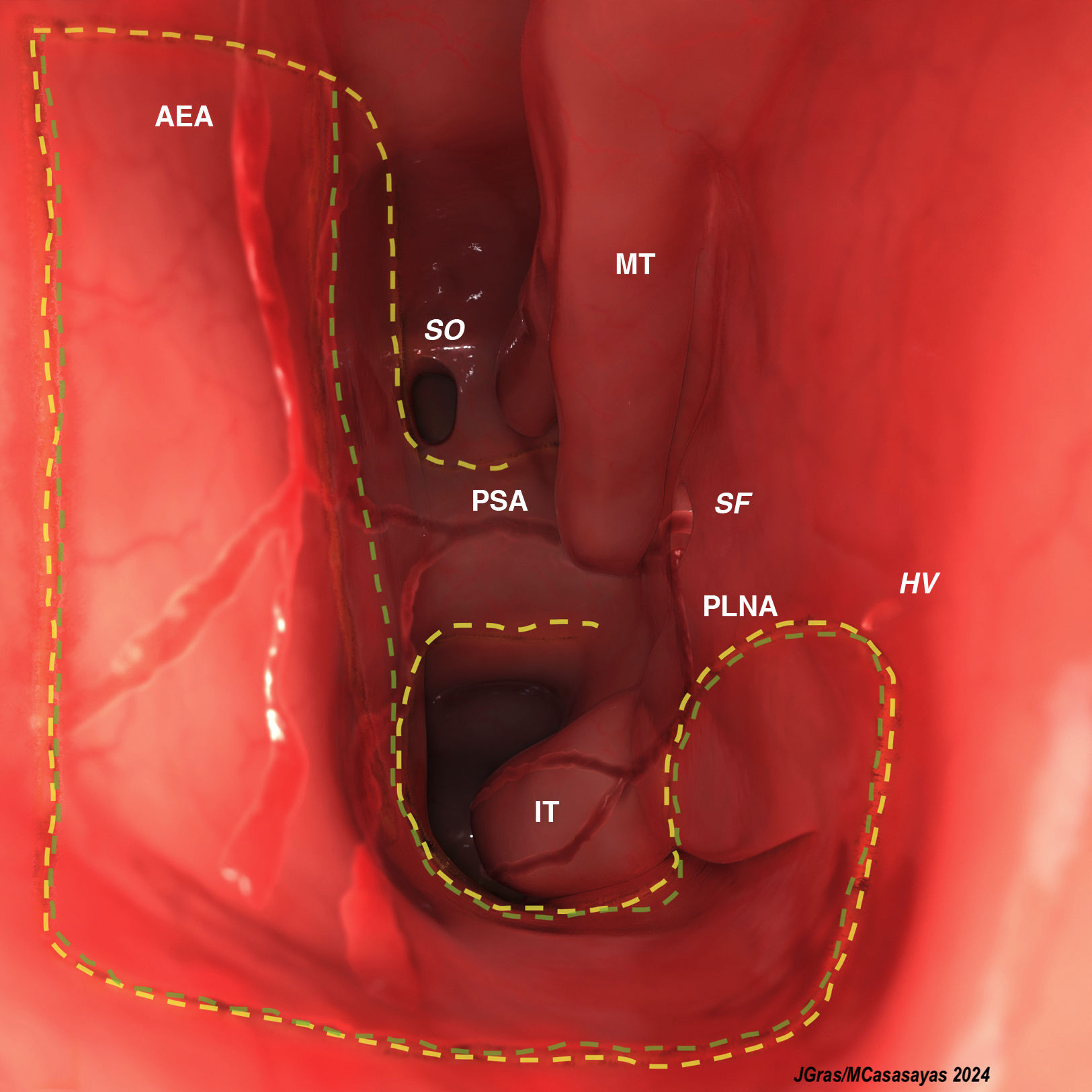
Nasoseptal or septal flaps extended to the floor of the fossa and inferior meatus are a resource in the reconstruction of extended endoscopic approaches. We propose the technique of sectioning and repositioning the inferior turbinate to facilitate the design of these extended pedicled flaps.
