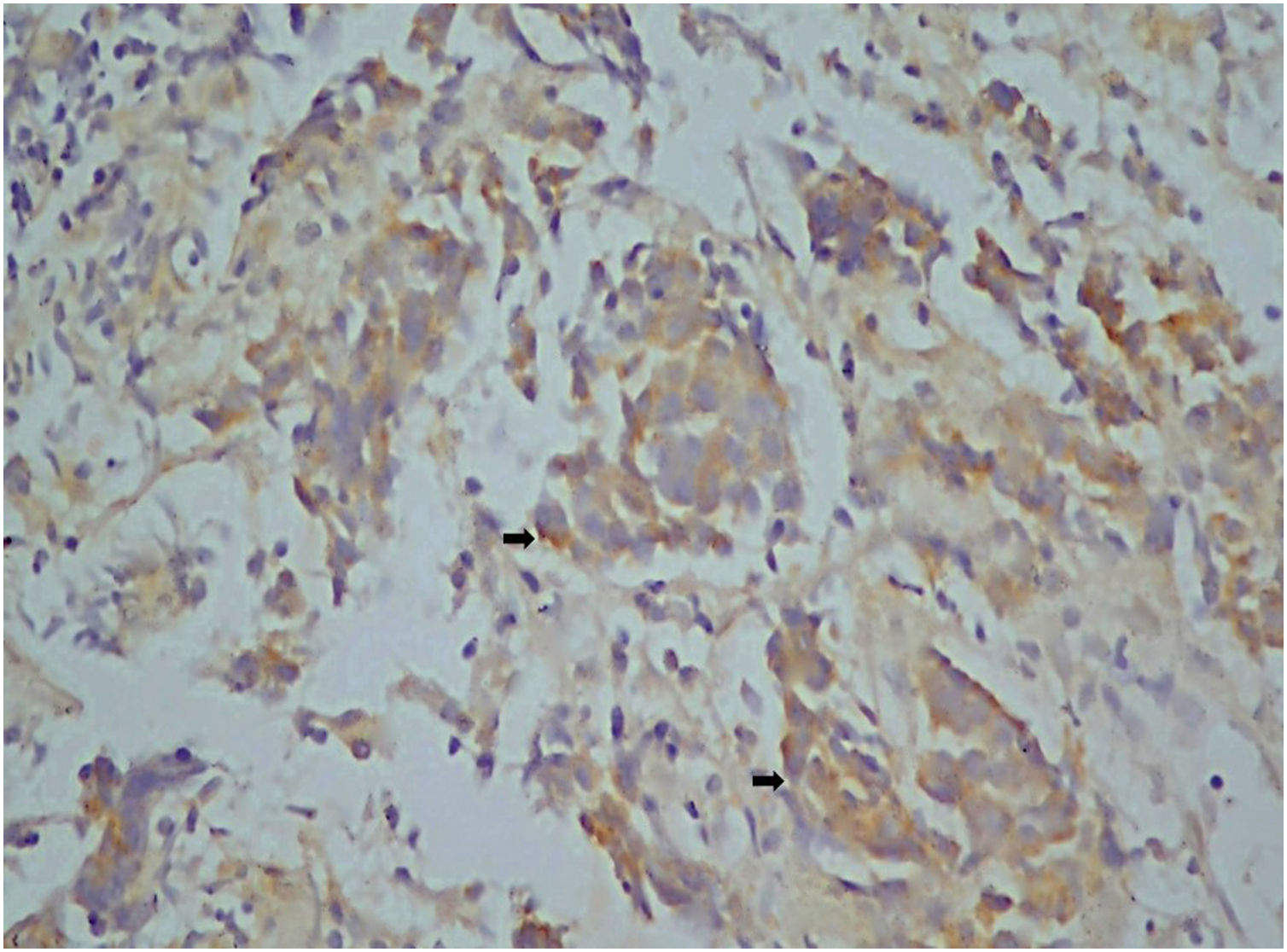
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a newly defined inflammatory cytokine that is a member of the interleukin-1 (IL-1) gene family. This cytokine is expressed in structural cells, such as the vascular endothelium, bronchial epithelial cells, keratinocytes, epithelial cells of the stomach, and fibroblastic reticular cells of lymphoid tissues. Several studies suggest that IL-33 plays a role in head-and-neck cancer. The aim of this study was to retrospectively examine IL-33 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and to evaluate its relationship between clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis.
