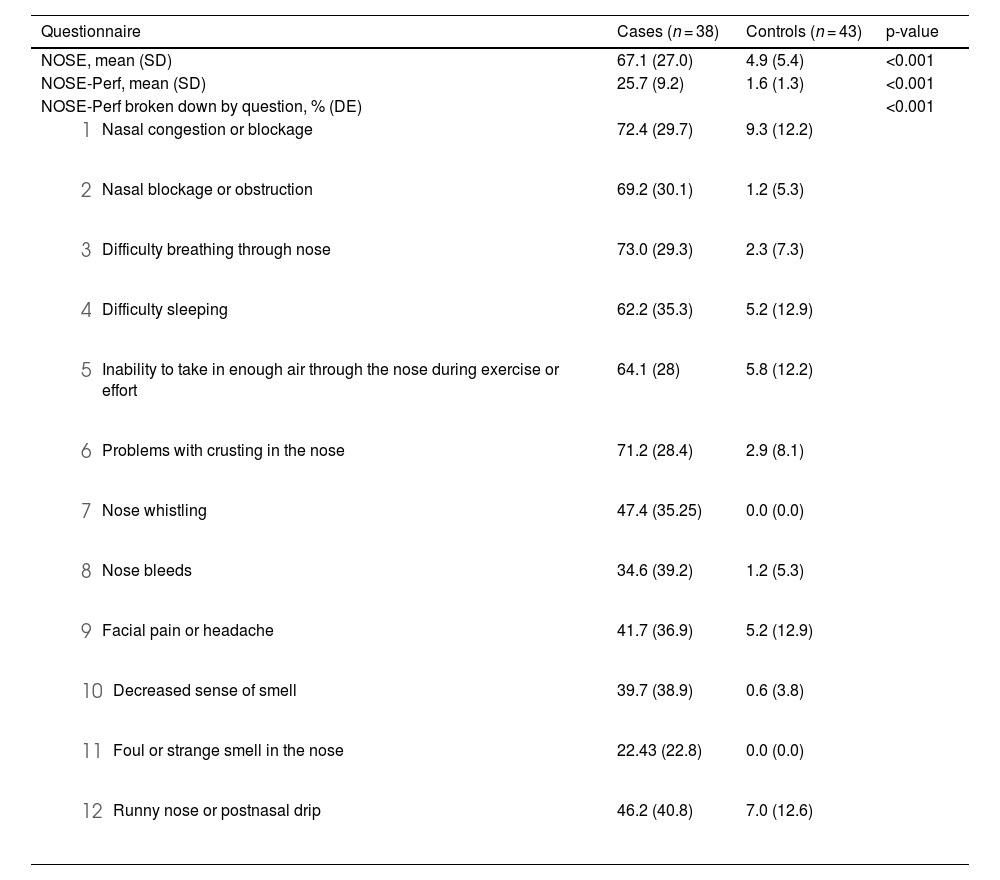
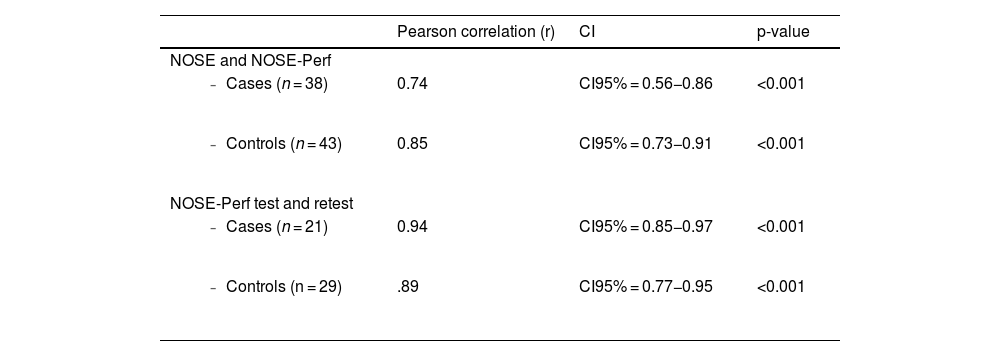
ResultsSignificant differences were found in the mean NOSE-Perf score and in the mean NOSE score (IC95% = 21.2–26.9; p < 0.001 and IC95% = 53.8–70.5; p < 0.001) between SP group and control group. Pearson's correlation between the two questionnaires NOSE-Perf and NOSE in the SP group was 0.74 (95% CI = 0.56−0.86; p < 0.001). In the control group it was r = 0.85 (95%CI = 0.73−0.91; p < 0.001). Cronbach's alpha coefficient of the NOSE-Perf was 0.95 (IC 95% = 0.93−0.96) for internal consistency. The reliability evaluation was carried out by test-retest, and a strong Pearson correlation was obtained between the questionnaires r = 0.94 (CI95% = 0.85−0.97; p < 0.001) and r = 0.89 (95%CI = 0.77−0.95; p < 0.001).
ConclusionsThe Spanish version of the NOSE-Perf is as reliable and valid as the English version, which makes it possible to assess the impact on quality of life that it causes in patients with perforations in the Spanish-speaking population.
Las perforaciones septales (PS) causan síntomas heterogéneos según la localización anatómica, destacando costras, obstrucción nasal y/o epistaxis. El uso de cuestionarios para determinar la calidad de vida en distintas patologías está en aumento en patología nasosinusal. En pacientes con PS se diseñó el cuestionario NOSE-Perf, actualmente validado en inglés. El objetivo del presente estudio es la traducción, adaptación transcultural y validación del cuestionario NOSE-Perf al español.
Material y métodosEstudio unicéntrico prospectivo de 81 pacientes, (38 con PS y 43 controles) visitados en sección de Rinología de un hospital terciario. Adaptación y traducción NOSE-Perf a lengua española y validación utilizando el cuestionario NOSE y NOSE-Perf en español.
ResultadosSe hallaron diferencias significativas en la puntuación media del NOSE-Perf y en la puntación media del NOSE (IC95% = 21,2–26,9; p < 0,001 y IC95% = 53,8–70,5; p < 0,001) entre el grupo PS y el grupo control. La correlación de Pearson entre los dos cuestionarios NOSE-Perf y NOSE en el grupo PS fue de r = 0,74 (IC 95% = 0,56−0,86; p < 0,001) mientras que en el grupo control fue de r = 0,85 (IC95% = 0,73−0,91; p < 0,001). El coeficiente alfa de Cronbach del NOSE-Perf fue de0,95 (IC 95% = 0,93−0,96) para la consistencia interna. La fiabilidad del NOSE-Perf se evaluó mediante el test-retest y se obtuvo una fuerte correlación de Pearson r = 0,94 (IC95% = 0,85−0,97; p < 0,001) y r = 0,89 (IC95% = 0,77−0,95; p < 0,001) respectivamente.
ConclusionesLa versión española del NOSE-Perf resulta tan fiable y válida como la versión inglesa, lo que permite evaluar el impacto en la calidad de vida que ocasiona en pacientes con perforaciones en población hispanohablante.