The objective was to determine the results of the treatment of severe and/or refractory epistaxis requiring hospital admission. In addition, the results of arterial ligation versus embolisation were compared.
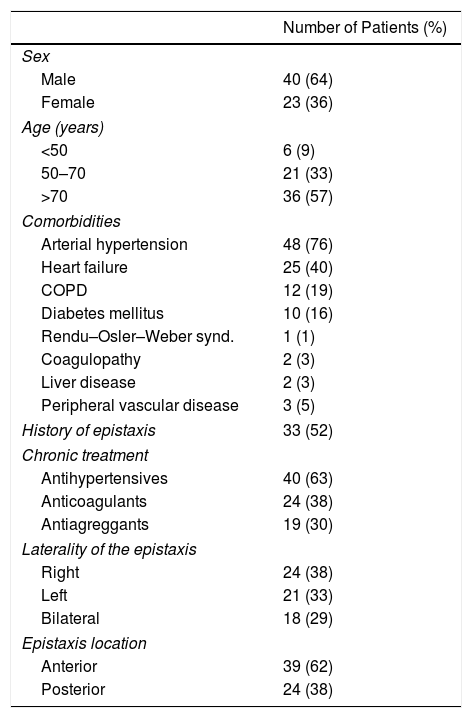
Material and methodSixty-three patients with severe and/or refractory epistaxis requiring hospital admission between August 2014 and December 2016 were included prospectively.
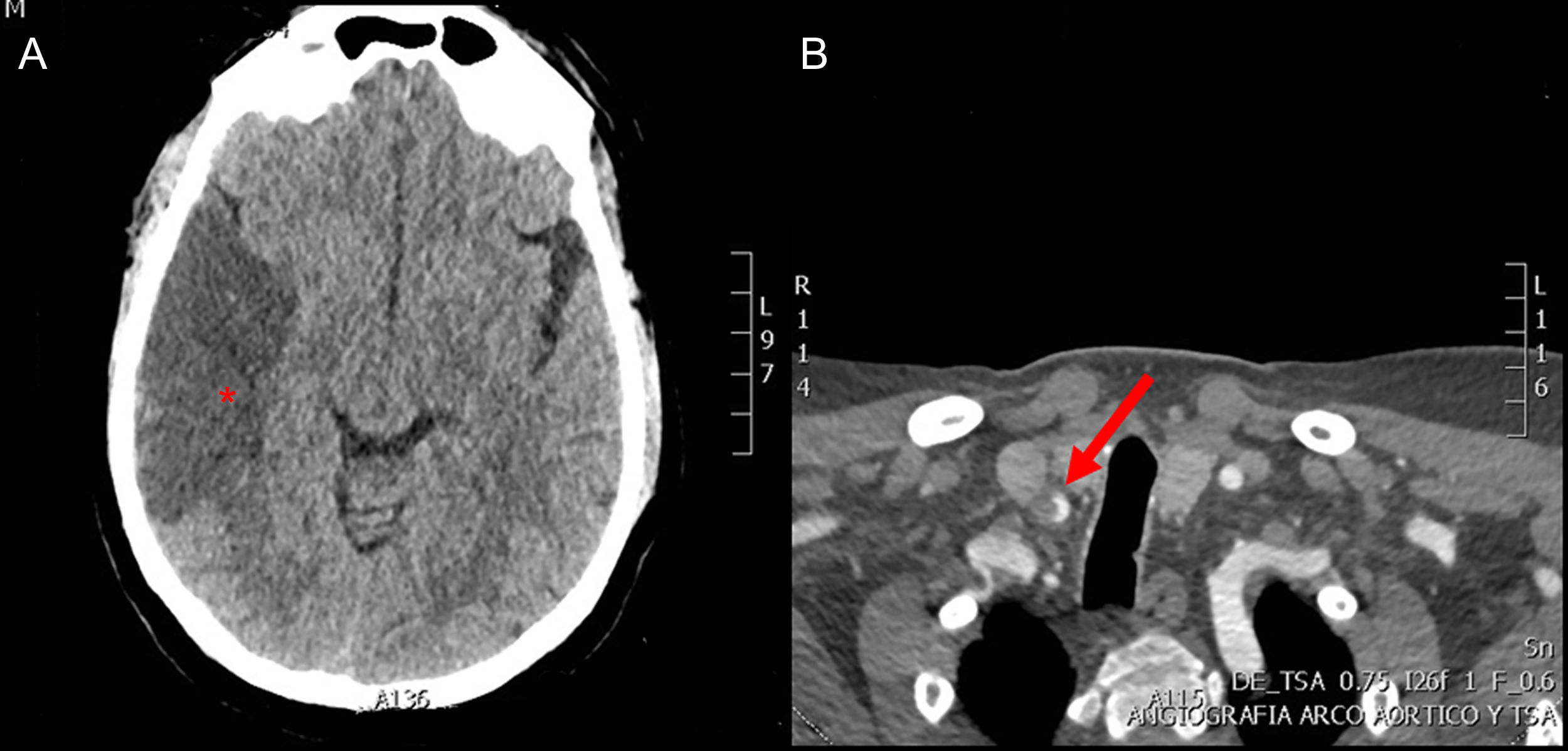
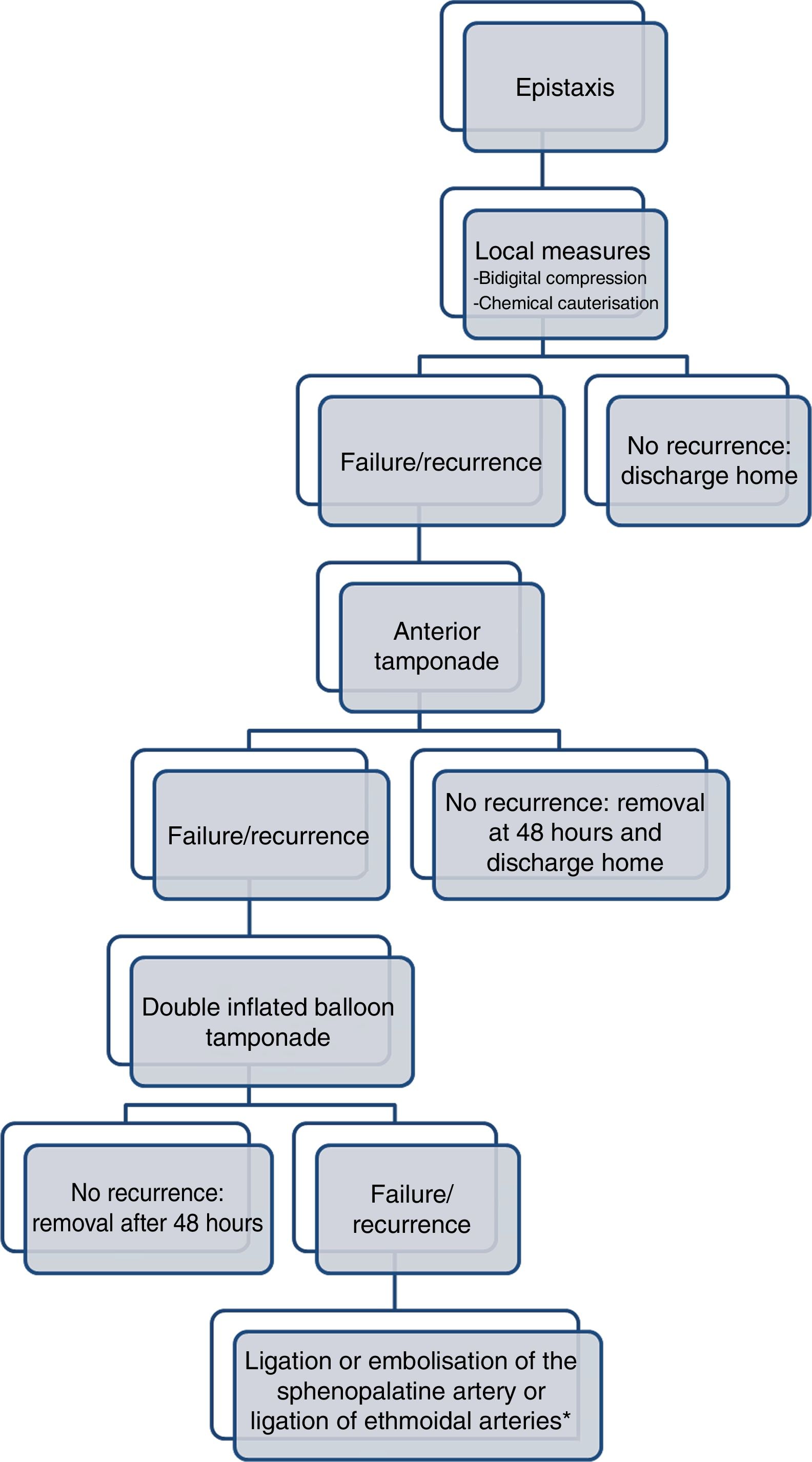
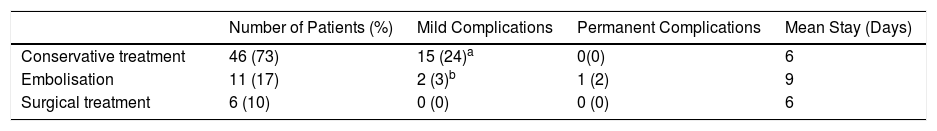
ResultsEleven patients (17%) underwent embolisation, 5 (8%) endoscopy ligation and the remaining 47 (75%) underwent conservative treatment with tamponade. The mean age of the patients in which conservative measures were sufficient was 72 years, while the age of those treated with embolisation was 71 years and of those who underwent surgery was 53 years. For the patients who underwent conservative treatment or surgery, the average stay was 6 days, compared to 9 days for those who underwent embolisation. One patient suffered a hemispheric stroke after embolisation. No post-surgical complications were observed.
