Actualmente no existe ningún marcador pronóstico para el carcinoma renal de células claras (CRCC). La proteína STAT3 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3) está implicada en la carcinogénesis del CRCC. Su activación se produce mediante fosforilación del residuo serina 727, translocándose al núcleo donde participa en la carcinogénesis y progresión tumoral. El objetivo primario del estudio fue evaluar la supervivencia cáncer-específica en una serie de 166 pacientes afectos de CRCC, y su posterior correlación con la expresión de pSer727-STAT3 como marcador pronóstico de CRCC.
Material y métodosRealizamos un estudio retrospectivo en 166 pacientes con CRCC intervenidos mediante nefrectomía parcial o radical entre 2000 y 2010. Se construyó un microarray de tejido tumoral y se analizó la expresión inmunohistoquímica de pSer727-STAT3. La variable principal del estudio fue la supervivencia cáncer-específica.
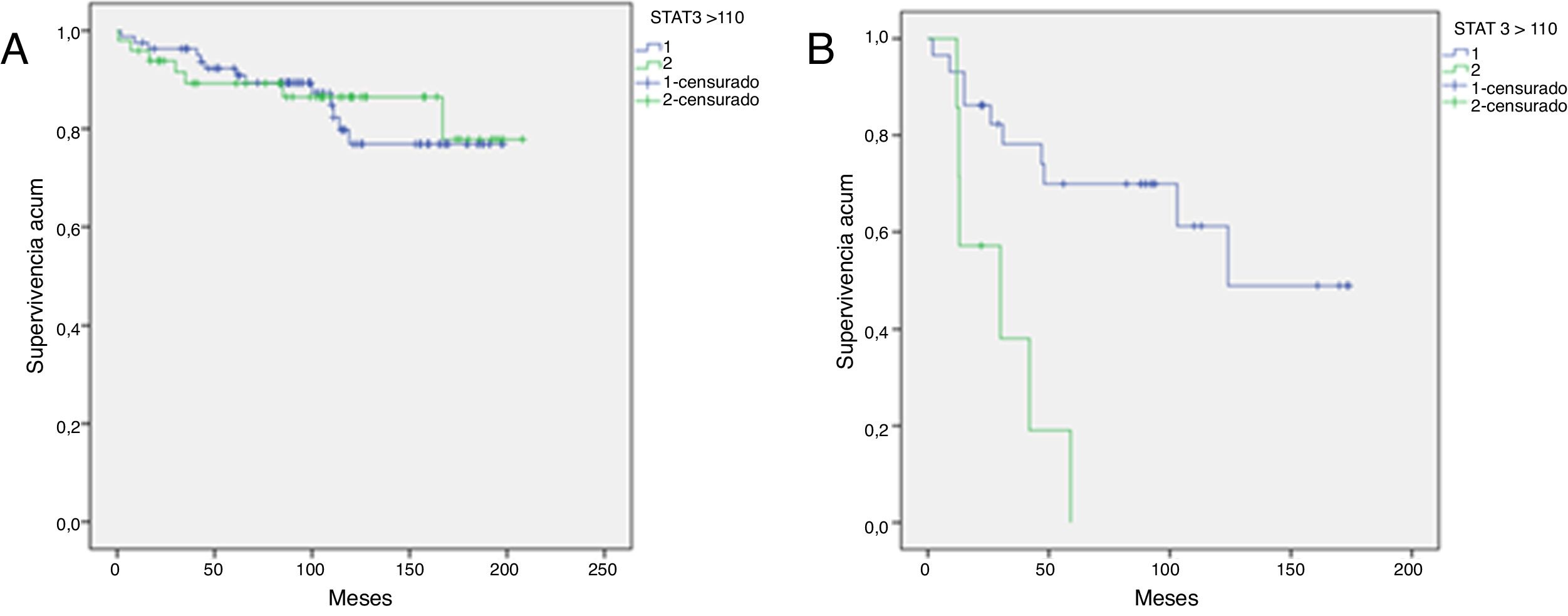
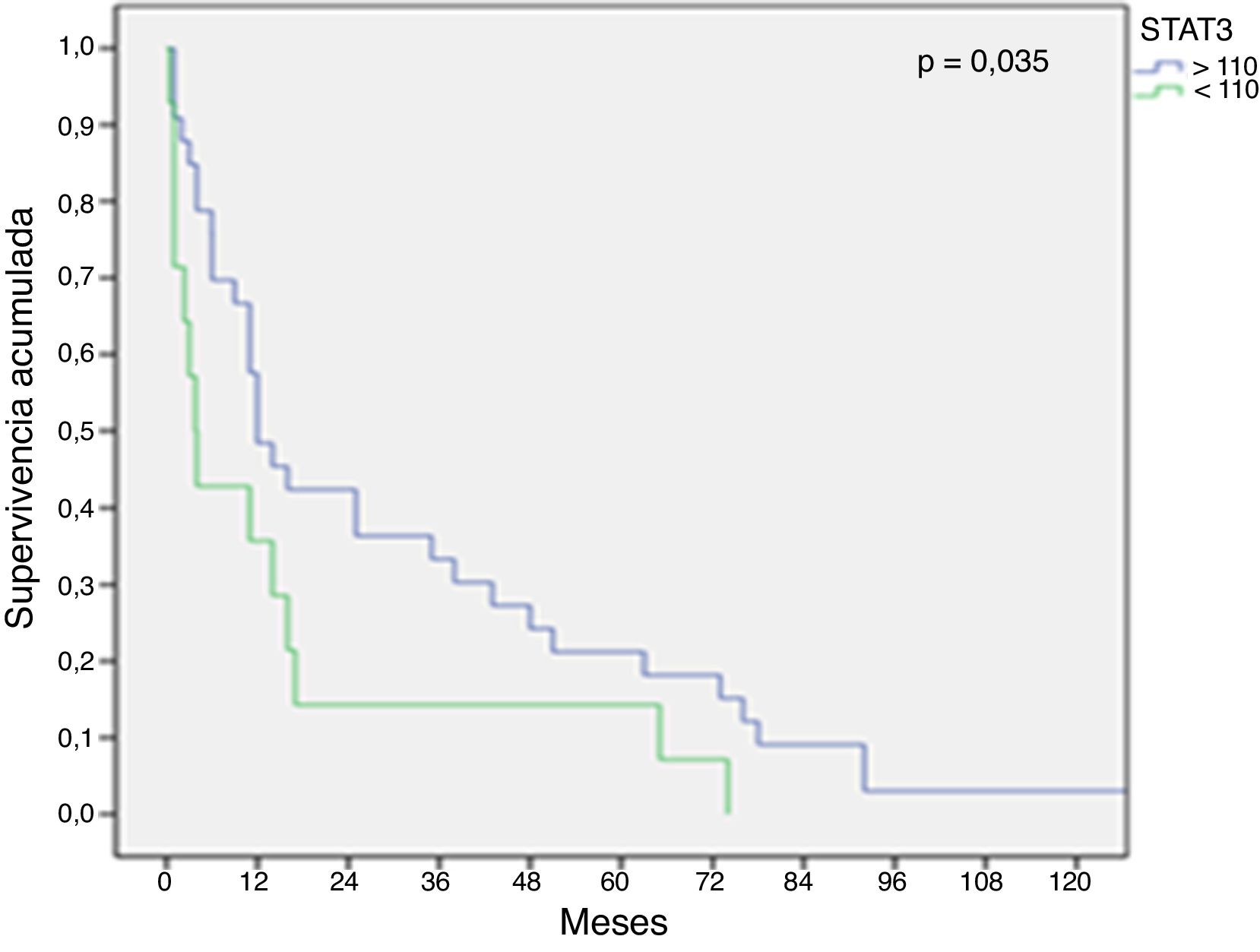
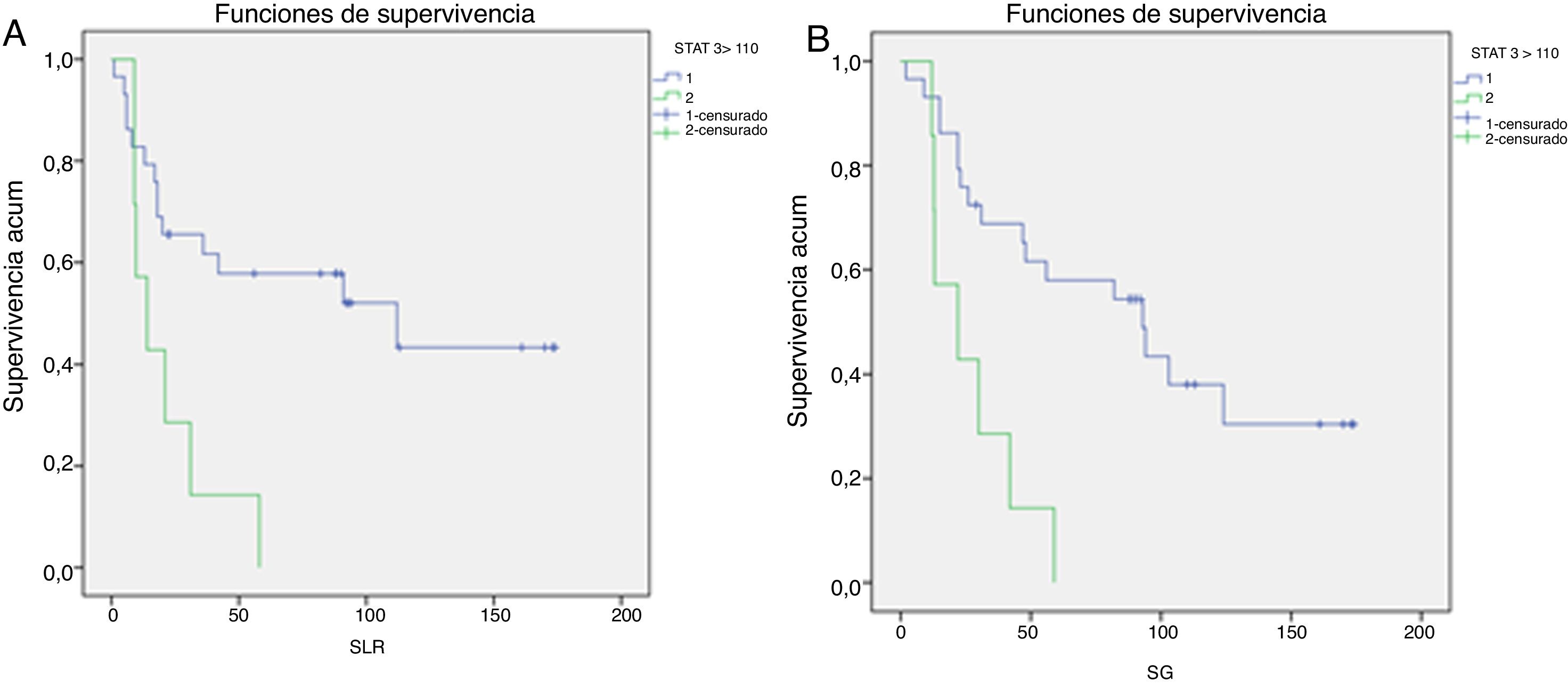
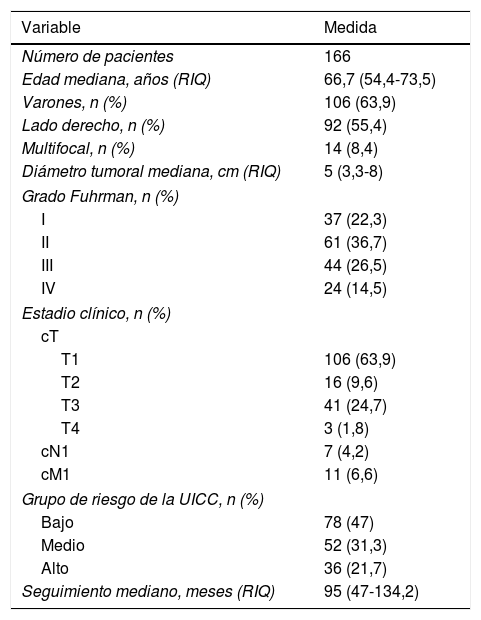
