To increase the knowledge of rhinotillexomania, or compulsive nose picking, as a manifestation of psychiatric disease through the presentation of a case series and a review of the literature.
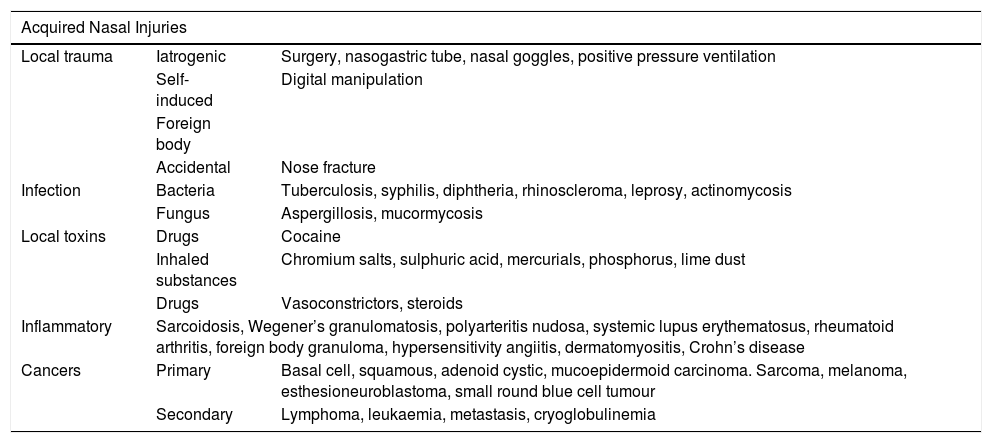
MaterialWe present three clinical cases with self-destructive nasal injuries as a symptom of different psychiatric diseases.
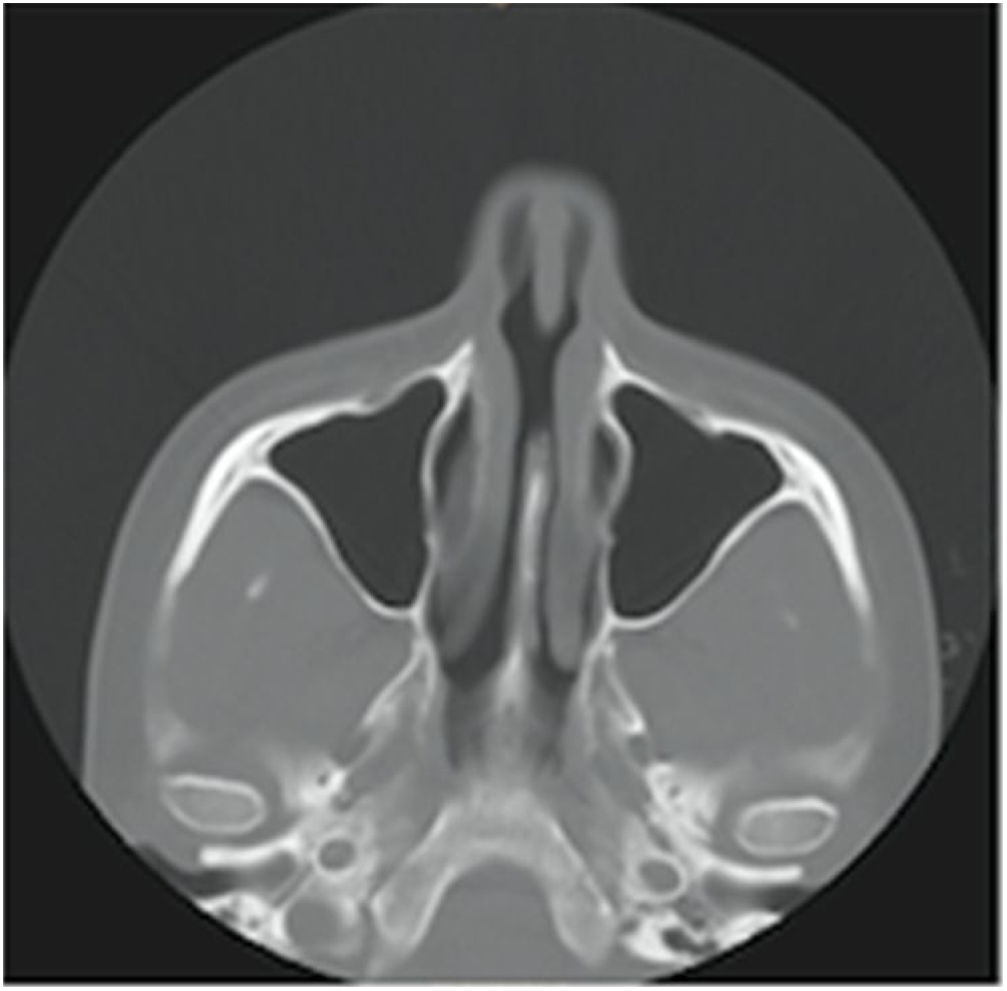
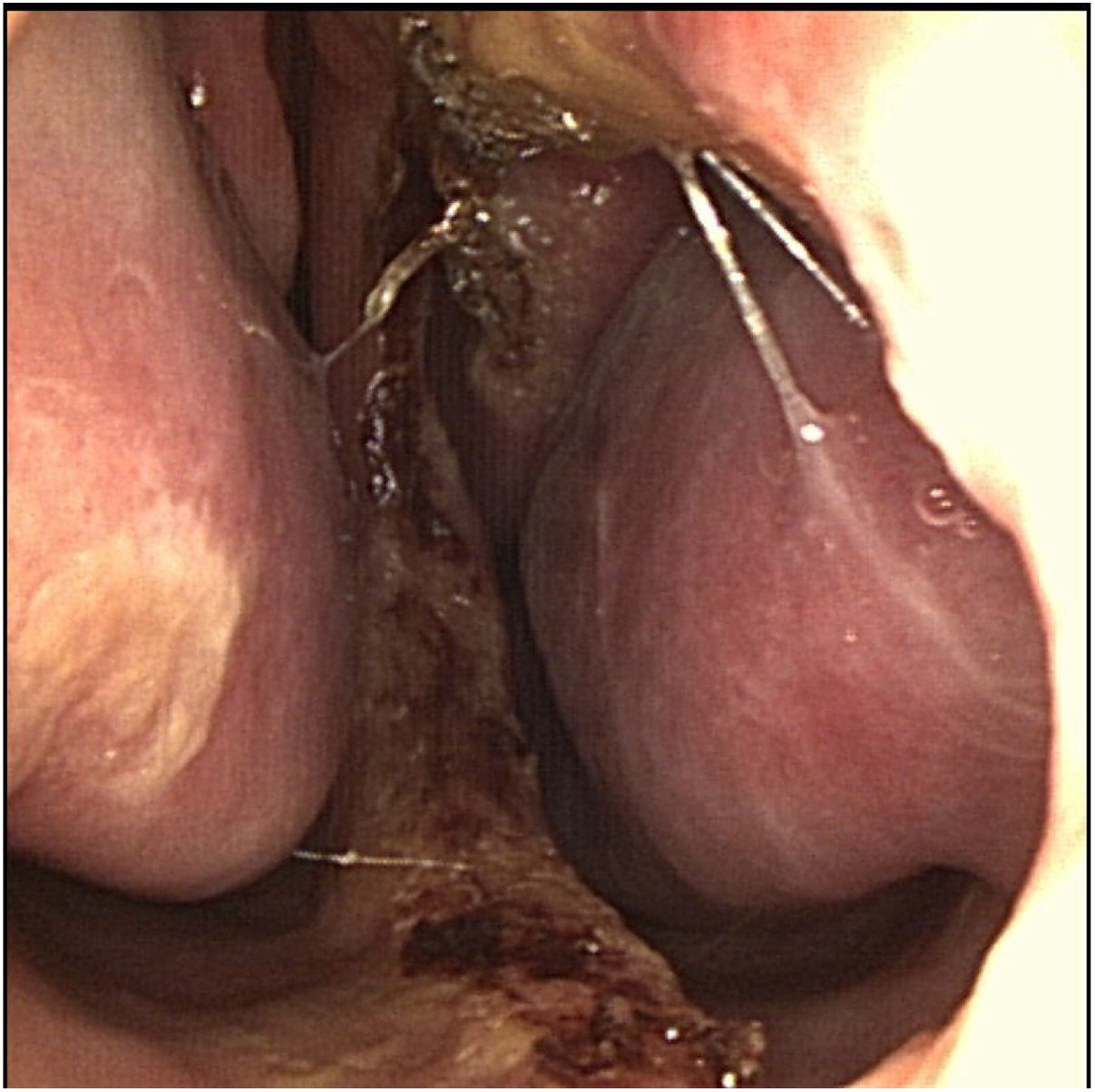
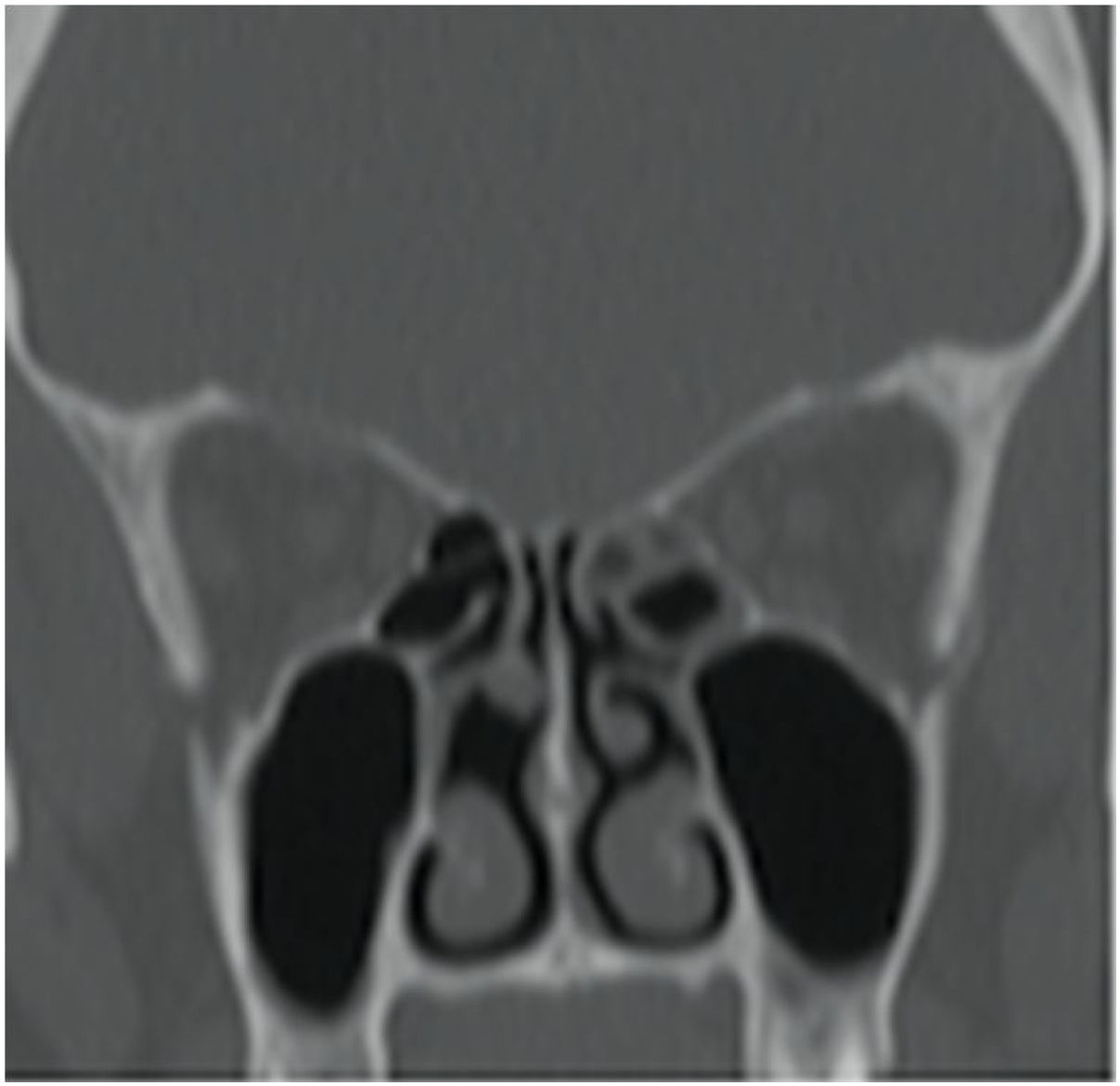
ResultsOne patient presented amputation of the middle turbinate as a manifestation of an obsessive-compulsive disorder of bipolar disease. Two patients had a septal perforation. In the first patient it was the first symptom of factitious dermatitis and in the second