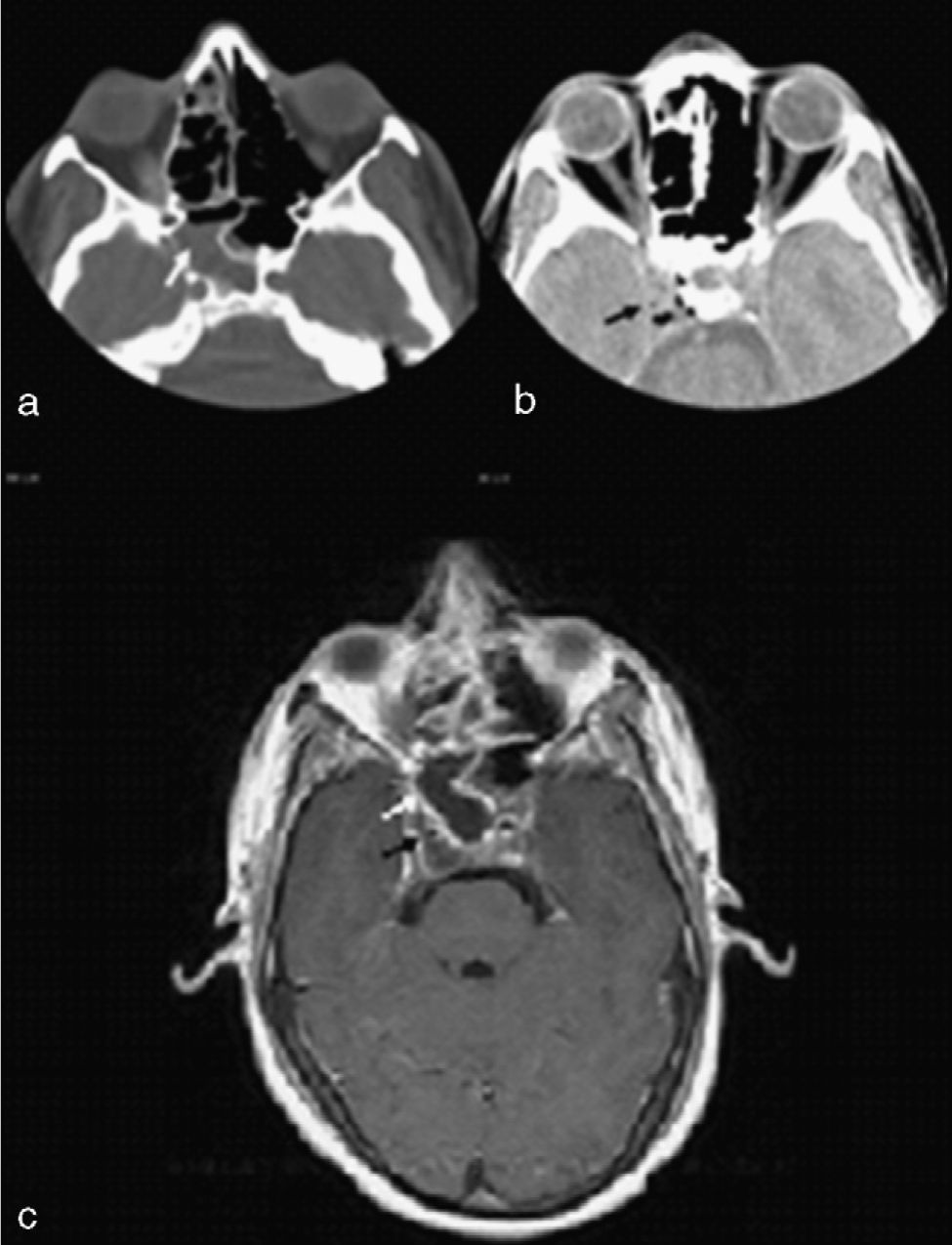
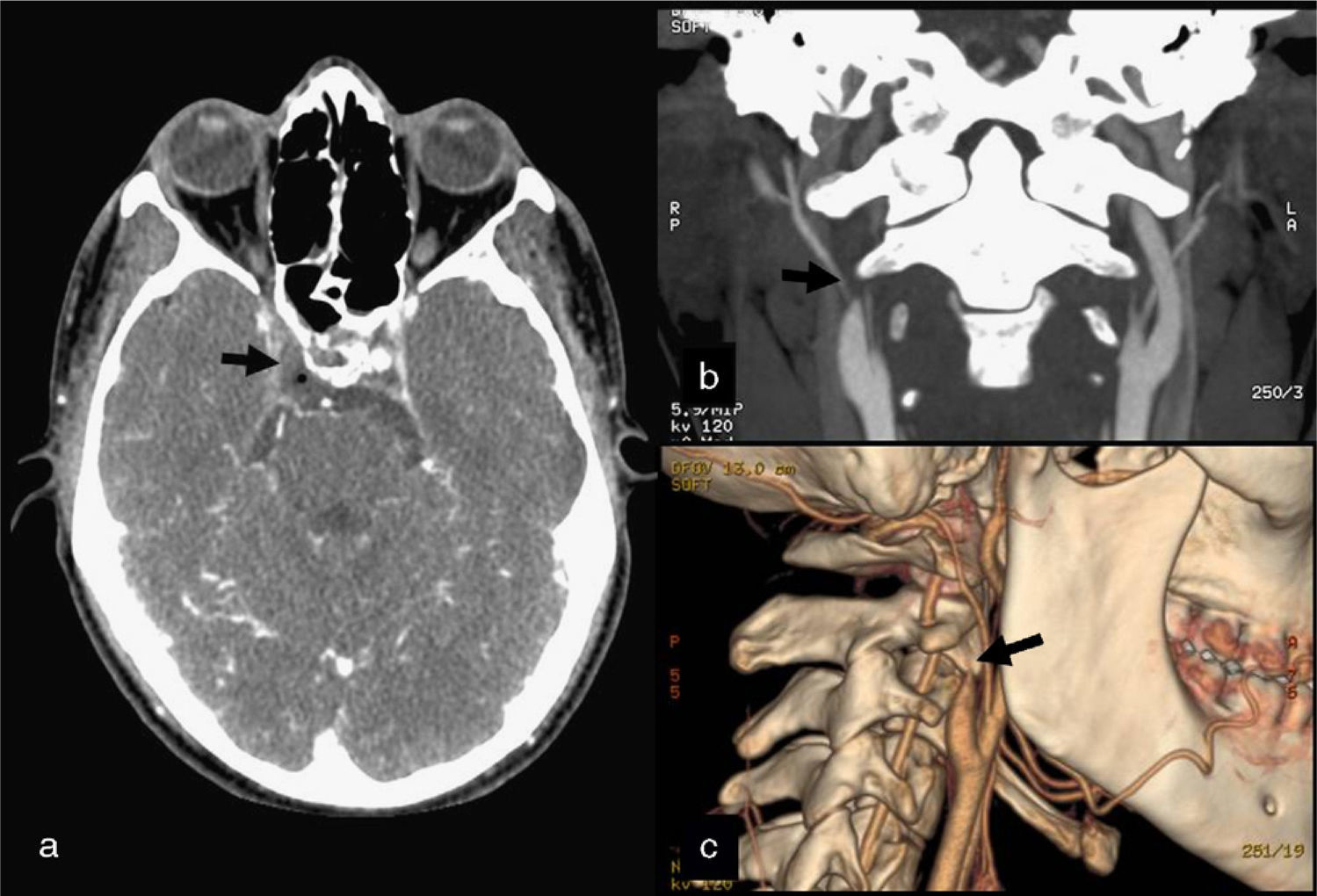
Lemierre syndrome typically consists of a septic thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum. We present an unusual variant of Lemierre syndrome with cavernous sinus thrombosis and occlusion of the ipsilateral internal carotid artery secondary to sphenoid sinusitis caused by Streptococcus viridans.
El sindrome de Lemierre consiste típicamente en una tromboflebitis séptica de la vena yugular interna causada por Fusobacterium necrophorum. Presentamos una variante excepcional del sindrome de Lemierre con trombosis del seno cavernoso y oclusión de la carótida interna ipsilateral secundaria a una sinusitis esfenoidal causada por Estreptococo Viridans.