ConclusionsMost cases of severe and/or refractory epistaxis are resolved by conventional tamponade. Endoscopy ligation is associated with a decrease in hospital stay, without serious complications. It is advisable to have all the possible therapeutic options available, for which the presence of interventional radiologists and experienced surgeons is essential to avoid complications and decide the treatment to be performed individually for each patient.
El objetivo fue determinar los resultados del tratamiento de las epistaxis graves y/o refractarias que requirieron ingreso hospitalario. Además se compararon los resultados del tratamiento mediante ligadura arterial o embolización.
Material y métodoSe incluyeron de forma prospectiva 63 pacientes con epistaxis grave y/o refractaria que requirieron ingreso hospitalario entre agosto de 2014 y diciembre de 2016.
ResultadosEn 11 pacientes (17%) se realizó embolización, 5 (8%) fueron intervenidos mediante endoscopia y en los 47 restantes (75%) se realizó tratamiento conservador. La edad media de los pacientes en los que las medidas conservadoras fueron suficientes fue de 72 años, mientras que la edad de aquellos tratados con embolización fue de 71 años y de los que fueron intervenidos quirúrgicamente fue de 53 años. En los pacientes sometidos a tratamiento conservador o a cirugía la estancia media fue de 6 días, frente a 9 días en aquellos en los que se realizó embolización. Un paciente sufrió un ictus hemisférico tras la embolización. No se observaron complicaciones posquirúrgicas.
ConclusionesLa mayoría de los pacientes con epistaxis graves y/o refractarias se resuelven mediante taponamiento convencional. El tratamiento mediante ligadura arterial está asociado a una disminución de la estancia hospitalaria, sin observarse complicaciones graves. Es aconsejable disponer de todas las opciones terapéuticas posibles para lo cual la presencia de radiólogos intervencionistas y cirujanos experimentados es fundamental para evitar complicaciones y decidir el tratamiento a realizar de forma individual en cada paciente.