Material and methodsWe evaluated 3 cases operated with a skull base lesion: a craniopharyngioma, a petroclival meningioma and a post-surgical fistula of cerebrospinal fluid in the cribiform plate, in which sectioning and repositioning of the inferior turbinate was performed prior to the design of a septal or nasoseptal flap extended to the floor and inferior meatus. To evaluate the anatomy and function of the inferior turbinate, we analysed the results of acoustic rhinometry three months after surgery with and without vasoconstrictor.
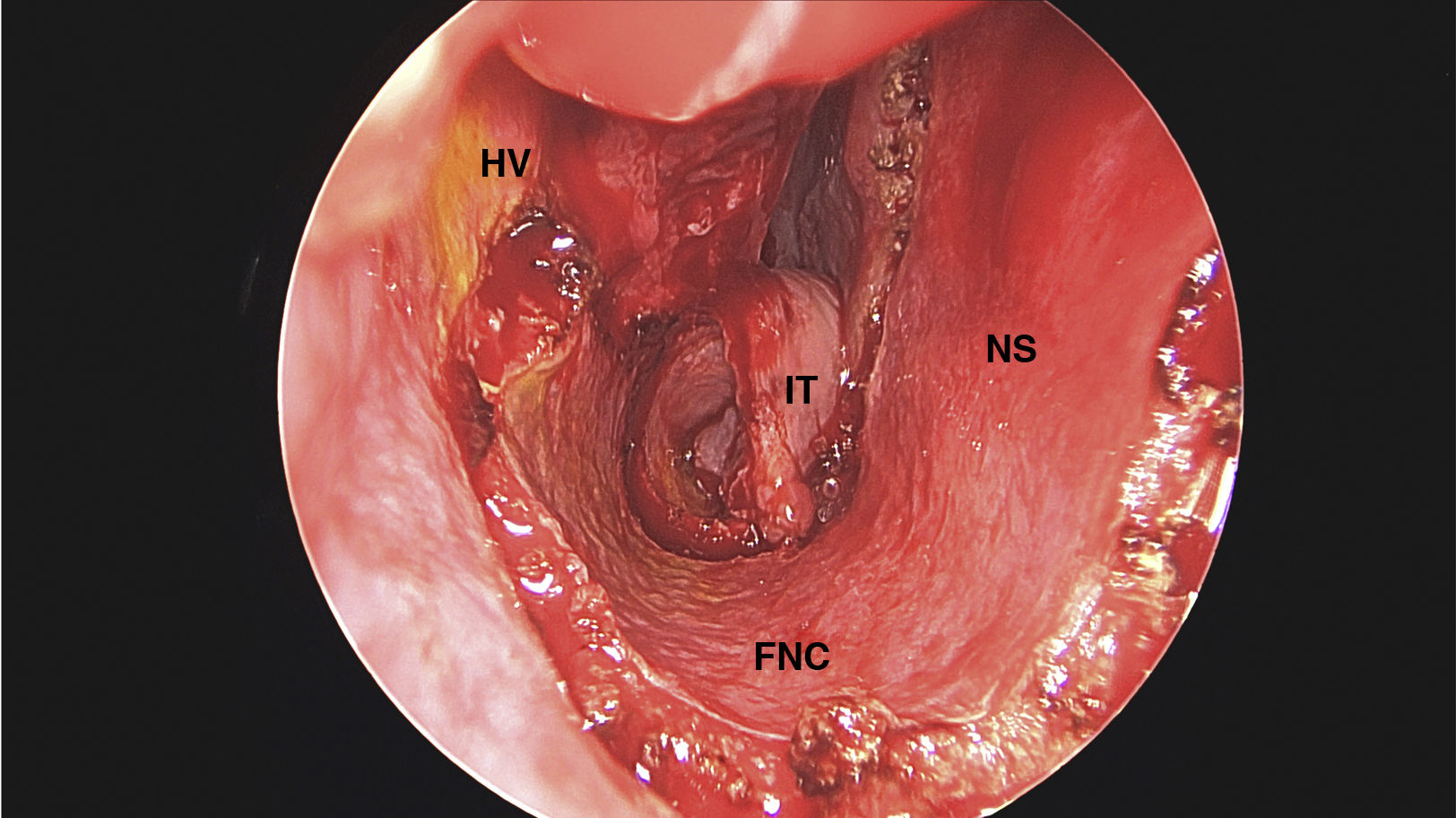
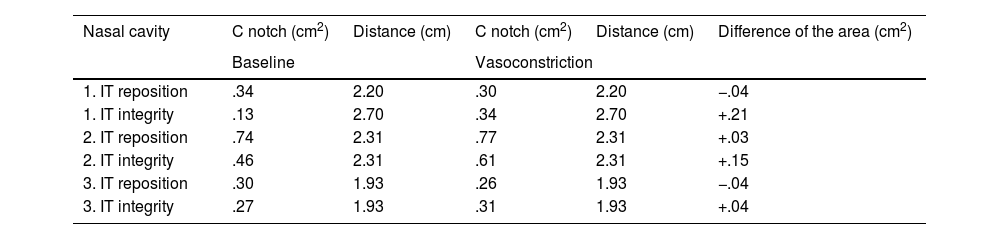
ResultsThe pedicled flaps remained visible and vital on endoscopic examination. The area of the C notch obtained by acoustic rhinometry, in the nostril where the turbinate was manipulated, was in all three cases the narrowest area of the nasal cavity. The mean area for the C-notch was .34 cm2, .74 cm2 and .30 cm2 at a distance from the nostril of 2.20 cm, 2.31 cm and 1.93 cm respectively.
ConclusionPerforming a section and subsequent repositioning of the inferior turbinate, prior to designing an endonasal pedicled flap that includes the mucosa of the floor and inferior meatus, can greatly facilitate obtaining a larger reconstruction flap without affecting the functionality of the inferior turbinate itself.
