Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is a sudden, unexplained unilateral hearing loss.
ObjectivesTo update the Spanish Consensus on the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of ISSNHL.
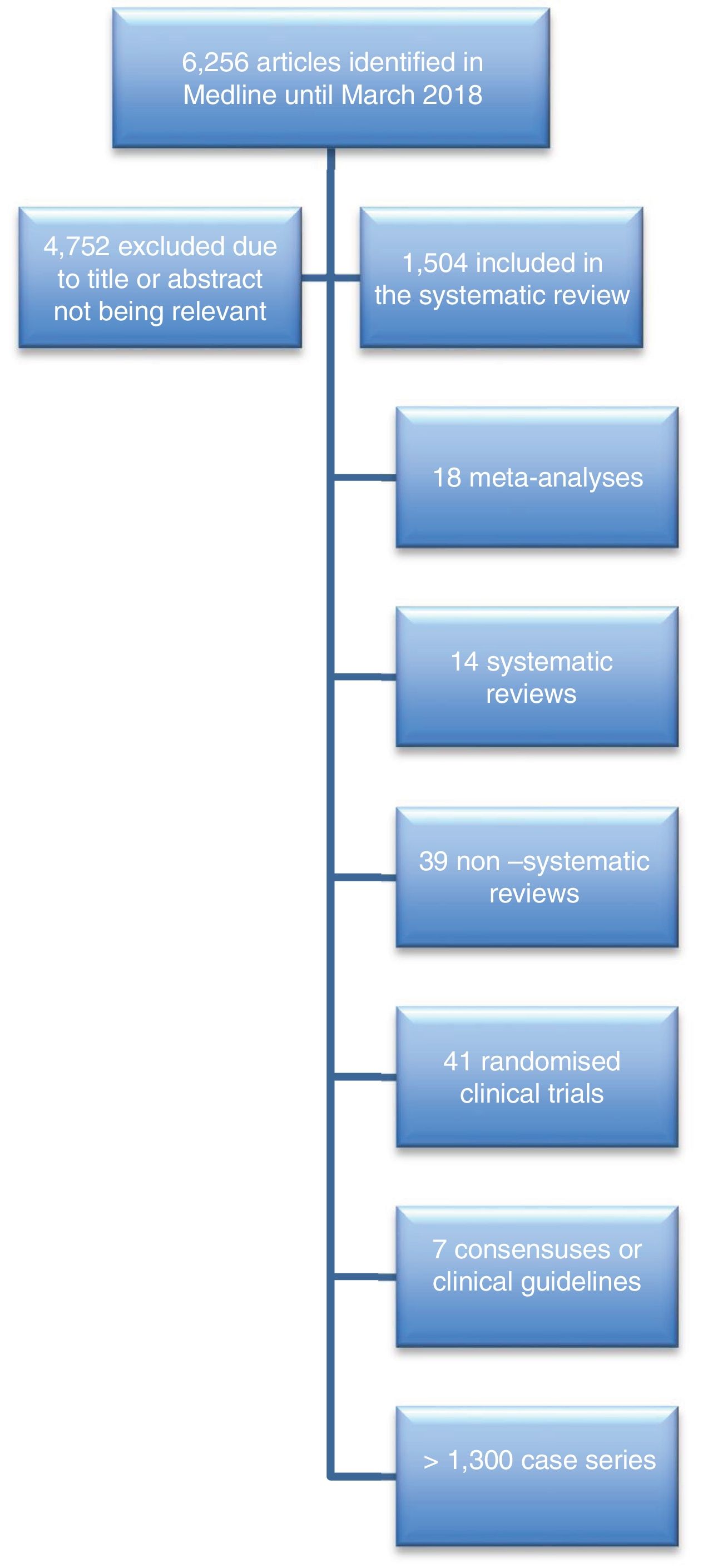
Material and methodsAfter a systematic review of the literature from 1966 to March 2018, on MESH terms "(acute or sudden) hearing loss or deafness", a third update was performed, including 1508 relevant papers.
ResultsRegarding diagnosis, once ISSNHL is clinically suspected, the following diagnostic tests are mandatory: otoscopy, acumetry, tonal audiometry, speech audiometry, and tympanometry, to discount conductive causes. After clinical diagnosis has been established, and before treatment is started, a full analysis should be performed. An MRI should then be requested, ideally performed during the first 15 days after diagnosis, to discount specific causes and to help to understand the physiopathological mechanisms in each case. Although treatment is very controversial, due to its effect on quality of life after ISSNHL and the few rare adverse effects associated with short-term steroid treatment, this consensus recommends that all patients should be treated with steroids, orally and/or intratympanically, depending on each patient. In the event of failure of systemic steroids, intratympanic rescue is also recommended. Follow-up should be at day 7, and after 12 months.
ConclusionBy consensus, results after treatment should be reported as absolute dBs recovered in pure tonal audiometry and as improvement in speech audiometry.
: La sordera súbita idiopática (SSI) es aquella hipoacusia neurosensorial de inicio súbito de causa desconocida.
Objetivos: Actualización del consenso sobre el diagnóstico, tratamiento y seguimiento de la SSI.
Material y métodosPresentamos una tercera actualización del consenso de SSI, mediante revisión sistemática de la literatura sobre la SSI desde 1966 hasta marzo de 2018, sobre los términos MESH "(acute or sudden) hearing loss or deafness", incluyendo 1.508 artículos relevantes.
ResultadosEn cuanto al diagnóstico, ante una sospecha clínica de SSI, las pruebas diagnósticas que se consideran necesarias son: otoscopia, acumetría, audiometría tonal, audiometría verbal y timpanograma para descartar causas transmisivas de sordera. Una vez hecho el diagnóstico clínico de SSI, antes de comenzar el tratamiento, se solicitará una batería analítica, debiendo completarse más tarde el estudio con RM de oído interno, idealmente en los primeros 15 días, para descartar causas específicas de sordera súbita neurosensorial y para contribuir a elucidar posibles mecanismos fisiopatológicos. A pesar de la controversia en cuanto el tratamiento de SSI se recomienda, por los efectos en la calidad de vida de la SSI y los raros eventos indeseables con tratamiento esteroide a corto plazo, que el tratamiento de la SSI esté basado fundamentalmente en los corticoides, pudiendo utilizarse la vía oral y/o intratimpánica, en función del paciente. En caso de fracaso de la vía sistémica, se recomienda usar corticoides intratimpánicos como rescate. Respecto al seguimiento, se realizará un control a la semana del inicio del mismo, a 7 días y hasta 12 meses.
ConclusionesComo consenso, el resultado de los tratamientos aplicados debería presentarse, tanto en cantidad de dBs recuperados en el umbral auditivo tonal, como con parámetros de audiometría verbal.