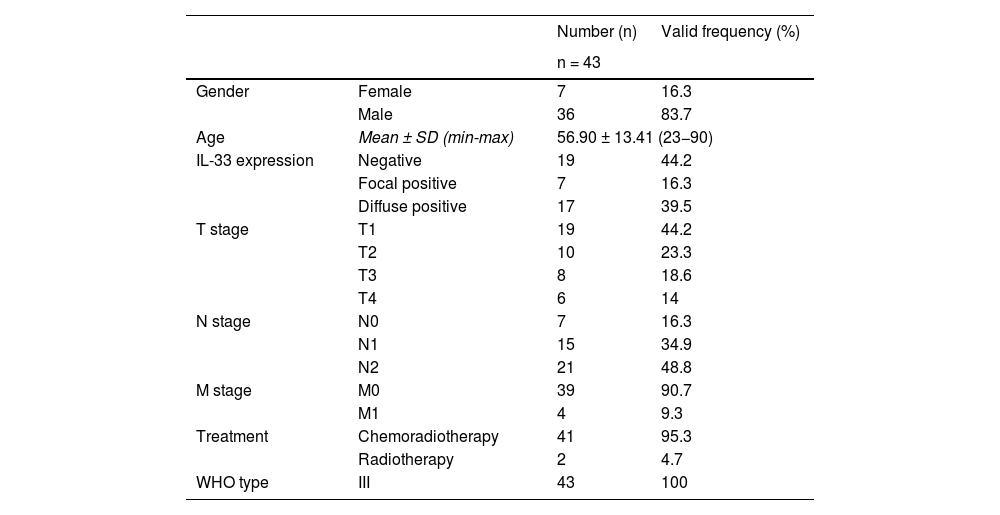
MethodsIn this monocentric, retrospective analysis, the data of 43 cases diagnosed with primary NPC and 20 cases with normal nasopharyngeal tissue (diagnosed between 2014 and 2020) were evaluated regarding the relationship between the immunohistochemically analyzed IL-33 expression status and corresponding clinicopathological parameters.
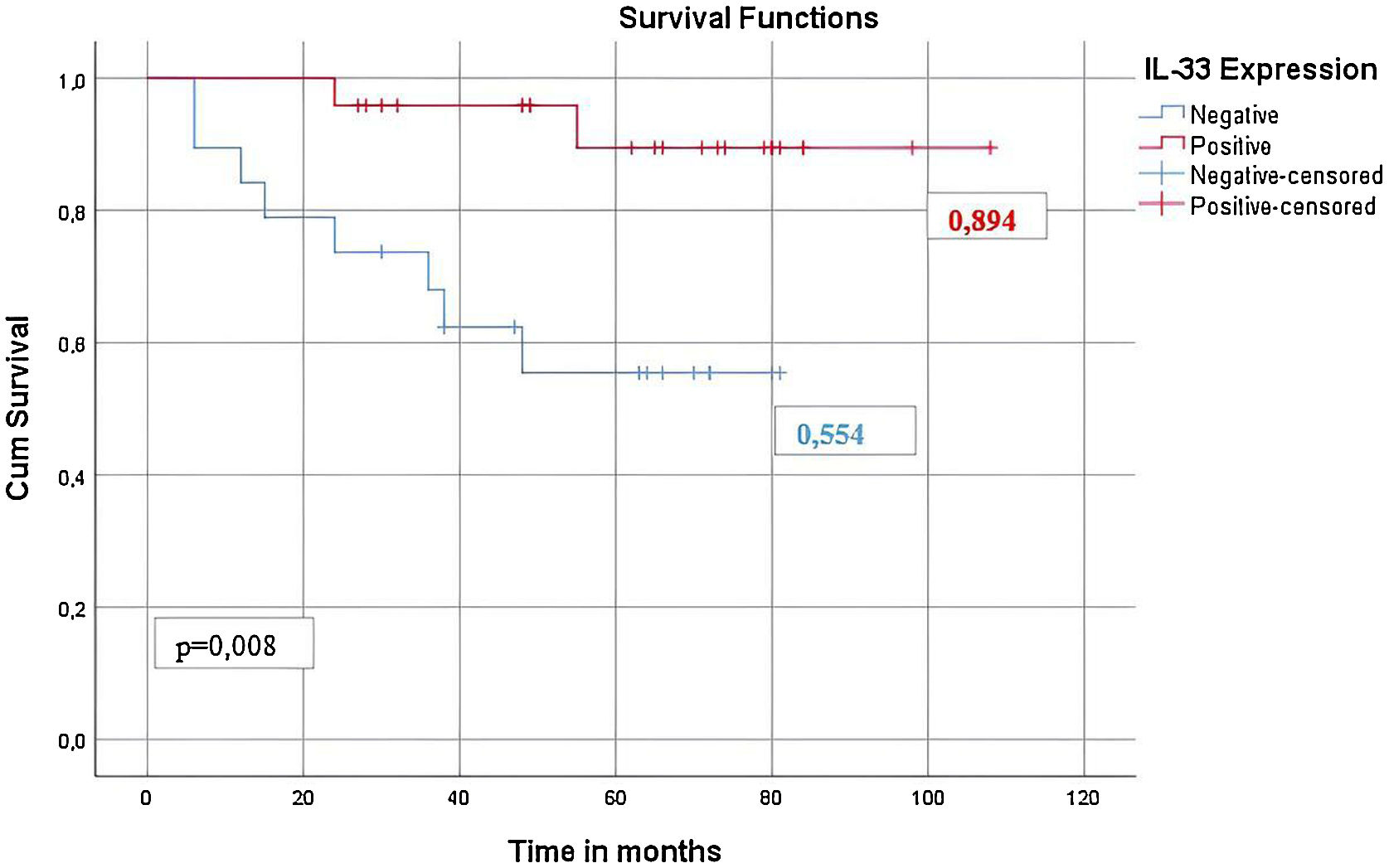
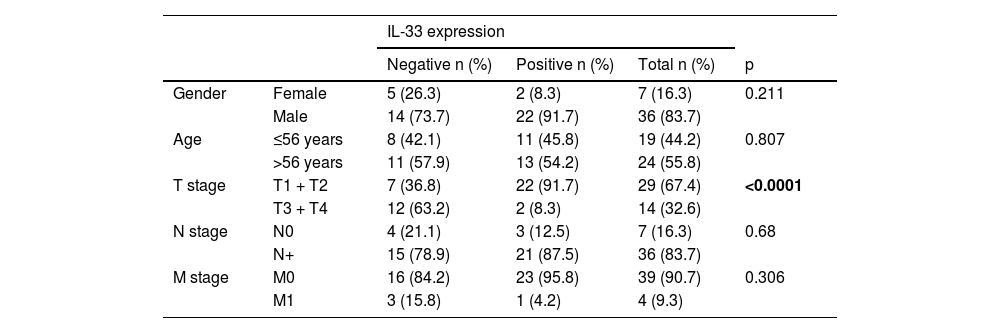
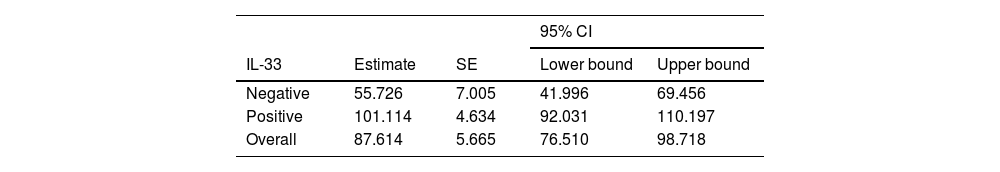
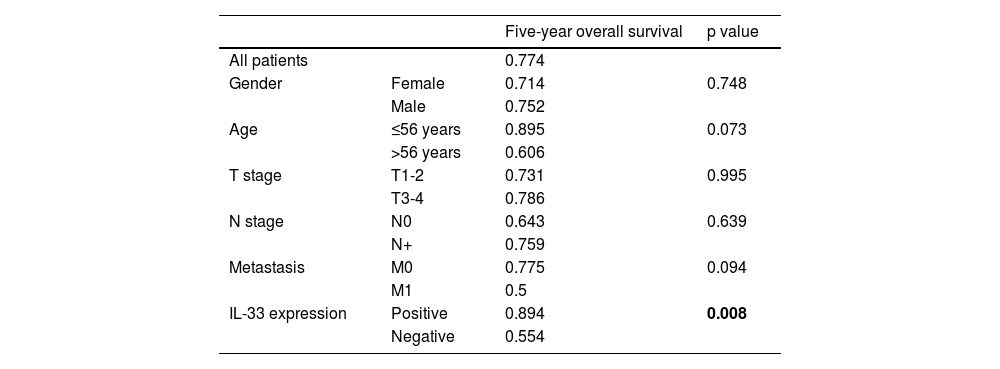
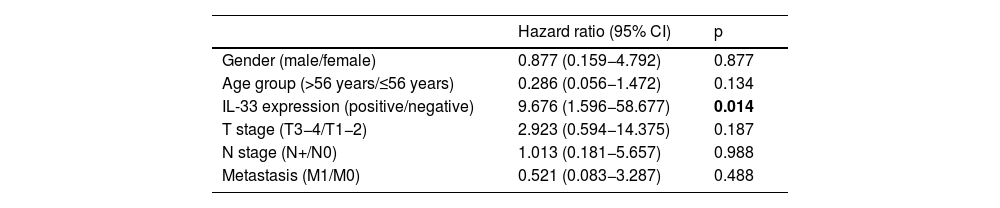
ResultsThe mean age was 56.9 years. The majority (67.4%) of the patients had an early tumor stage (T1–T2). IL-33 expression was positive in 56% of the cases. The five-year overall survival rate was 77% for all patients, 90% for the patients with positive IL-33 expression, and 55% for those without IL-33 expression (p = 0.008, univariate analysis). In multivariate analysis, IL-33 expression was shown to be the only independent prognostic marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (p = 0.014).
