To evaluate success rate of type I tympanoplasty in adults and to investigate the importance of selected prognostic factors on graft uptake.
Material and methodsRetrospective medical chart review of 155 patients who underwent Type I Tympanoplasty, in our department, from January 2013 to December 2017. Graft uptake rate was evaluated and the effects of prognostic factors on surgical outcome such as sex, smoking and otological surgery history, status of the contralateral ear, size and location of the perforation, middle ear mucosa status, surgical approach and graft material. Preoperative and postoperative audiometric data were collected, and the functional success was determined.
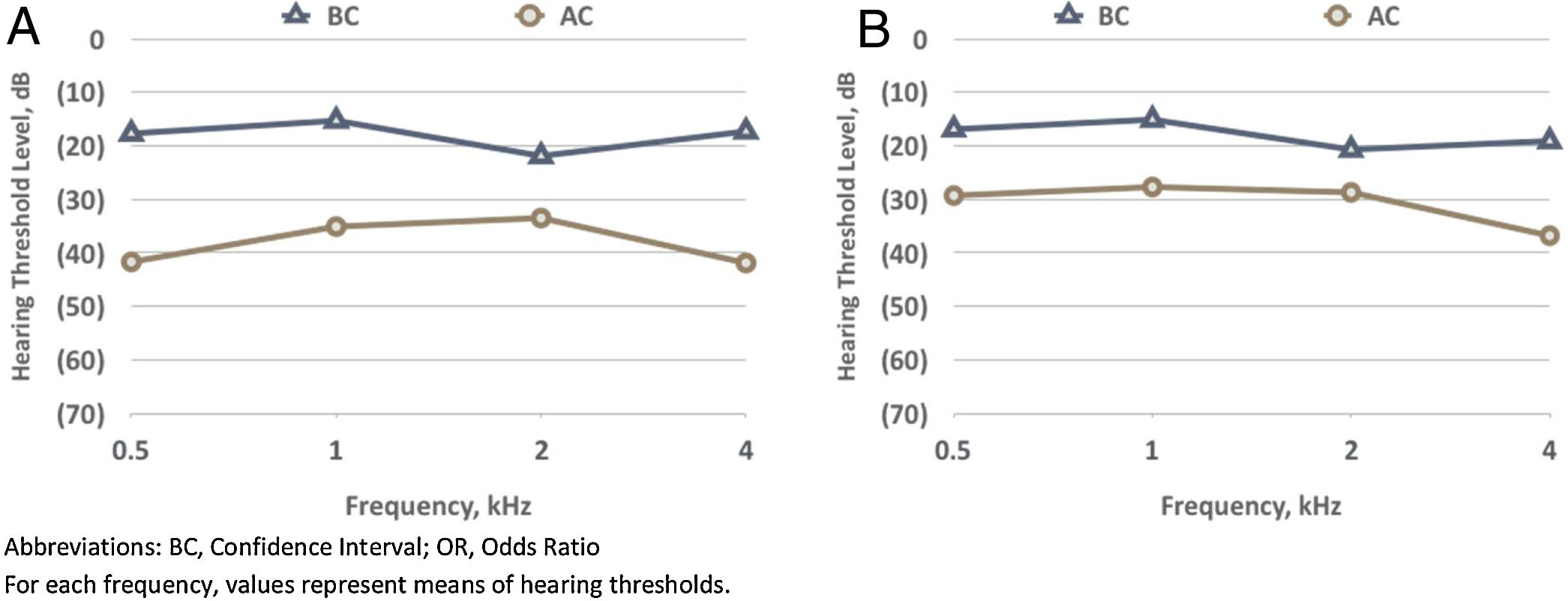
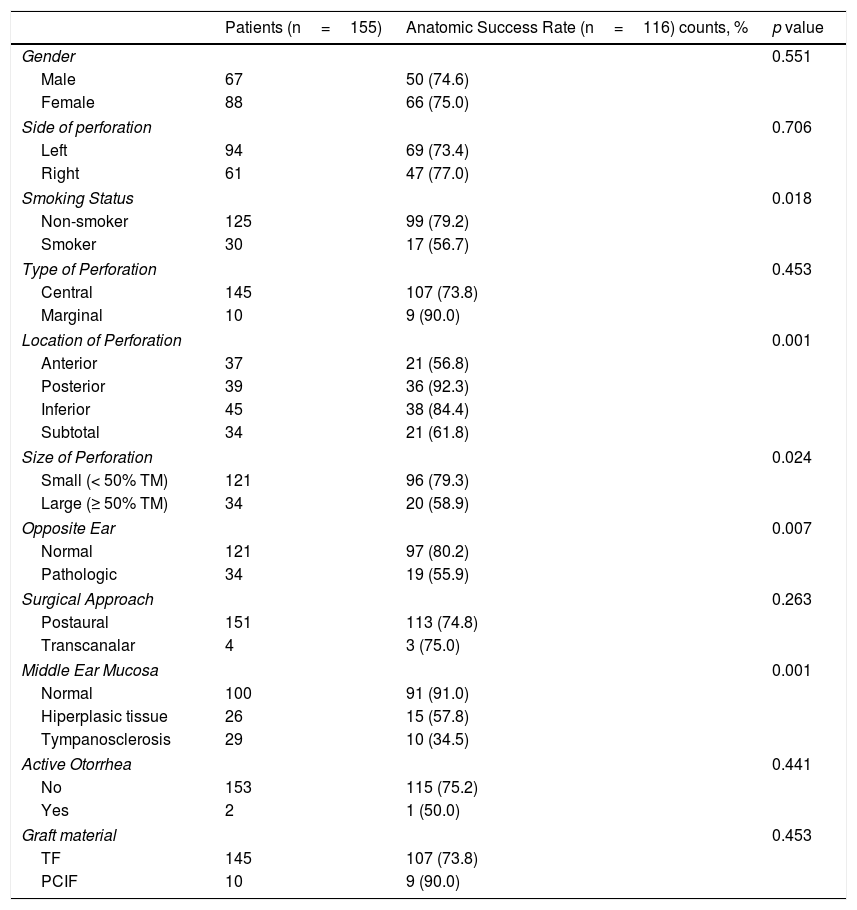
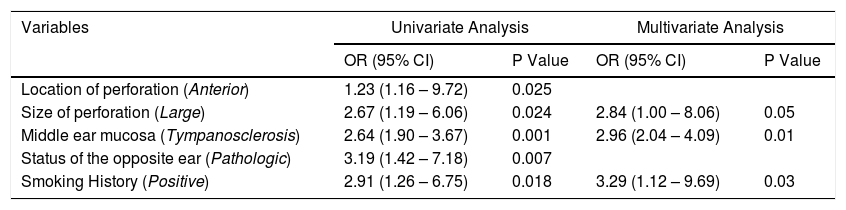
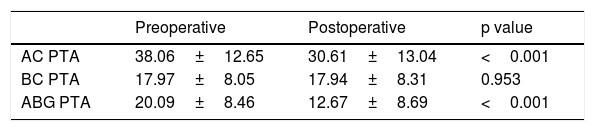
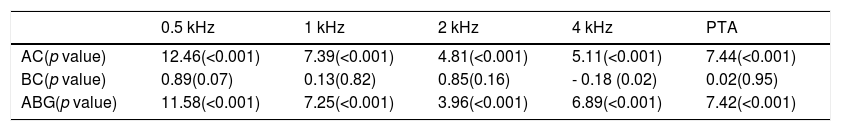
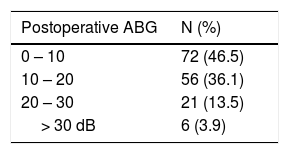
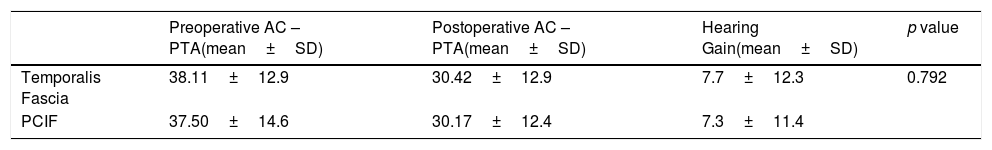
ResultsThe overall surgical anatomical success rate was 75%. Analysis of the selected variables, identified as independent prognostic factors of anatomical unsuccess (95% CI): smoking (OR=3.29, p<.01), middle ear tympanosclerosis (OR=2.96; p=.04). Perforations above 50% of the tympanic membrane area had a borderline effect on graft uptake (p=.05). There was a significative improvement in the average air conduction thresholds of 7.44dB and an ABG closure rate at 10dB and 20dB was achieved in 47% and 84.5%, respectively. Patients who received temporalis fascia graft had similar hearing gain compared to patients who underwent cartilage tympanoplasty (7.7 vs. 7.3dB, p=.79).
