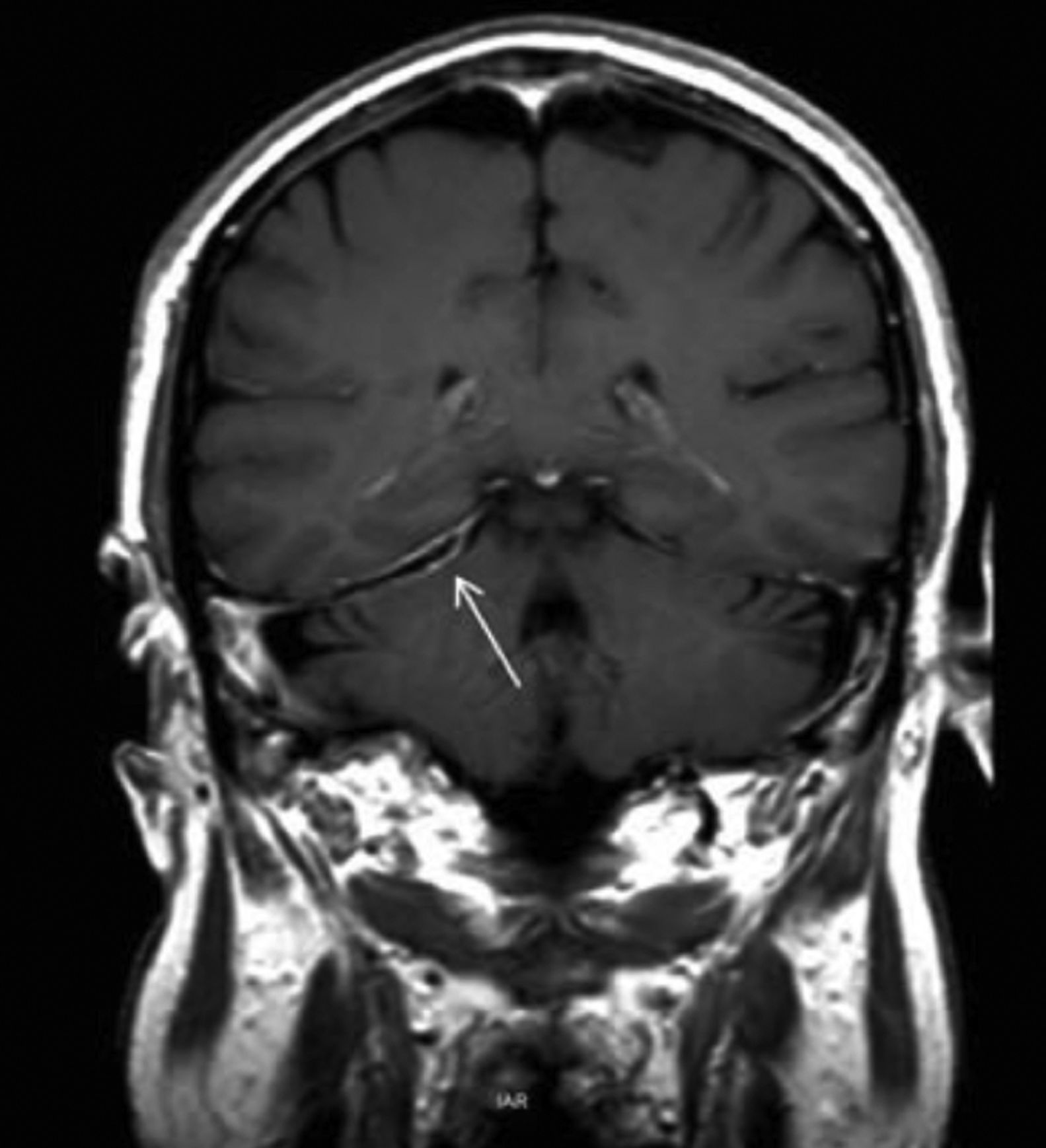
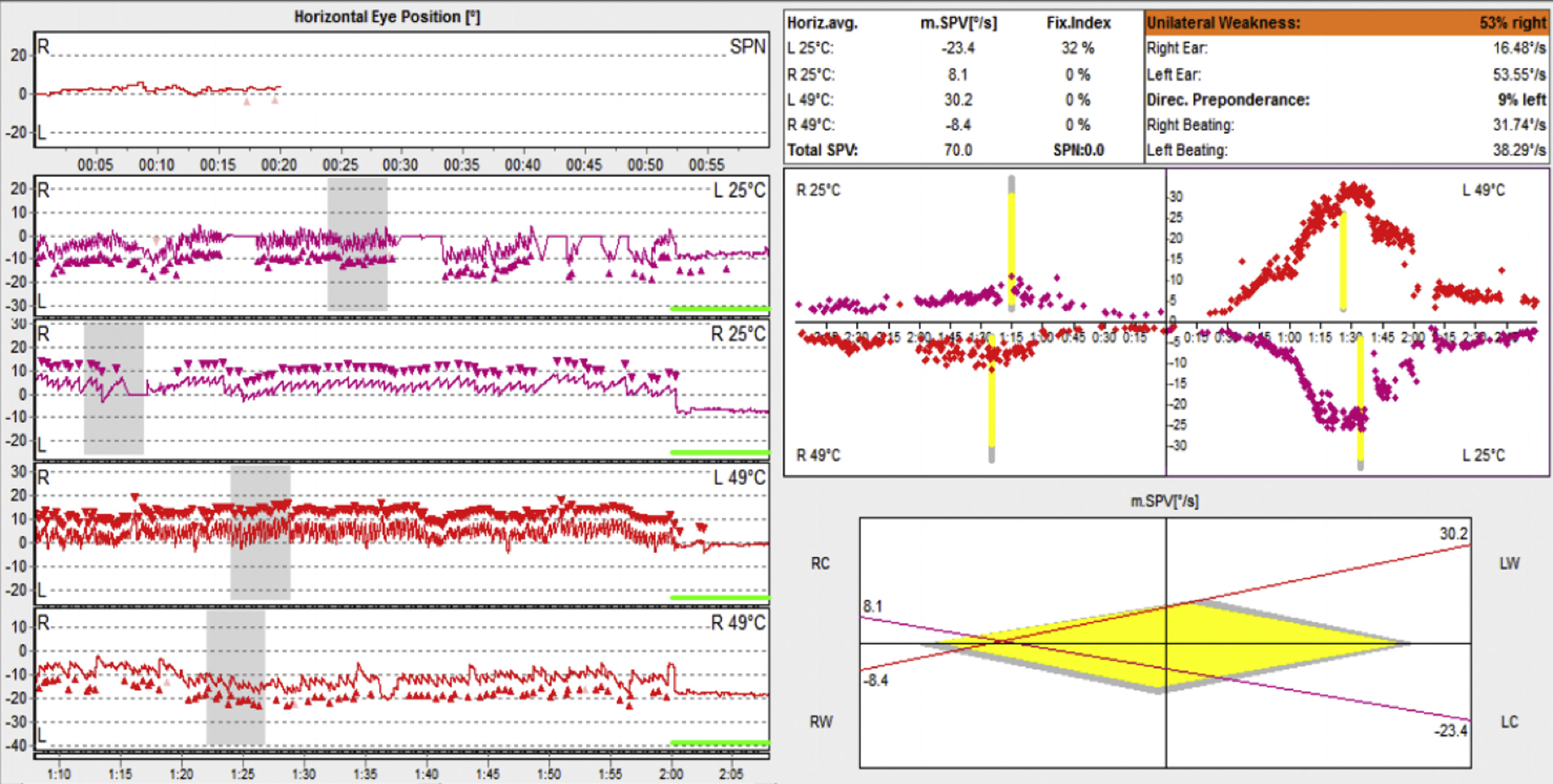
Hypertrophic pachymeningitis is an infrequent inflammatory disease resulting in thickening and fibrosis of the dura mater. In most cases, the cause in unknown and is called idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis (IHP). Audiovestibular symptoms are infrequent and the pathogenesis is still unclear.
Materials and methodsA systematic literature review of cases with IHP and vestibular symptoms from 2000 to February 2020 was performed. PRISMA Checklist was followed and PubMED database, Web of Science and Cochrane library were searched. We report a case of an adolescent with a diagnosis of vestibular neuritis in the context of IHP attended in our clinic.