it was during the course of schizophrenia. Only control with psychological treatment and psychotropic drugs stabilised the nasal injury.
ConclusionSelf-induced injuries are a diagnostic and treatment challenge for the ENT specialist. A knowledge of psychiatric diseases related to destructive injuries to the nose will improve the approach to patients and prevent the progression of local damage and its complications.
Incrementar el conocimiento de la rinotilexomanía o manipulación compulsiva intranasal como manifestación de enfermedades psiquiátricas mediante la exposición de una serie de casos y revisión de la literature.
MaterialPresentamos 3 casos clínicos con lesiones autodestructivas nasales como síntoma de diferentes enfermedades psiquiátricas.
ResultadosUn paciente presentó una amputación del cornete medio como manifestación de un trastorno obsesivo-compulsivo de una enfermedad bipolar. Dos pacientes tuvieron una perforación septal. El primero como primer síntoma de una dermatitis facticia y el segundo en el transcurso de una esquizofrenia. Sólo el control con tratamiento psicológico y fármacos psicótropos consiguió la estabilización de la lesión nasal.
ConclusiónLas lesiones autoinducidas son un reto diagnóstico y de tratamiento para el otorrinolaringólogo. El conocimiento de las enfermedades psiquiátricas relacionadas con lesiones destructivas centradas en la nariz mejora el abordaje del paciente evitando la progresión de la destrucción local y sus complicaciones.