Medir la tolerancia del estudio urodinámico (EUD) en el paciente pediátrico, mediante una escala visual analógica. Analizar qué variables clínicas y relacionadas con el EUD influyen en la percepción del dolor.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal de 139 pacientes pediátricos tras un EUD (entre diciembre del 2013 a mayo del 2018). Criterio de inclusión: entender y expresar su experiencia tras el EUD (edad preescolar y escolar). No se incluyeron adolescentes.
La herramienta de evaluación: escala visual analógica del dolor (EVA 0-10). Se obtuvieron otras variables clínicas y asociadas al EUD. Análisis estadístico: U de Mann-Whitney, Kruskal-Wallis. Análisis de correlación de Spearman (rs). Análisis multivariante mediante regresión logística ordinal. Significación p < 0,05.
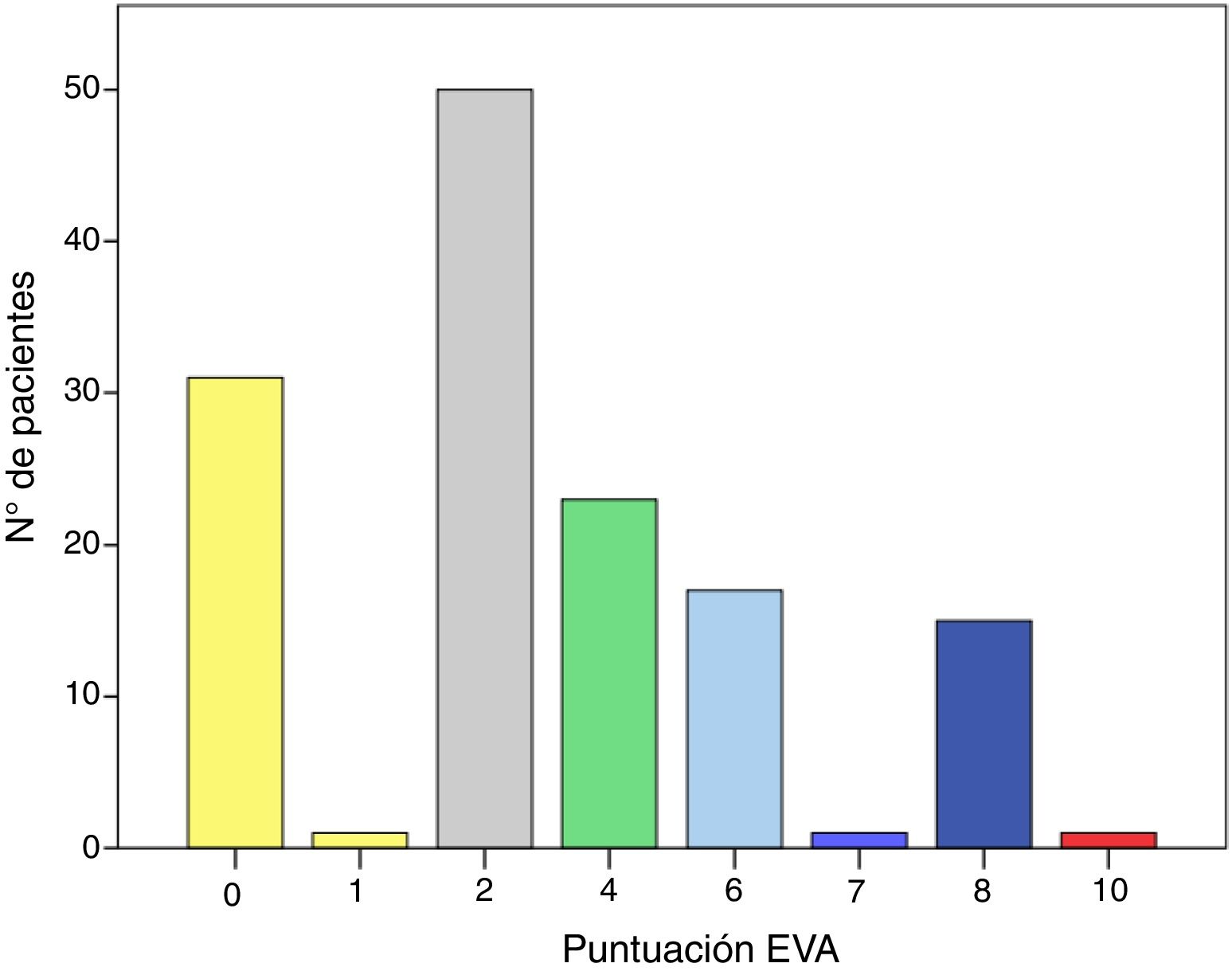
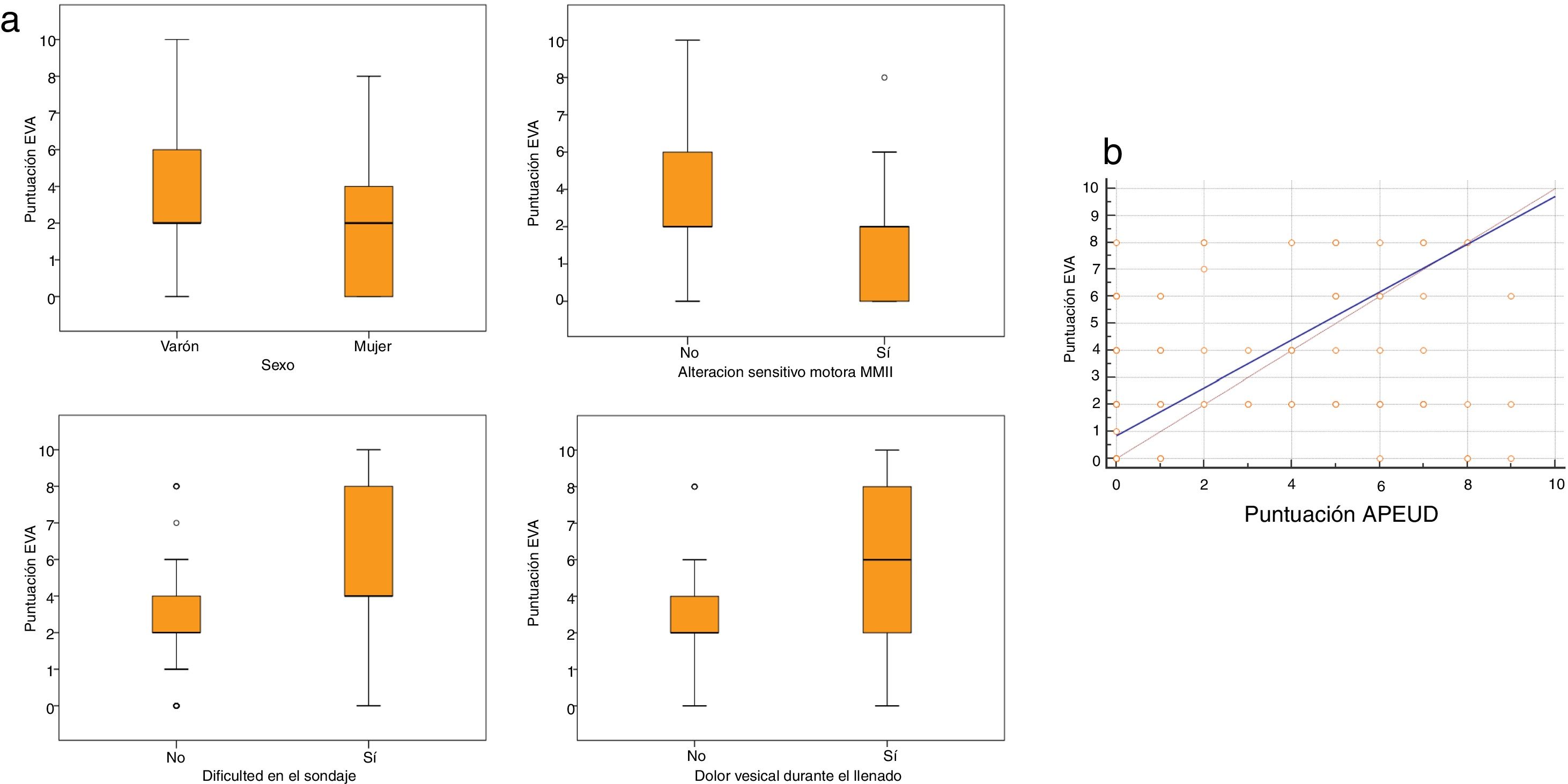
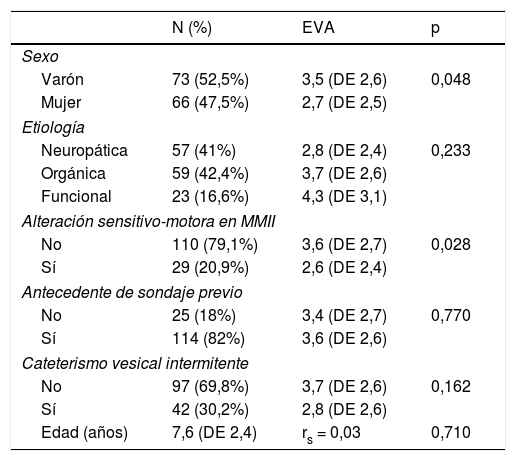
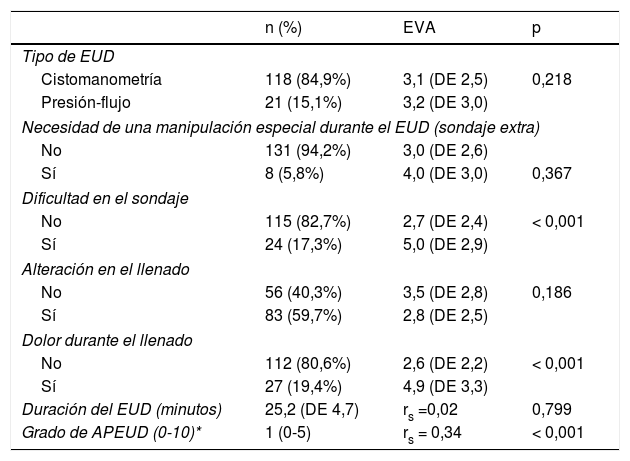
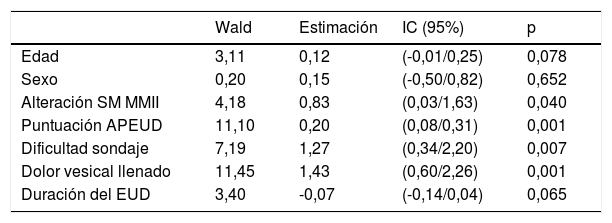