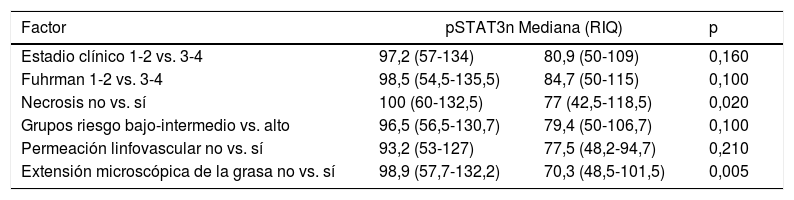
ResultadosEl grupo de riesgo según la UICC fue en 78 pacientes (47%) bajo, en 52 (31,3%) intermedio y en 36 (21,7%) alto; 11 pacientes (6,7%) debutaron con enfermedad metastásica. Durante un seguimiento medio de 97,2 meses (1-208), 37 pacientes (22,3%) desarrollaron recurrencia local y/o a distancia. La mortalidad cáncer-específica fue del 28,3% y la mortalidad global del 67,5%. La expresión media de pSer727-STAT3 fue de 92,9 (IC 95%:84,6-101,1) sin observarse relación con grupos de riesgo u otros factores pronósticos. En un análisis de regresión logística de Cox, pSer727-STAT3 no se comportó como un predictor independiente de mortalidad cáncer-específica. Sin embargo, en pacientes de alto riesgo y metastásicos, la supervivencia cáncer-específica fue significativamente mayor cuando la expresión de pSer727-STAT3 fue inferior a 110, HR: 5,4 (IC 96%:1,8-16,4) y HR: 2,3 (IC 95%: 1,1-4,6) respectivamente, p<0,001.
