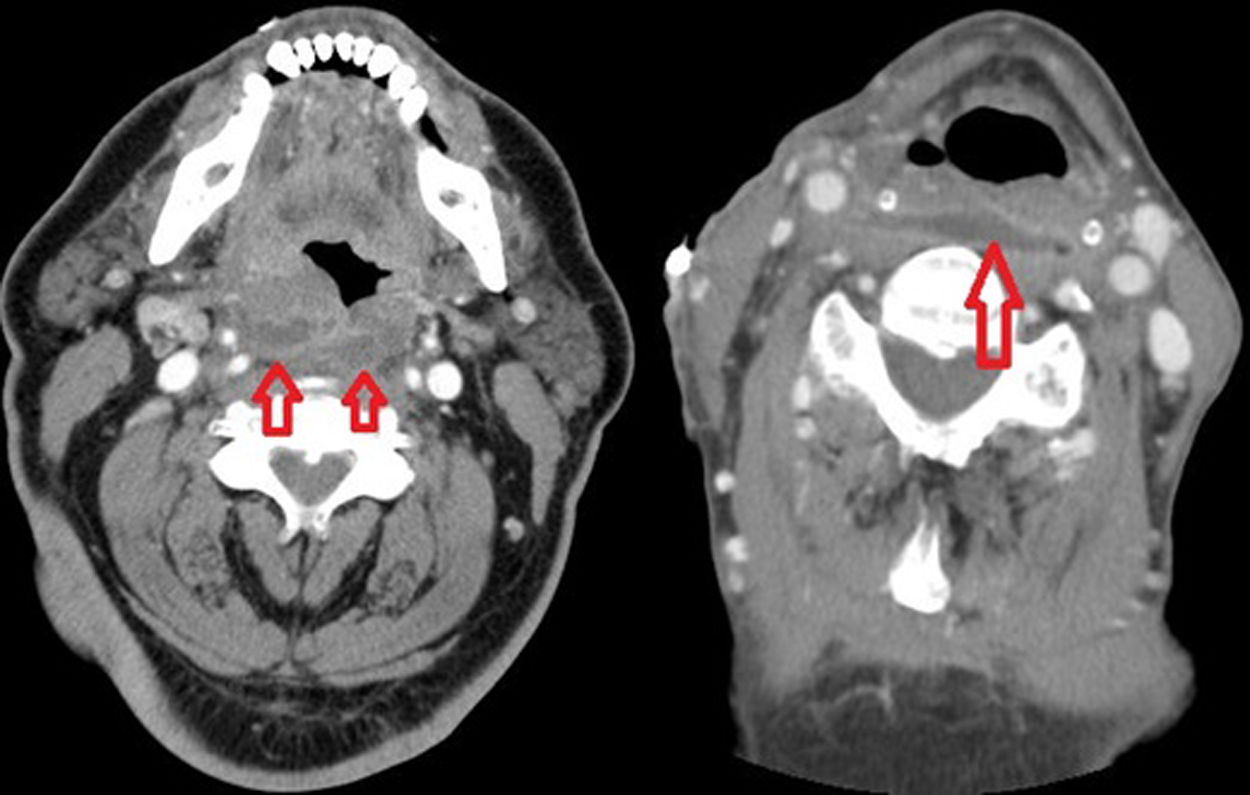
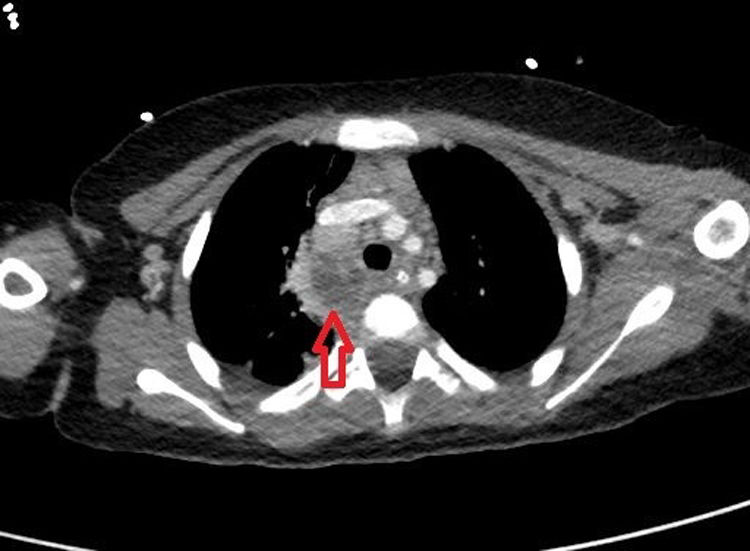
Retropharyngeal abscess is a serious condition. Its rare occurrence, thus sharing symptoms with other processes, make it a diagnostic challenge for the clinician. Therefore, it is critical to make an early diagnosis to prevent delaying treatment and avoid complications.
ObjectivesTo gain knowledge of the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, the most commonly implicated microorganisms, the type of treatment used, morbidity and mortality of retropharyngeal abscesses at a tertiary institution over the last 25 years.