ConclusionThis retrospective study showed that IL-33 expression could be considered an independent factor affecting positively prognosis in NPC.
Interleucina-33 (IL-33) es una citocina inflamatoria de nueva definición, que es miembro de la familia genética de interleucina-1 (IL-1). Dicha citocina se expresa en las células estructurales, tales como el endotelio vascular, las células epiteliales bronquiales, los queratinocitos, las células epiteliales del estómago y las células reticulares fibroblásticas de los tejidos linfoides. Diversos estudios sugieren que IL-33 juega un papel en el cáncer de cabeza y cuello. El objetivo de este estudio fue examinar retrospectivamente la expresión de IL-33 en el cáncer de nasofaringe (CN) y evaluar la relación entre las características clínicopatológicas y el pronóstico.
MétodosEn este análisis monocéntrico y retrospectivo se evaluaron los datos de 43 casos diagnosticados de CN primario y 20 casos con tejido nasofaríngeo normal (diagnosticados entre 2014 y 2020), en términos de relación entre el estatus de la expresión de IL-33 analizada mediante inmunohistoquímica y los parámetros clínicopatológicos correspondientes.
ResultadosLa edad media de los pacientes fue de 56,9 años. La mayoría de ellos (67,4%) tenía tumor temprano en estadio (T1–T2). La expresión de IL-33 fue positiva en el 56% de los casos. La tasa de supervivencia global a cinco años fue del 77% para todos los pacientes, del 90% para los pacientes con expresión positiva de IL-33, y del 55% para aquellos sin expresión de IL-33 (p = 0,008 en el análisis univariante). En el análisis multivariante, la expresión de IL-33 fue el único marcador pronóstico independiente del cáncer de nasofaringe (p = 0,014).
ConclusiónEste estudio retrospectivo reflejó que la expresión de IL-33 podría ser considerada un factor independiente, que afecta positivamente al pronóstico de CN.