Tinnitus is a symptom experienced by millions of people around the world, generating psychological, physical and social consequences. There are different therapeutic options that seek to reduce the symptom and the related consequences. One of the newest alternatives is training with Neurofeedback, a neuromodulation technique that looks for modify brain activity. The objective of this research was to determine the efficacy of Neurofeedback treatment parameters in reducing the perception of tinnitus and in reducing the behavioral consequences triggered by the symptom, through a systematic review between 2010 and 2020.
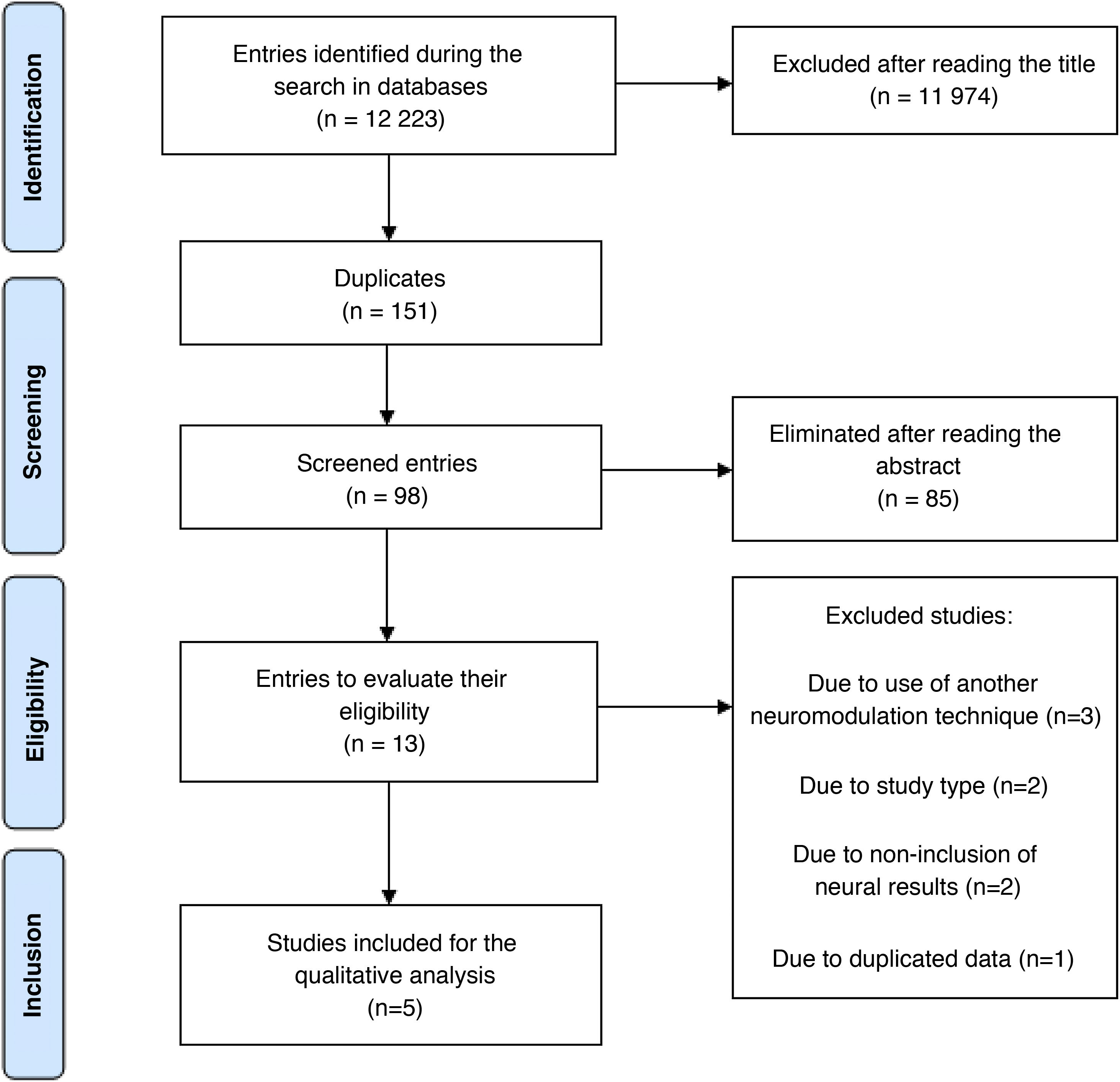
Materials and methodsThe data search was carried out in Spanish and English on PubMed/MedLine, EBSCO Host, Embase, Scopus, CENTRAL, SpringerLink and OpenGrey databases. The systematic review was carried out according to the stages established by PRISMA and five studies were identified to be included in the qualitative analysis.