ConclusionType I tympanoplasty is an effective and safe procedure with a high anatomical success rate in the treatment of mucosal COM. Poorer outcomes were found in patients with smoking habits, in those with tympanosclerosis of middle ear mucosa and in larger perforations. These prognostic factors should be considered in surgical planning and patients should be advised to quit smoking. Tympanoplasty with cartilage graft had a hearing outcome comparable to temporalis fascia graft and should be considered in high-risk patients.
Evaluar la tasa de éxito de la timpanoplastia tipo I en adultos e investigar la importancia de los factores pronósticos seleccionados en la absorción del injerto.
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de los registros médicos, de 155 pacientes que se sometieron a timpanoplastia tipo I en nuestro departamento, desde enero de 2013 hasta diciembre de 2017. Se evaluó la tasa de absorción del injerto y los efectos de los factores pronósticos en el resultado quirúrgico, como el sexo, el tabaquismo y la cirugía otológica. antecedentes, estado del oído contralateral, tamaño y ubicación de la perforación, estado de la mucosa del oído medio, abordaje quirúrgico y material de injerto. Se recogieron datos audiométricos preoperatorios y postoperatorios y se determinó el éxito funcional.
ResultadosLa tasa general de éxito anatómico quirúrgico fue del 75%. Análisis de las variables seleccionadas, identificadas como factores pronósticos independientes de fracaso anatómico (IC 95%): tabaquismo (OR = 3,29, p < 0,01), timpanosclerosis del oído medio (OR = 2,96; p = 0,04). Las perforaciones por encima del 50% del área de la membrana timpánica tuvieron un efecto límite en la absorción del injerto (p = 0,05). Hubo una mejora significativa en los umbrales promedio de conducción de aire de 7,44 dB y se logró una tasa de cierre ABG con 10 dB y 20 dB en 47% y 84,5%, respectivamente. Los pacientes que recibieron injerto de fascia temporal tuvieron una ganancia auditiva similar en comparación con los pacientes que se sometieron a timpanoplastia de cartílago (7,7 frente a 7,3 dB, p = 0,79).
ConclusiónLa timpanoplastia tipo I es un procedimiento efectivo y seguro con una alta tasa de éxito anatómico en el tratamiento de la otitis media crónica. Se encontraron resultados más pobres en pacientes con hábito de fumar, en aquellos con timpanosclerosis en la mucosa del oído medio y en perforaciones más grandes. Estos factores pronósticos deben considerarse en la planificación quirúrgica y se debe aconsejar a los pacientes que dejen de fumar. La timpanoplastia con injertos de cartílago tuvo un resultado auditivo comparable al injerto de fascia temporal y debe considerarse en pacientes de alto riesgo.