In our country, there are no series of patients that have described the incidence of the different diseases which cause balance disorders (BD) in primary care. The objective of this study is to calculate the incidence of each disease to propose specific training measures.
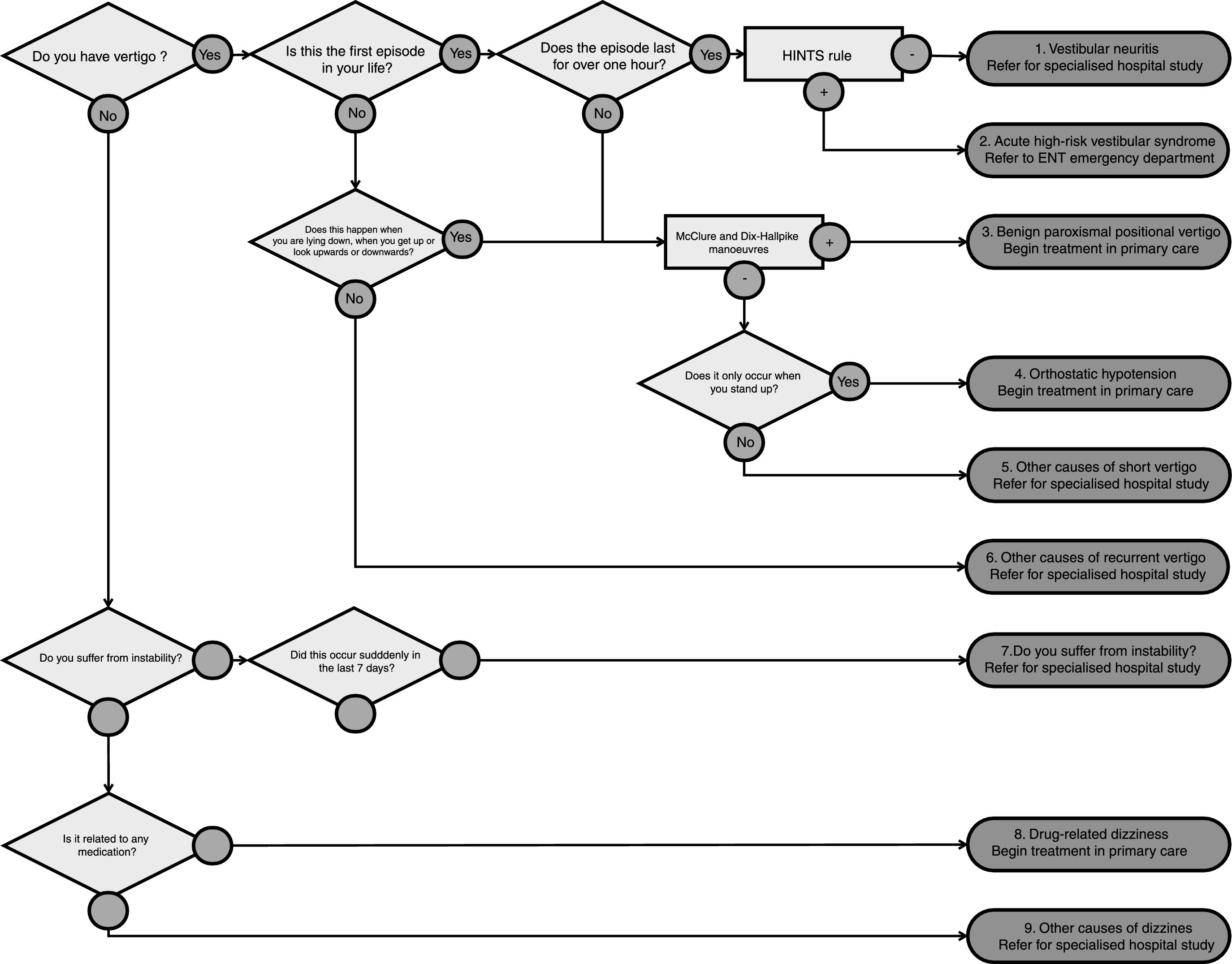
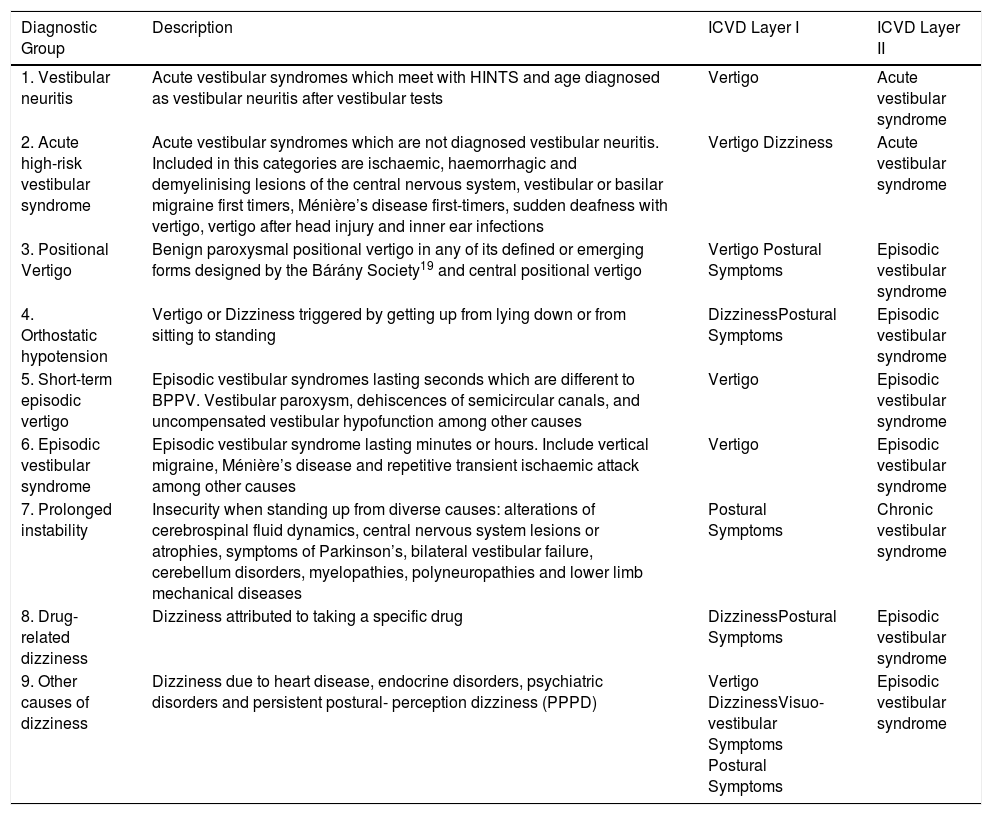
Materials and methodProspective cross-sectional study. Patient data of five primary care physicians in five different primary care centres in our hospital area were collected. All patients who attended consultations for any type of vertigo, imbalance or dizziness over one year were recruited as well as the main reason for consultation. Using a diagnostic-therapeutic algorithm, patients were diagnosed and treated in primary care or referred for study in hospital care.