MethodsA retrospective study was conducted by reviewing medical records of all patients diagnosed with retropharyngeal abscess in a single centre between 1 January 1990 and 31 February 2016. Thirty-three patients were included in our study. Data such as personal history, present illness, diagnoses and treatment procedures were collected from the medical records.
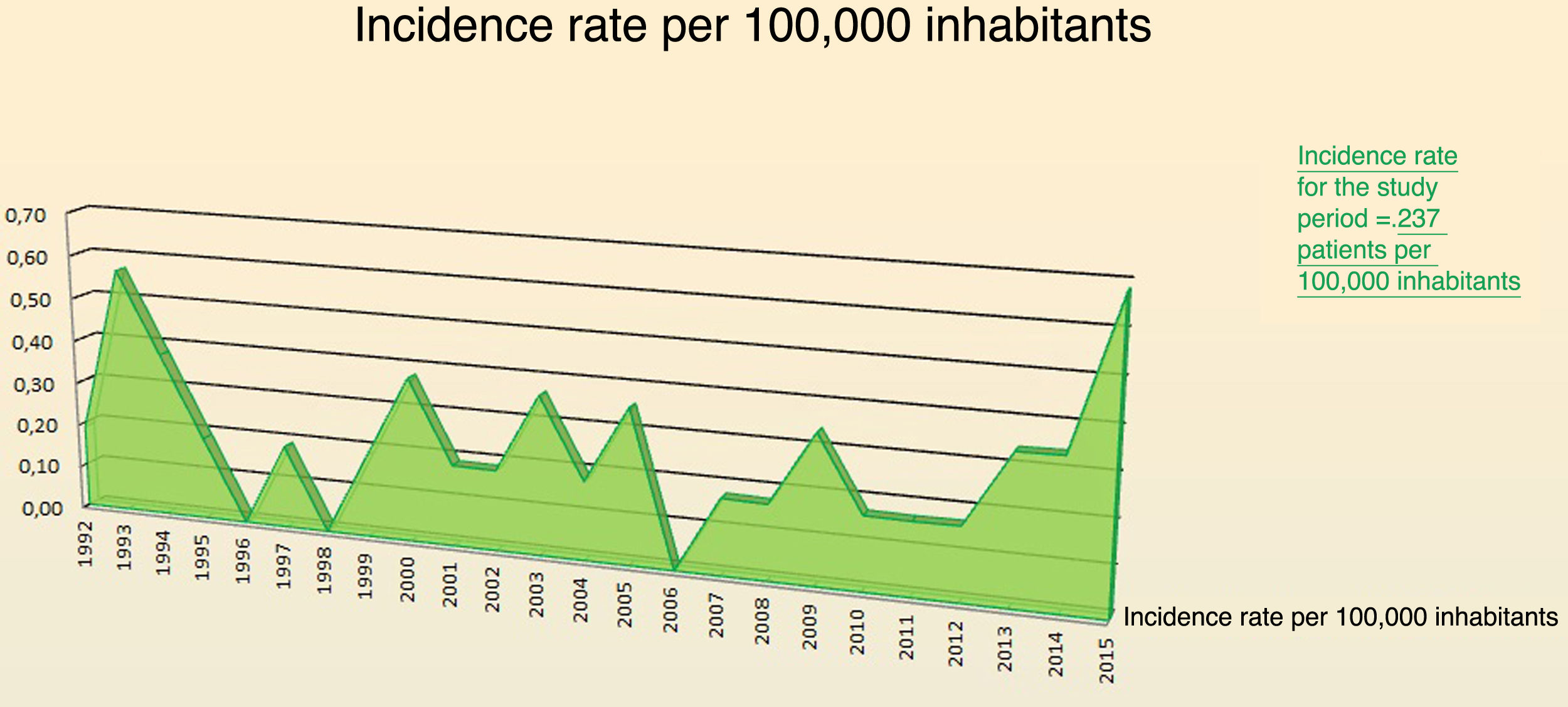
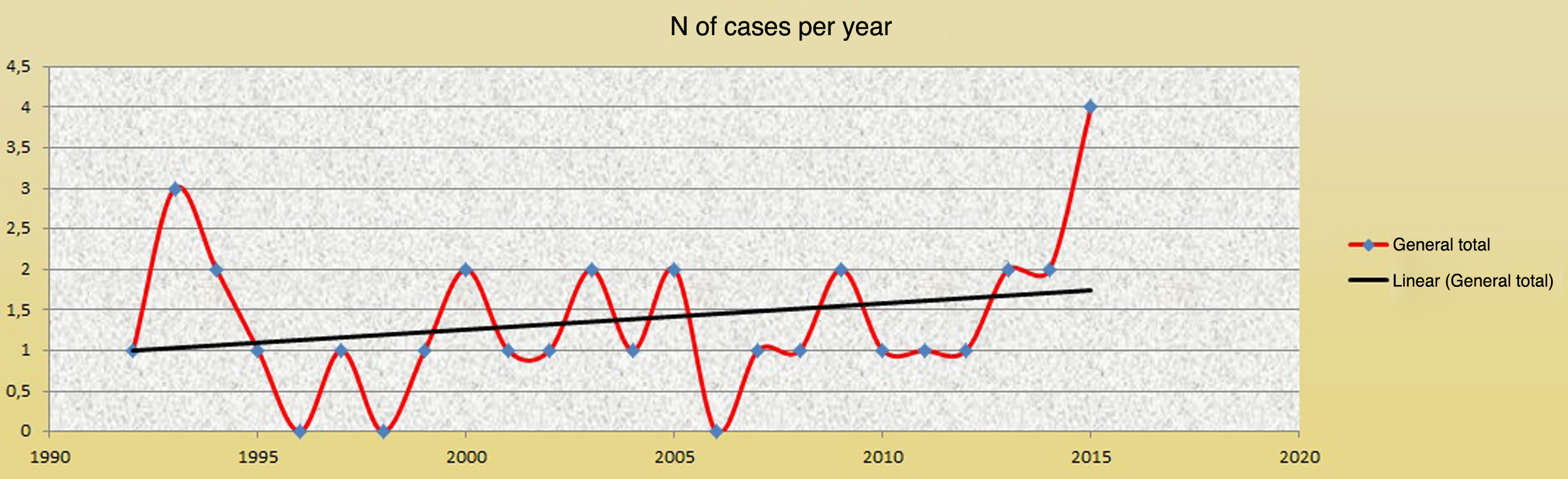
ResultsThe incidence during the years of study was 0.2 cases/100000 inhabitants/year. Personal medical histories most often associated were alcoholism, smoking, diabetes and obesity. The most common aetiology found was impaction of a foreign body (especially fishbone). The most common presenting symptoms were odynophagia and neck pain accompanied by fever. Preventive tracheotomy was performed in the initial management of the patient in 9 cases (27%). The most frequent complication was descending necrotising mediastinitis. Surgical drainage of the abscess was required in 27 patients (82%), especially with external approaches (17 cases). Two patients had sequelae: paralysis of unilateral vocal cord and Horner's syndrome. No mortality was observed in the patients of the study.
ConclusionRetropharyngeal abscesses must be considered medical-surgical emergencies as they are likely to produce serious complications. We must pay attention to the warning symptoms such as odynophagia and cervical pain, associated or otherwise with dyspnoea, stridor, trismus, and neck stiffness. Advances in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures together with advances in critical care have been a key factor in improving the prognosis and mortality of these patients.
Los abscesos retrofaríngeos constituyen una entidad grave. Debido a su escasa frecuencia y a compartir sintomatología con otros procesos, constituyen un reto diagnóstico para el clínico, siendo esencial realizar un diagnóstico temprano para no demorar el tratamiento y evitar así complicaciones.
