Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs) are useful for studying the disturbances along nerve pathways implicated in the transmission of neurological information from otolithic organs related to vestibular function. This study aims to determine the differences in VEMPs in patients affected with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
MethodsWe recruited 36 patients, 9 diagnosed with recurrent BPPV (rBPPV), 9 with only one episode of vertigo (iBPPV), and 18 as a control group. We performed cervical and ocular VEMPs (cVEMPs and oVEMPs).
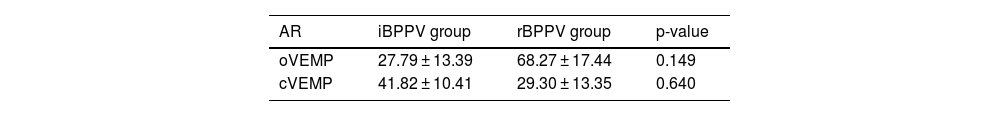
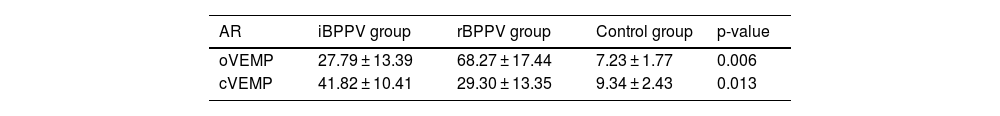
ResultsWe observed differences in asymmetry ratio, which was 41.82% in cVEMPs in iBPPV and 68.27% in oVEMPs in rBPPV, while no asymmetry was found in control cases. Also, there was a lack of both VEMP responses in 22.2% of cases and an absence of cVEMP in 11.1% in iBPPV; in rBPPV, 11.1 % presented no responses in cVEMPs or oVEMPs, 22.2% showed no oVEMP, and 11.1% showed no cVEMP. These values were normal in the control group.
ConclusionThe value of VEMPs in BPPV demonstrates the implication of vestibular damage, mainly utricle damage. For better sensitivity in detecting otolith abnormalities, we should perform oVEMPs and cVEMPs in recurrent BPPV and early stages of BPPV.
Los potenciales evocados miogénicos vestibulares (PEMVs) son útiles para el estudio de alteraciones en la transmisión de la información neurológica relacionada con la función vestibular procedente de los órganos otolíticos. Este estudio trata de determinar las diferencias en los PEMVs en los pacientes afectados por vértigo posicional paroxístico benigno (VPPB).
MétodosReclutamos 36 pacientes, 9 diagnosticados de VPPB recurrente (VPPBr), 9 con un solo episodio de vértigo (VPPBi) y 18 como grupo control. Realizamos PEMVs cervicales y oculares (cVEMPs y oVEMPs).
ResultadosObservamos diferencias en la ratio de asimetría, que fue del 41,.82% en los cVEMPs del grupo VPPBi y del 68,27% en los oVEMPs del grupo VPPBr, mientras que no hubo asimetría en el grupo control. También se observó una ausencia de ambas respuestas de PEMVs en el 22,2% de los casos y una ausencia de los cVEMPs en el 11,1% en el grupo VPPBi; en el grupo de VPPBr, el 11,1% no presentaron respuestas de cVEMPs ni oVEMPs, un 22,2% no presentaron respuestas oVEMPs y un 11,1% no presentaron respuestas cVEMPs. Estos valores fueron normales para el grupo control.
ConclusiónEl valor de los PEMVs en el VPPB demuestra la implicación del daño vestibular, principalmente el daño utricular. Para una mayor sensibilidad en la detección de anormalidades en los otolitos, deberíamos realizar tanto oVEMPs como cVEMPs en los casos de VPPB recurrente y en estadíos iniciales de VPPB.