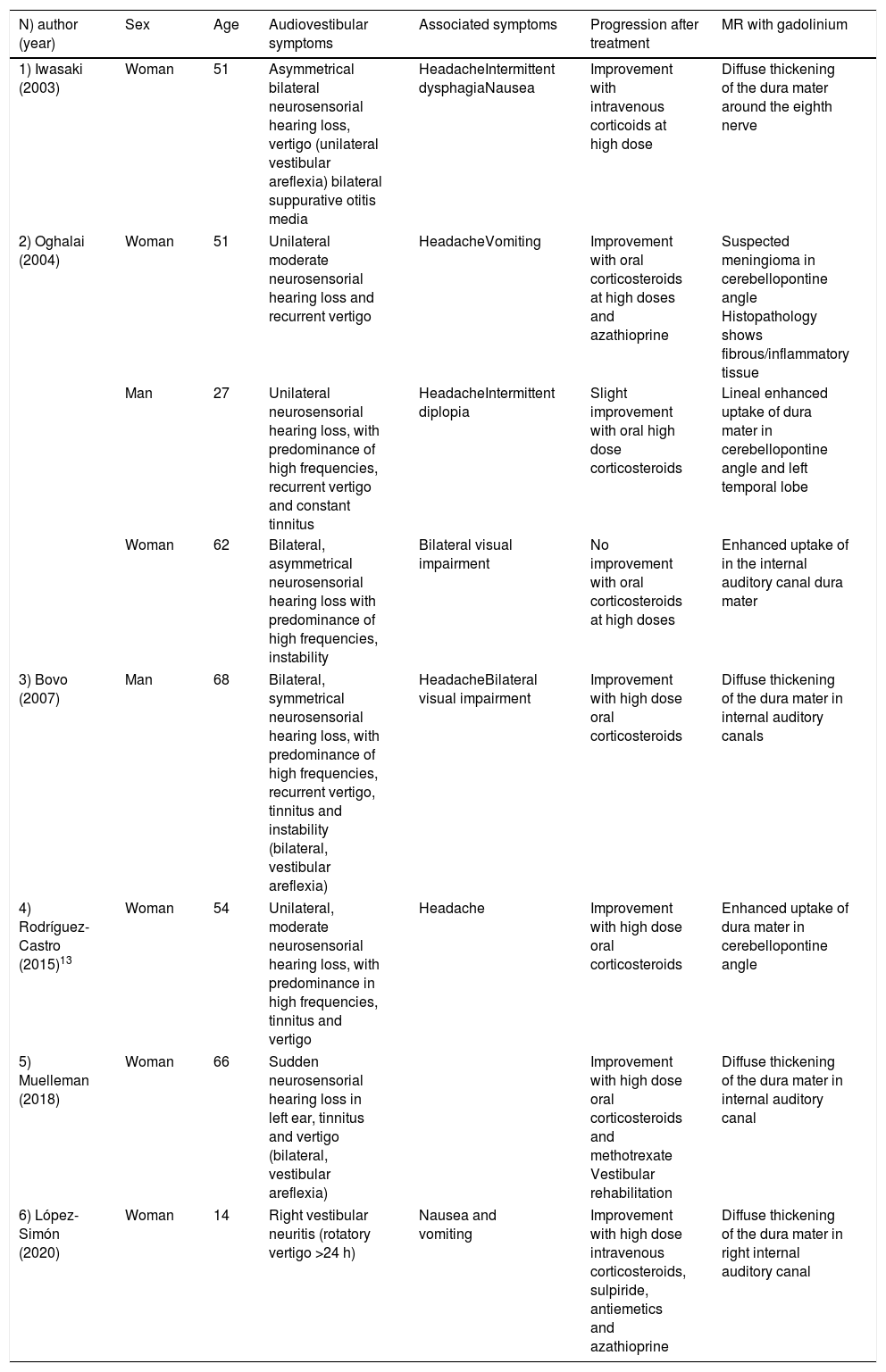
ResultsWe reviewed 5 articles related to IHP and vestibular disorders. A total of 7 cases (5 women and 2 men), with ages between 27 and 68 years with IHP were found. They all had audiovestibular symptoms. In contrast to our patient, uni or bilateral neurosensorial hearing loss was reported in all cases. Furthermore, there is no other case report published describing the association between IHP and vestibular neuritis. High dose steroids improved symptoms in 85.7% of the patients.
ConclusionVestibular symptoms in IHP are uncommon and the pathogenesis is still debatable. Entrapment of nerves in the internal auditory canal and secondary neuronal damage could be suspected as the main cause of hearing and vestibular loss.
La paquimeningitis hipertrófica es un proceso inflamatorio fibrosante infrecuente de la duramadre intracraneal. En la mayor parte de los casos la causa es desconocida y se denomina paquimeningitis hipertrófica idiopática (PHI). La sintomatología audiovestibular asociada es poco frecuente y su patogenia no está aclarada.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó una revisión sistemática de literatura médica de los casos publicados de PHI asociados a sintomatología audiovestibular desde el año 2000 a febrero 2020. Se siguieron los criterios PRISMA para revisiones sistemáticas evaluando las bases de datos electrónicas PubMED, Web of Science y Cochrane. Se complementa con el caso clínico de una adolescente que debutó con neuritis vestibular en el contexto de PHI atendida en nuestro servicio.
ResultadosSe han revisado 5 artículos con casos publicados de PHI que asociaban sintomatología audiovestibular. Se encontraron un total de 7 casos (5 mujeres y 2 varones), con edades comprendidas entre los 27 y 68 años, con diagnóstico de PHI. El 100% presentaron sintomatología audiovestibular. A diferencia de nuestra paciente, todos presentaron hipoacusia neurosensorial uni o bilateral. No se ha encontrado ningún otro caso descrito de asociación entre PHI y neuritis vestibular. El tratamiento empleado fueron los corticoides consiguiendo mejoría en el 87,5% de los pacientes.
ConclusionesLas manifestaciones vestibulares en el contexto de una PHI son muy poco fre-cuentes. La patogénesis no está clara. La principal causa de la hipoacusia y la sintomatologíavestibular podría ser el atrapamiento de los nervios en el conducto auditivo interno con dañoneuronal secundario.