Los colgajos nasoseptales o septales ampliados al suelo de la fosa y meato inferior son un recurso en la reconstrucción de los abordajes endoscópicos extendidos. Planteamos la realización de la técnica de sección y reposición del cornete inferior para facilitar el diseño de estos colgajos pediculados ampliados.
Material y métodosSe evaluaron 3 casos operados de una lesión en la base de cráneo: un craneofaringioma, un meningioma petroclival y una fístula postquirúrgica de líquido cefalorraquídeo en la lámina cribosa, en los que se realizó una sección y reposición del cornete inferior previo al diseño de un colgajo septal o nasoseptal ampliado al suelo y meato inferior. Para valorar la anatomía y la función del cornete inferior se analizaron los resultados de rinometría acústica a los 3 meses de la cirugía con y sin vasoconstrictor.
ResultadosLos colgajos pediculados permanecieron visibles y vitales en la exploración endoscópica. El área de la escotadura C obtenida por rinometría acústica, en la fosa nasal donde se manipuló el cornete, fue en los tres casos el área más estrecha de la fosa nasal. El área de la escotadura C obtenida por rinometría acústica fue de 0,34 cm2, 0,74 cm2 y de 0,30 cm2 a una distancia de la narina de 2,20 cm, 2,31 cm y 1,93 cm respectivamente.
ConclusiónLa realización de una sección y posterior reposición del cornete inferior, previo al diseño de un colgajo pediculado endonasal que incluye la mucosa del suelo y del meato inferior, puede facilitar de manera considerable la obtención de un mayor colgajo de reconstrucción sin afectar a la funcionalidad del propio cornete inferior.