to investigate auditory and language skills in children with repaired cleft lip and palate.
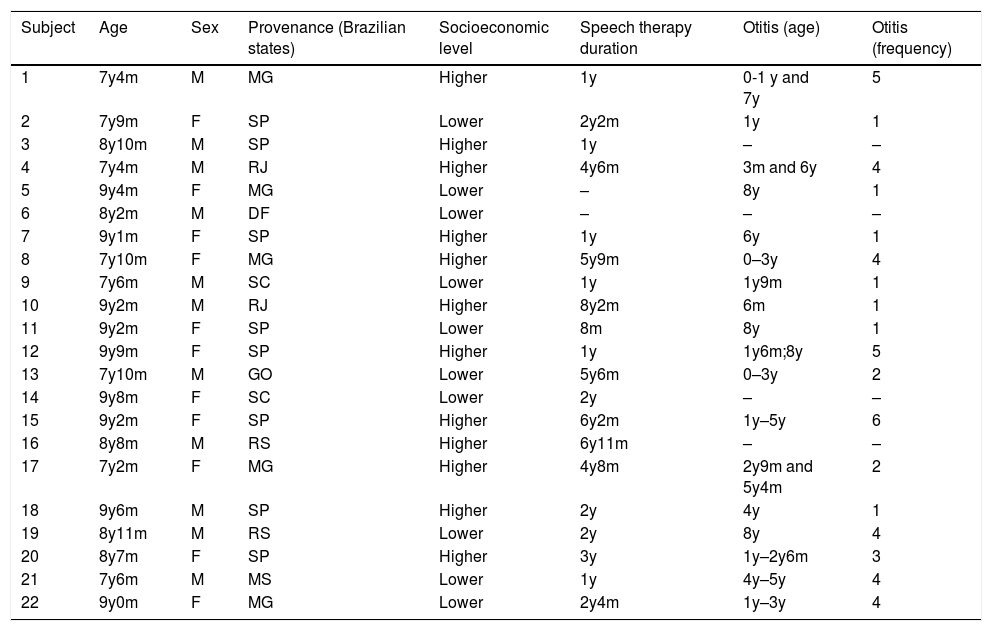
MethodsThe sample was composed of 22 children registered at the hospital where the study was conducted, seven to nine years old, 50% being female, with repaired unilateral cleft lip and palate (right or left), without associated malformations. Auditory skills were assessed using four central auditory processing tests: Random Gap Detection Test, Dichotic Digit Test, Dichotic Non-Verbal Test, Sustained Auditory Attention Ability Test. Language performance was evaluated by four standardized instruments: Illinois Psycholinguistic Skills Test, Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test, Token Test and Phonological Skills Profile. The association between auditory and language skills was evaluated by the Fisher exact test at a significance level of 5% (p<.05).
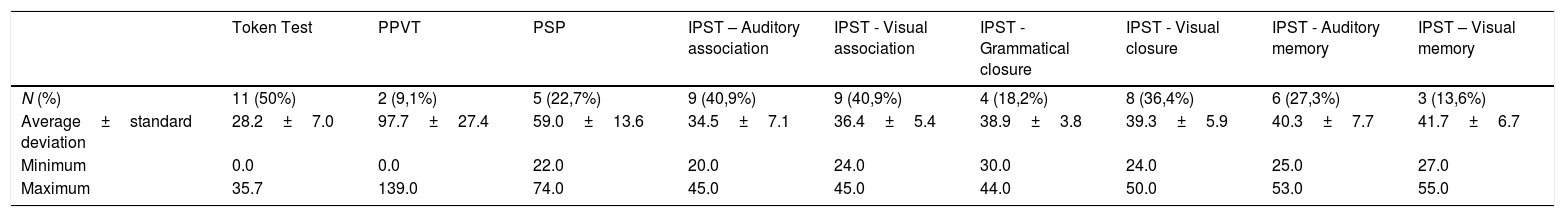
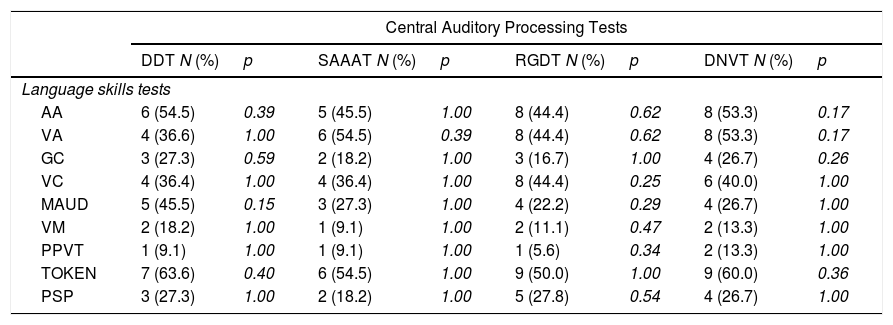
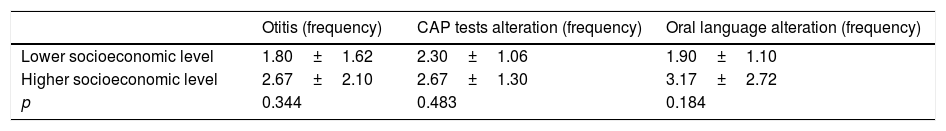
ResultsThe central auditory processing tests evidenced that only one child presented adequate performance in all skills analysed, five children presented impaired performance in all skills, and 16 exhibited deteriorations in one to three auditory skills, highlighting that temporal resolution was the most impaired skill (81%). Concerning language, three children presented adequate performance in all tests applied, and Visual Association and Auditory Association were the most impaired skills (40%). No association was observed between deteriorations in auditory and language skills.
ConclusionThere was high occurrence of impairment of auditory skills, which compose the central auditory processing, as well as of language skills, with greatest impairment of receptive language.
Investigar las habilidades auditivas y lingüísticas en niños con labio leporino y paladar reparados.
MétodosLa muestra se compuso de 22 niños registrados en el hospital en el que se realizó el estudio, de 7 a 9 años de edad, siendo el 50% niñas con labio leporino unilateral y paladar (derecho o izquierdo) reparados, sin malformaciones. Las habilidades auditivas se evaluaron utilizando 4 pruebas de procesamiento auditivo central: Random Gap Detection Test, Dichotic Digit Test, Dichotic Non-Verbal Test y Sustained Auditory Attention Ability Test. El desempeño lingüístico se evaluó utilizando diversos instrumentos estandarizados: Illinois Psycholinguistic Skills Test, Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test, Token Test y Phonological Skills Profile. La asociación entre las habilidades auditivas y lingüísticas se evaluó mediante la prueba exacta de Fisher, con un nivel de significación del 5% (p<0,05).
ResultadosLas pruebas de procesamiento auditivo central evidenciaron que solo un niño presentó un desempeño adecuado en todas las habilidades analizadas, 5 niños presentaron una alteración del desempeño en todas las habilidades y 16 niños mostraron alteraciones en una de las 3 habilidades auditivas, subrayando que la resolución temporal fue la habilidad más deficiente (81%). Con relación al lenguaje, 3 niños presentaron un desempeño adecuado en todas las pruebas aplicadas, siendo las habilidades más deficientes la asociación visual y la asociación auditiva (40%). No se observó asociación entre las alteraciones de las habilidades auditivas y lingüísticas.
ConclusiónExistió una alta incidencia de alteraciones de las habilidades auditivas que componen el procesamiento auditivo central, así como habilidades lingüísticas con gran alteración del lenguaje receptivo.