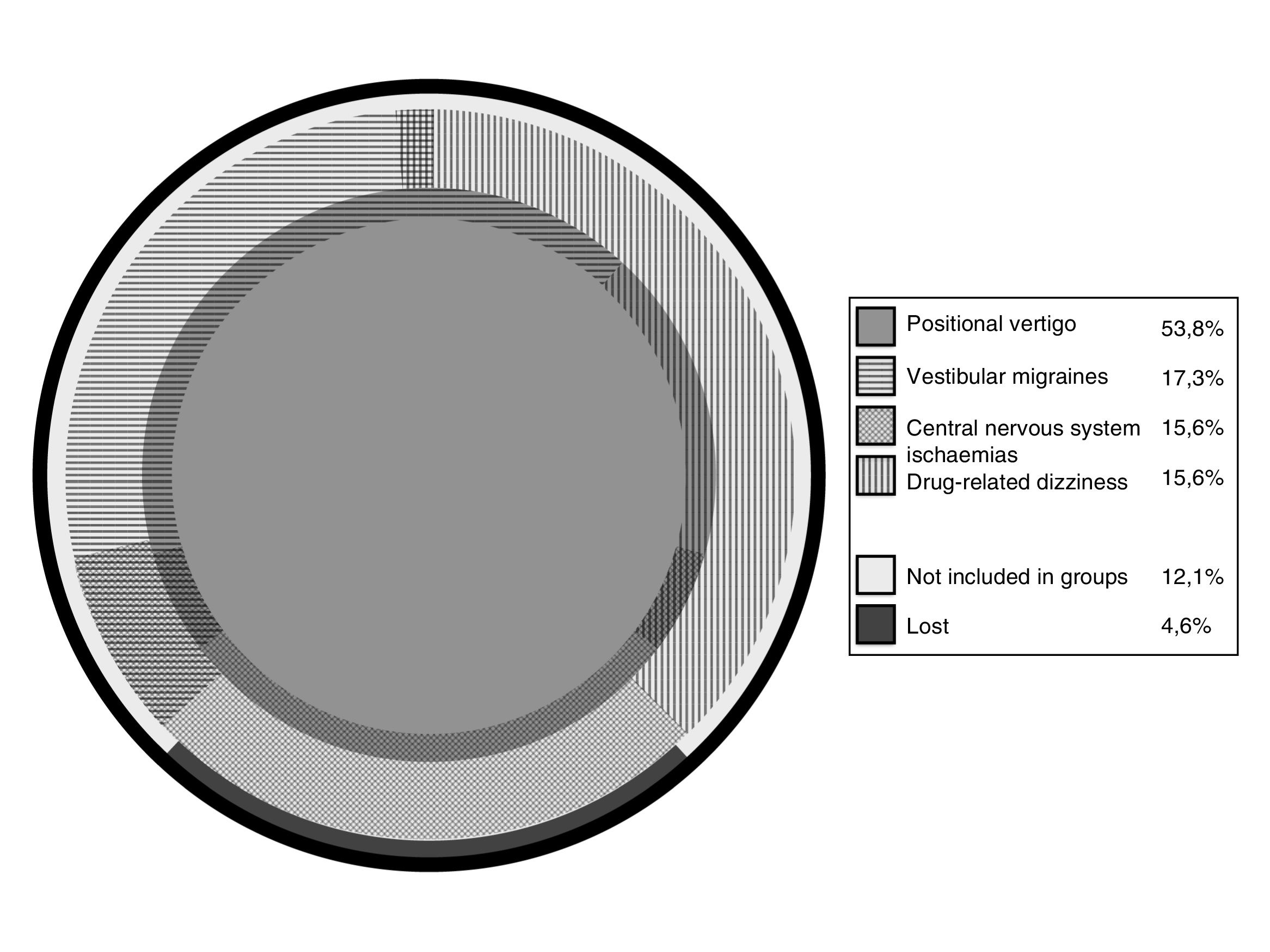
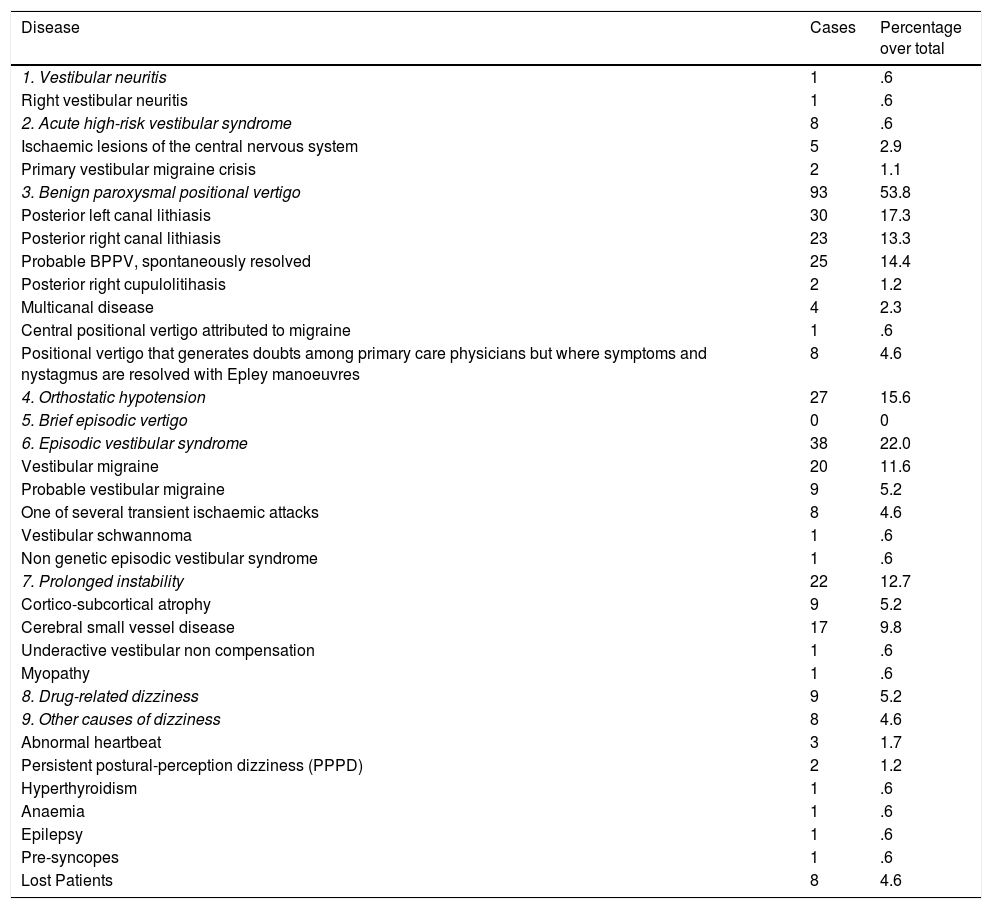
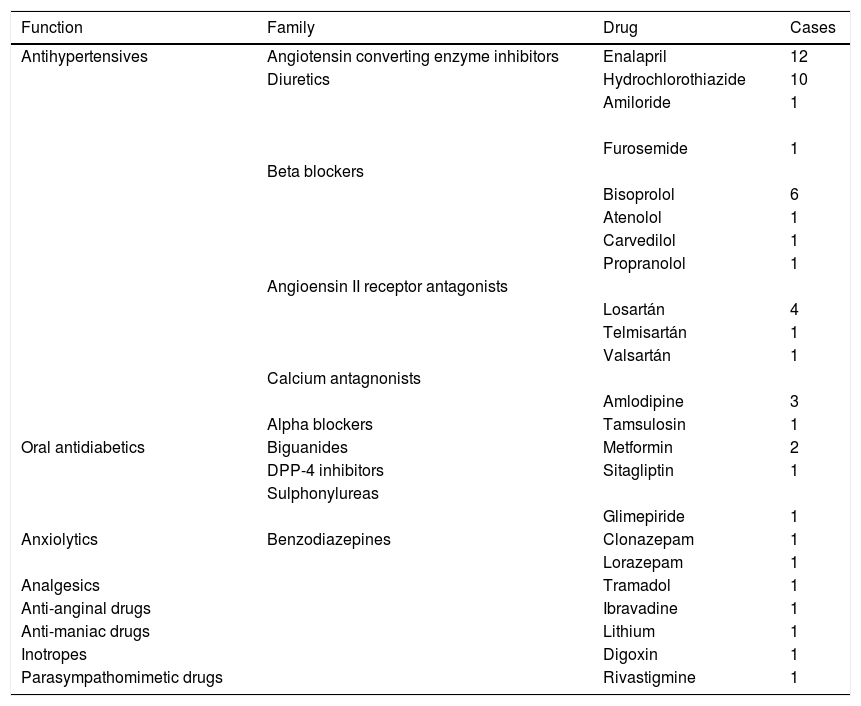
ResultsThe population studied was 7896 people. An annual incidence of BD of 2.2% was detected. Of the cases, 56.1% could be diagnosed and treated in primary care. Of the patients, 53.8% were diagnosed with some type of positional vertigo; the next three most frequent diagnoses were vestibular migraine, central nervous system ischaemia and medication side effects. These four groups accounted for 87.9% of the population.
ConclusionsThe incidence of BD in primary care requires an approach that includes training in the diagnosis and treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, headache, cardiovascular risk factors and pharmacology. It is not necessary to prescribe vestibular suppressants in most patients.
