La dehiscencia glandular (DG) es una de las principales complicaciones que se producen tras la cirugía de hipospadias. Existe un número limitado de publicaciones sobre la DG en la literatura.
ObjetivoEsta revisión tiene como objetivo revelar los factores que afectan la DG mediante una revisión bibliográfica.
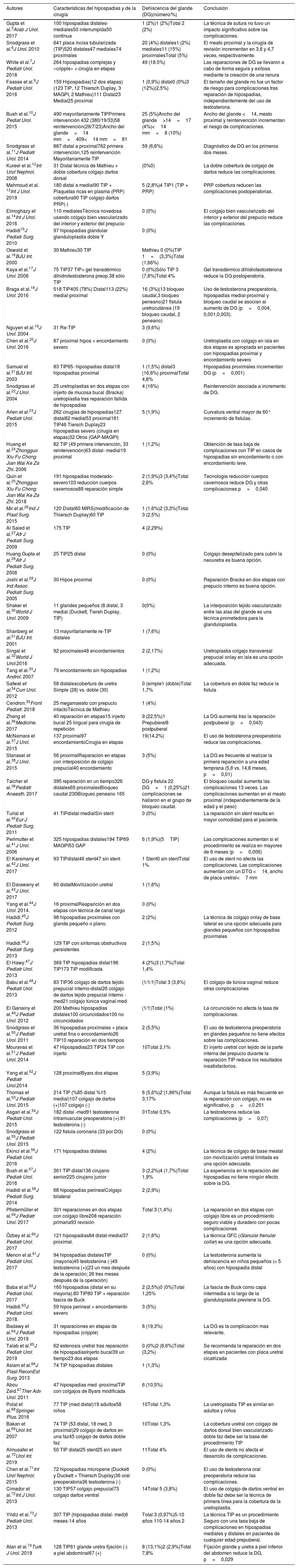
Adquisición de la evidenciaSe realizó una búsqueda literaria de artículos relacionados en la base de datos utilizando el término de búsqueda dehiscencia del glande sin establecer límite temporal ni ningún otro límite. Se incluyeron en este estudio todos los artículos relacionados con la dehiscencia del glande tras la cirugía de hipospadias. Tras recopilar la información de los textos completos, se incluyeron 71 artículos en esta revisión sistemática. Se obtuvieron los siguientes datos para la realización del estudio: la localización del meato hipospádico, el tipo de cirugía, y otros datos clínicos que se consideraron factores de riesgo de la DG. Se utilizó la prueba de X2 para comprobar las diferencias entre los distintos parámetros, considerando un valor p < 0,05 como estadísticamente significativo.
ResultadosTras evaluar los 71 artículos que cumplían los criterios de inclusión, en esta revisión se detectaron 309 casos (3,48%) de DG tras 8.858 reparaciones de hipospadias. Las tasas de DG fueron significativamente altas en el caso de las reparaciones de hipospadias proximales (5%), las reparaciones en dos tiempos quirúrgicos (5%) y las reintervenciones (8,75%) (p = 0,002, 0,022 y 0,004, respectivamente). El ancho del glande de < 14 mm y de la placa uretral de < 7 mm, las cirugías de hipospadias realizadas antes de los seis meses de edad y después de la pubertad, y la anestesia de bloqueo caudal aumentaron la tasa de DG.
ConclusionesEl aumento de la tasa de DG se asocia a cirugías de hipospadias proximales, cirugías previas fallidas (cripple) y reparación por etapas, al ancho de glande < 15 mm y al ancho de la placa uretral (PU) < 8 mm, la cirugía en edad postpuberal y el uso de anestesia caudal durante el procedimiento.
Glanular dehiscence (GD) is one of the main complications after hypospadias surgery. There is a limited number of publications regarding GD in the literature.
ObjectiveThe aim of this work is to reveal the factors that affect GD after a literature review.
Evidence acquisitionA literature search for relevant articles was performed in database using the search term glans dehiscence without setting date range limit or any other limits. All articles related to GD after hypospadias surgery were included in this study. After collecting the information from full text articles, 71 articles were included in this systematic review. In these studies, localization of hypospadic meatus, type of surgery, and other clinical data which were thought to behave as risk factors for GD were obtained. Chi-Square test was used to evaluate the differences between the parameters, where p < 0.05 was taken as statistically significant.
ResultsAfter evaluating the 71 articles that met the inclusion criteria, 309 cases (3.48%) of GD after 8858 hypospadias repairs were obtained in this review. GD rates were found significantly high for proximal hypospadias (5%), two-stage hypospadia repairs (5%) and re-do hypospadias repair (8.75%) (p = 0.002, 0.022, and 0.004, respectively). Glans width < 14 mm, urethral plate (UP) width < 7 mm, hypospadias surgeries performed before 6 months of age and after puberty, and caudal block anesthesia increased the rate of GD.
ConclusionsThe rate of GD increases after proximal, cripple and staged hypospadias surgeries, a glans width < 15 mm and UP width < 8 mm, postpubertal surgeries, and caudal anesthesia use during surgery.