ResultadosMedia de edad 7,7 años (DE 2,4), mediana puntuación EVA, 2 (2-6). En un 41% (n = 57), la puntuación fue ≥ 4 (dolor moderado). Análisis multivariante. Variables explicativas de obtener una puntuación EVA alta: puntuación APEUD alta (identificar en el paciente nerviosismo previo al EUD), alteración sensitivo-motora de MMII, una dificultad en el sondaje vesical y que aparezca dolor durante el llenado. La edad y el tiempo de duración del EUD no han influido en dicha puntuación EVA.
ConclusionesAunque el EUD ha generado que un 40% de los pacientes pediátricos de nuestro estudio expresaran molestias o dolor, es una prueba bien tolerada.
Las variables que han influido en la percepción del dolor han sido: el nerviosismo del paciente previo al EUD, una alteración sensitivo-motora localizada en metámeras lumbosacras, una dificultad en el sondaje vesical y que aparezca dolor durante el llenado vesical.
To measure the tolerance of urodynamic testing (UDT) in the pediatric patient by means of the Visual Analog Scale (VAS). To analyze which clinical and UDT-related variables influence pain perception. Material and methods. Cross-sectional study of 139 pediatric patients undergoing UDT (December 2013 - May 2018). Inclusion criteria: understanding and expressing their experience after UDT (preschool and school age). No adolescents were included.
Measurement instrument Visual Analog Scale (0-10). Other clinical and UDT-associated variables were obtained. Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal Wallis test. Spearman's rank correlation analysis (rs). Multivariate analysis through ordinal logistic regression. Significance p < 0.05.
ResultsMean age 7.7 years (SD 2.4), median VAS score, 2 (2-6). In 41% (n = 57), the score was ≥ 4 (moderate pain). Multivariate analysis. Explanatory variables for obtaining a high VAS score: high APUDT score (identifying patient anxiety prior to UDT), sensory-motor alteration in the lower limbs, difficult bladder catheterization and the appearance of pain during the filling phase. Age and duration of the UDT have not influenced the VAS score.
ConclusionsAlthough the UDT has resulted in 40% of the pediatric patients in our study expressing discomfort or pain, it is a well-tolerated test.
The variables that have influenced on pain perception were patient's anxiety prior to UDT, a sensory-motor alteration located in the lumbosacral metameres, difficult bladder catheterization and the appearance of pain during bladder filling.