Actualmente, no existen series de pacientes que hayan descrito la incidencia de cada una de las enfermedades que causan alteraciones del equilibrio (AE) en Atención Primaria. El objetivo de este estudio es calcular la incidencia de cada una de ellas para proponer medidas formativas específicas.
Materiales y métodoEstudio transversal prospectivo. Se obtuvieron los datos de los pacientes de cinco cupos de médicos en cinco centros diferentes de Atención Primaria de nuestra área hospitalaria. Durante un año, se reclutaron a todos los pacientes que acudieron a consultas por cualquier tipo de vértigo, inestabilidad o mareo como motivo principal de consulta. Mediante un algoritmo diagnóstico-terapéutico, los pacientes fueron diagnosticados y tratados en Atención Primaria o derivados para su estudio en Atención Hospitalaria.
ResultadosLa población estudiada fue de 7896 personas. Se detectó una incidencia anual de AE del 2,2%. El 56,1% de los casos pudo ser diagnosticado y tratado en Atención Primaria. El 53,8% de los pacientes fue diagnosticado de algún tipo de vértigo posicional; los siguientes tres diagnósticos más frecuentes fueron migraña vestibular, isquemia del sistema nervioso central y efectos secundarios de medicamentos. Estos cuatro grupos sumaron un 87,9% de la población.
ConclusionesLa incidencia de las AE en Atención Primaria requiere un abordaje en el que se incluya formación en el diagnóstico y tratamiento del vértigo posicional paroxístico benigno, la cefalea, los factores de riesgo cardiovascular y de Farmacología, no siendo necesario prescribir sedantes vestibulares en la mayoría de los casos.