ConclusionespSer727-STAT3 no es un marcador de supervivencia en los pacientes con CRCC. Sin embargo, en pacientes de alto riesgo, es un marcador de supervivencia cáncer-específica, incluso en pacientes metastásicos que reciben tratamiento con antiangiogénicos.
Currently, clear cell renal carcinoma (CCRCC) has no prognostic markers. STAT3 protein (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3) is involved in the carcinogenesis of CCRCC. Its activation is produced by phosphorylation of the serine 727 residue, translocating to the nucleus where it is involved in carcinogenesis and tumor progression. The primary objective of the study was to evaluate cancer-specific survival rates in a series of 166 patients with CCRCC, and its subsequent correlation with the expression of pSer727-STAT3 as a prognostic marker of CCRCC.
Material and methodsWe conducted a retrospective study on 166 patients with CCRCC undergoing partial or radical nephrectomy between 2000 and 2010. A tumor tissue microarray was constructed for immunohistochemical analysis of pSer727-STAT3 expression. The main variable of the study was cancer-specific survival.
ResultsPatients were classified according to the UICC risk groups as follows: low in 78 patients (47%), intermediate in 52 (31.3%) and high 36 (21.7%); 11 patients (6.7%) were diagnosed with metastatic disease. During a mean follow-up of 97.2 months (1-208), 37 patients (22.3%) developed local and/or distant recurrence. Cancer-specific and overall mortality rates were 28.3% and 67.5%, respectively. The mean expression of pSer727-STAT3 was 92.9 (95% CI: 84.6-101.1) without showing any relationship with risk groups or other prognostic factors. In a Cox logistic regression analysis, pSer727-STAT3 did not behave as an independent predictor of cancer-specific mortality. However, in high-risk and metastatic patients, cancer-specific survival was significantly higher when the expression of pSer727-STAT3 was lower than 110, HR: 5.4 (96% CI: 1.8-16.4) and HR: 2.3 (95% CI: 1.1-4.6) respectively, P<.001.
ConclusionspSer727-STAT3 is not a survival marker in patients with CCRCC. However, it is a cancer-specific survival marker in high-risk patients, even in metastatic patients undergoing treatment with antiangiogenic agents