ObjetivosConocer la epidemiología, etiopatogenia, manifestaciones clínicas, microorganismos más frecuentemente implicados, tipo de tratamiento realizado y morbimortalidad de los abscesos retrofaríngeos en un hospital terciario en 25 años.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo descriptivo mediante la revisión de historias clínicas de todos los pacientes diagnosticados con absceso retrofaríngeo en un centro entre el 1 de enero de 1990 hasta el 31 de febrero de 2016. Treinta y tres pacientes diagnosticados con absceso retrofaríngeo durante dicho periodo fueron incluidos en nuestro estudio. De la historia clínica se recogieron diferentes variables que fueron agrupadas en las siguientes categorías: antecedentes personales, enfermedad actual, procedimientos diagnósticos realizados y tratamiento.
ResultadosLa incidencia durante los años de estudio fue de 0,2 casos/100.000 habitantes/año. Los factores de riesgo más frecuentemente asociados fueron la diabetes de tipo II y la obesidad, siendo la impactación de un cuerpo extraño la etiología más frecuentemente encontrada (sobre todo, espina de pescado). Los síntomas/signos más frecuentes de presentación fueron la odinofagia y fiebre. La traqueotomía preventiva en el manejo inicial del paciente se realizó en nueve pacientes (27%). La complicación más frecuente fue la mediastinitis necrosante descendente. Se precisó un drenaje quirúrgico del absceso en 27 pacientes (82%), sobre todo con abordajes por vía externa (17 casos). Dos pacientes presentaron secuelas relacionadas con el tratamiento quirúrgico: una parálisis de cuerda vocal unilateral y un síndrome de Horner. No se objetivó mortalidad en los pacientes del estudio.
ConclusionesLos abscesos retrofaríngeos deben ser considerados urgencias médico-quirúrgicas, ya que son susceptibles de producir complicaciones graves. Debemos prestar atención a los síntomas de alarma como son la odinofagia y el dolor cervical, asociado o no, disnea, estridor, trismus, rigidez cervical y síndrome febril. Los avances en procedimientos diagnósticos, terapéuticos y en los cuidados del paciente crítico han sido decisivos en la mejora del pronóstico y mortalidad de estos pacientes.