La cistectomía radical asistida por robot (CRAR) con derivación urinaria intracorpórea (DUIC) es un procedimiento técnicamente complejo. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar el impacto de la curva de aprendizaje (CA) de la CRAR con DUIC sobre los resultados perioperatorios y patológicos.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 62 pacientes consecutivos intervenidos mediante CRAR con DUIC por tumor vesical entre 2015 y 2020. Se compararon 3 grupos consecutivos de 20 (G1), 20 (G2) y 22 (G3) pacientes para analizar el impacto de la CA. Los casos de G1 fueron intervenidos por un cirujano sénior con experiencia en cirugía robótica y los de G2-G3 por 2cirujanos júnior sin experiencia, pero tutorizados por el sénior.
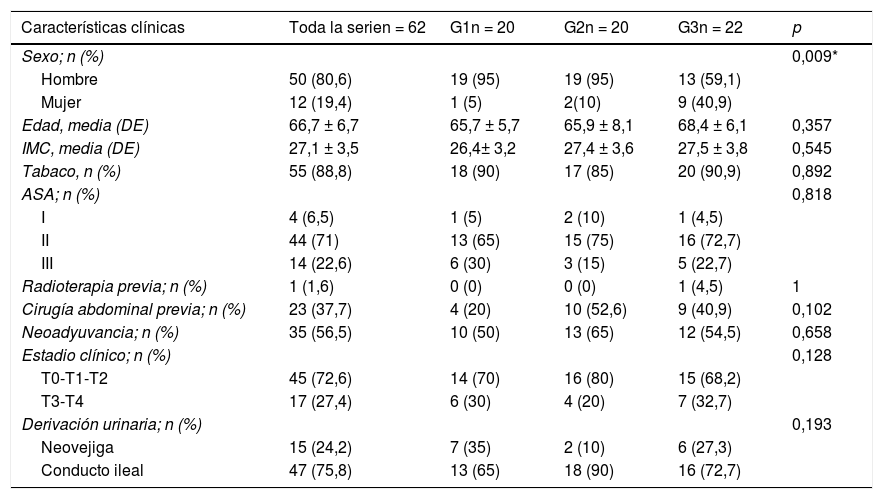
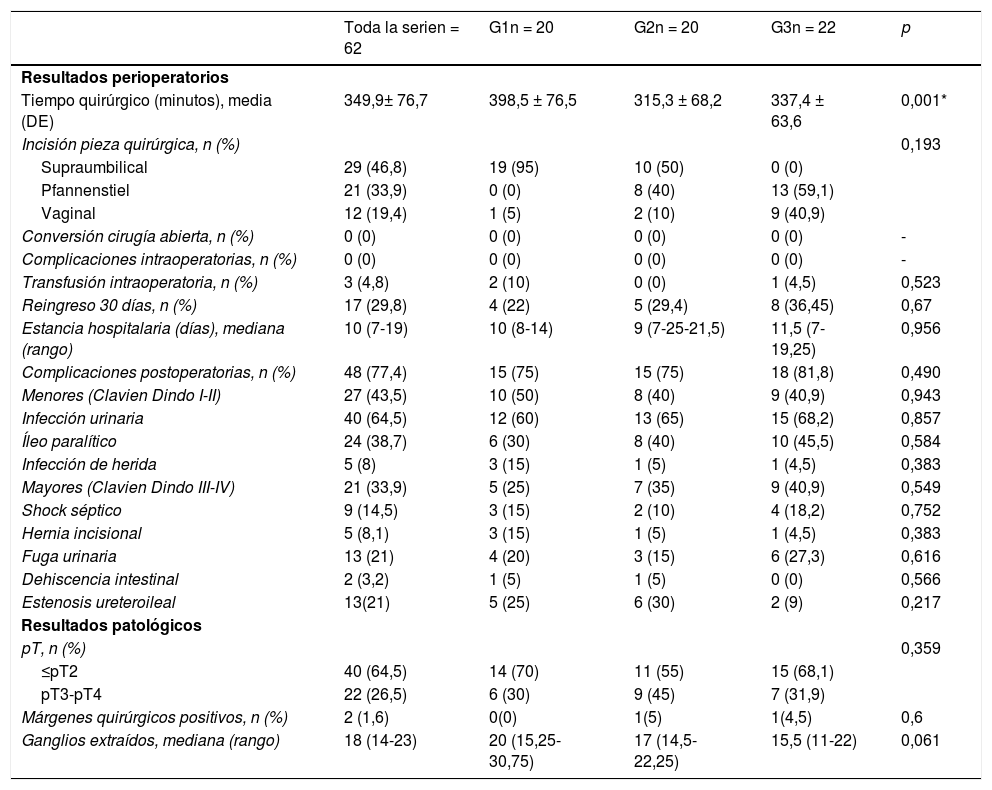
ResultadosLos 3grupos tenían características clínico-patológicas similares. A 15 pacientes (24%) se les realizó una neovejiga y a 47 (75%) un conducto ileal. El tiempo medio operatorio descendió 60 min entre G1 y G3 (p=0,001). Ningún paciente precisó conversión a cirugía abierta ni tuvo complicaciones intraoperatorias. No se objetivaron diferencias en la tasa de márgenes positivos (p=0,6) ni en el número de ganglios extraídos (p=0,061) entre los grupos. La tasa de complicaciones postoperatorias fue del 77% y no varió durante la CA (p=0,49). Se objetivó una tendencia en la reducción de tasa de estenosis ureteroileal del 25% en G1 al 9% en G3 (p=0,217).
ConclusionesLa incorporación de cirujanos júnior a un programa de CRAR con DUIC a partir de los 20 primeros casos no compromete los resultados perioperatorios ni patológicos. Durante la CA se podría reducir el tiempo operatorio y la tasa de estenosis ureteroileal.
Robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with intracorporeal urinary diversion (ICUD) is a technically difficult procedure. Our aim was to evaluate the potential impact of the learning curve (LC) on perioperative and pathological outcomes of RARC with ICUD.
Material and methodsRetrospective study of 62 consecutive patients who underwent RARC with ICUD for bladder cancer between 2015-2020. We compared 3 consecutive groups of 20 (G1), 20 (G2), and 22 (G3) patients to analyze the impact of the LC. G1 cases were performed by a senior surgeon experienced in robotic surgery, while G2-G3 were performed by 2 junior surgeons without experience under the mentorship of the senior surgeon.
ResultsThe 3 groups had similar clinical and pathological characteristics. A total of 15 patients (24%) received a neobladder and 47 (75%) an ileal conduit. The mean operative time decreased 60minutes between G1-G3 (P=0.001). No conversions to open approach or intraoperative complications were reported. There were no differences between groups regarding positive margin rates (P=0.6) or the number of lymph nodes removed (P=0.061). The postoperative complication rate was 77% and did not change during the LC (P=0.49). Uretero-enteric stricture rate decreased from 25% in G1 to 9% in G3 (P=0.217).
ConclusionsThe inclusion of júnior surgeons to a RARC with ICUD program after the initial 20 cases does not have an impact on the perioperative and pathological outcomes of the procedure. The operative time and the uretero-enteric stricture rate could be reduced during the LC.