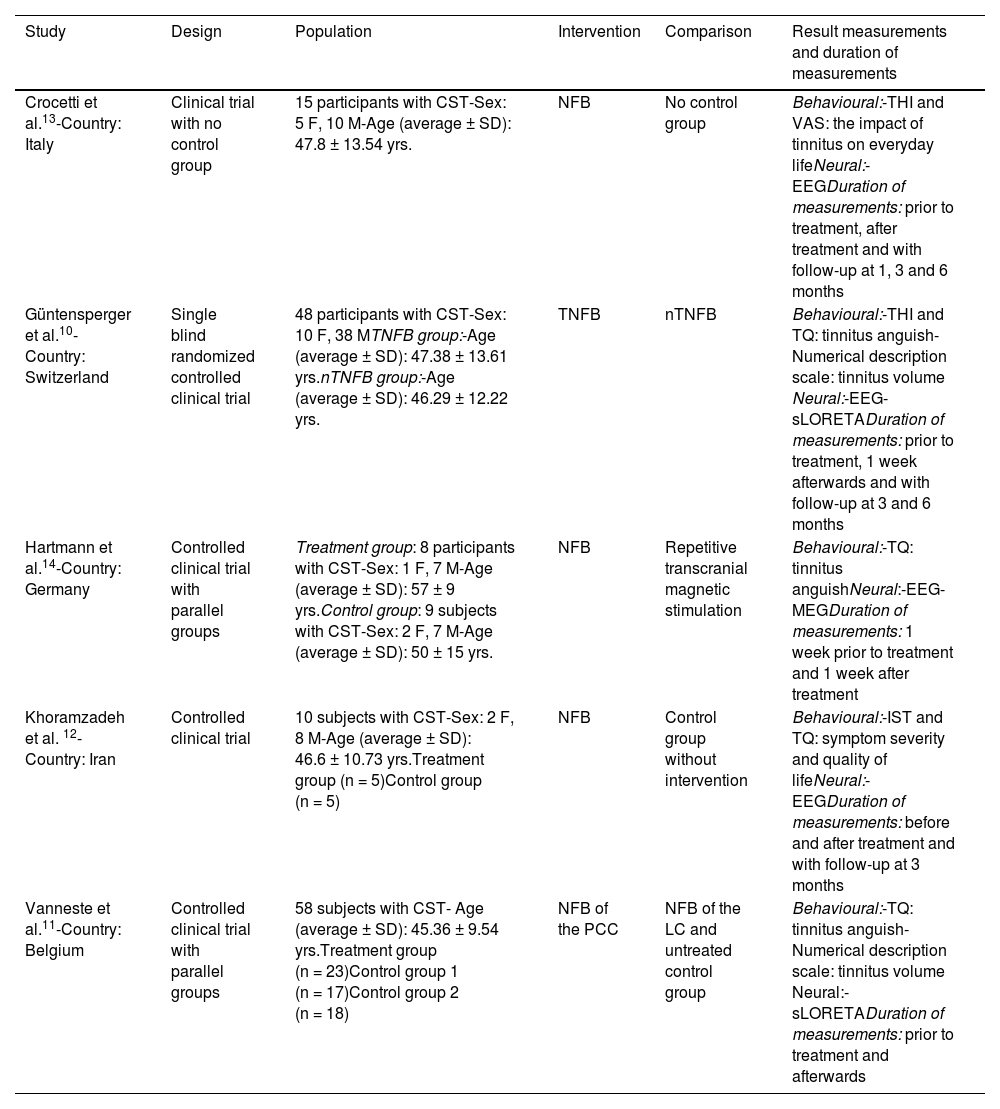
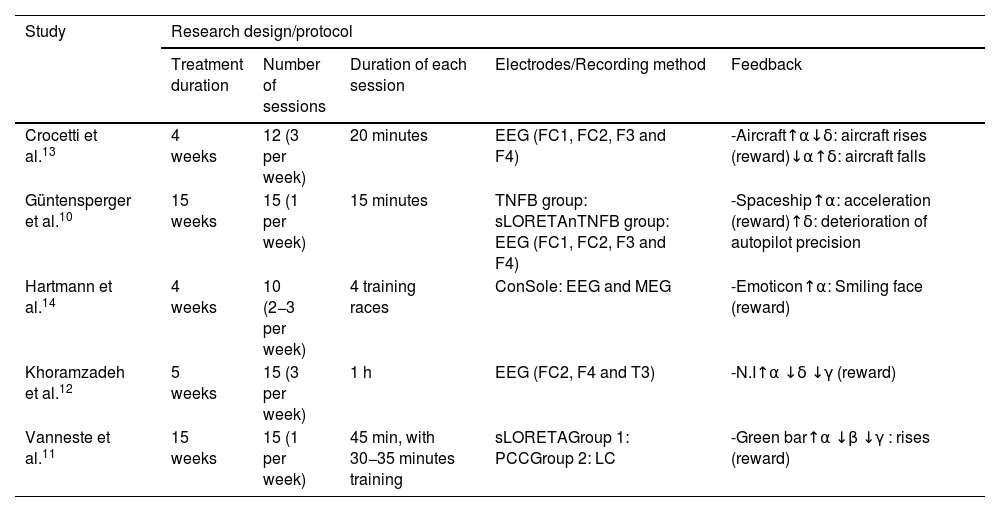
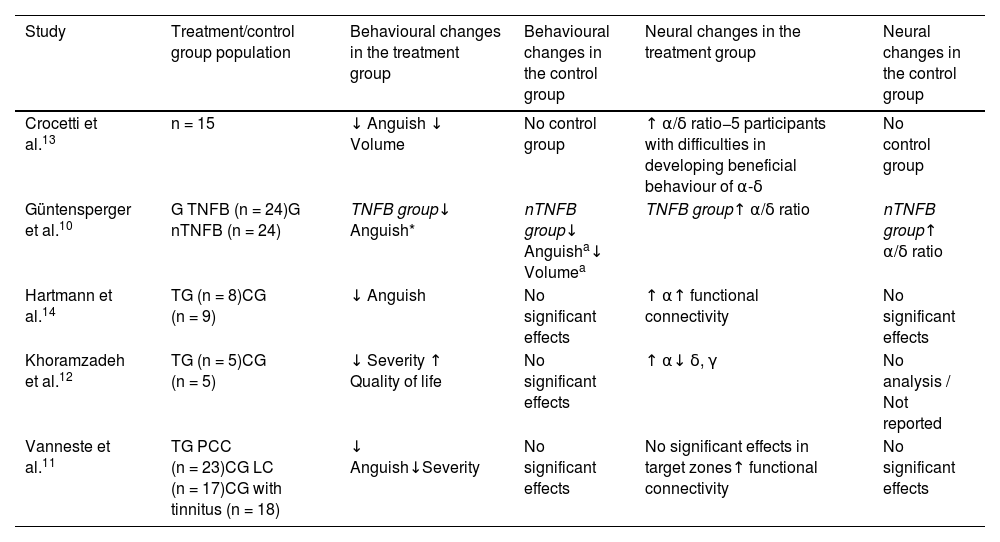
ResultsAll studies demonstrated that NFB training for tinnitus decreases symptom perception and related consequences. At the neural level, there was an increase in the activity of the alpha wave and a decrease in the activity of delta, gamma and beta.
ConclusionsNeurofeedback has a modulating effect on brain activity patterns. However, although all the studies reported a decrease in the consequences related to the symptom at the behavioral level after treatment, due to the lack of development of this technique for the symptom and the characteristics of the studies reviewed, it cannot be certainty of efficacy on behavioral and neurophysiological consequences.
El tinnitus es un síntoma experimentado por millones de personas alrededor del mundo, genera consecuencias a nivel psicológico, físico y social. Existen diferentes opciones terapéuticas que buscan disminuir el síntoma y las consecuencias relacionadas. Una de las alternativas más novedosas es el entrenamiento con Neurofeedback, una técnica de neuromodulación en la que se busca modificar la actividad cerebral. El objetivo de esta investigación fue determinar la eficacia de los parámetros del tratamiento con Neurofeedback en la reducción de la percepción del tinnitus y en la disminución de las consecuencias conductuales desencadenadas por el síntoma, mediante una revisión sistemática comprendida entre el año 2010 y 2020.
Materiales y métodosLa búsqueda de datos fue realizada en español e inglés y se llevó a cabo en las bases de datos PubMed/MedLine, EBSCO Host, Embase, Scopus, CENTRAL, SpringerLink y OpenGrey. La revisión sistemática fue realizada conforme las etapas establecidas por PRISMA y se identificaron cinco estudios para ser incluidos en el análisis cualitativo.
ResultadosLa totalidad de los estudios reportaron que el entrenamiento con Neurofeedback para el tinnitus disminuyó la percepción del síntoma y las consecuencias relacionadas. A nivel neural se dio un aumento de la actividad de la onda alfa y la disminución de la actividad de delta, gamma y beta.
ConclusionesEl Neurofeedback posee un efecto modulador sobre los patrones de actividad cerebral. Sin embargo, aunque la totalidad de los estudios reportaron una disminución de las consecuencias relacionadas con el síntoma a nivel conductual después del tratamiento, debido a la falta de desarrollo de esta técnica para el síntoma y las características de los estudios revisados, no se puede tener certeza de la eficacia sobre las consecuencias conductuales y neurofisiológicas.