El balón de dilatación uretral Optilume® es una alterativa a los tratamientos endoscópicos convencionales, combinando la dilatación mecánica con la liberación local de paclitaxel.
ObjetivoDescribir el porcentaje de éxito y analizar la seguridad del dispositivo en la práctica clínica real. Evaluar posibles factores predictores de fracaso en el tratamiento.
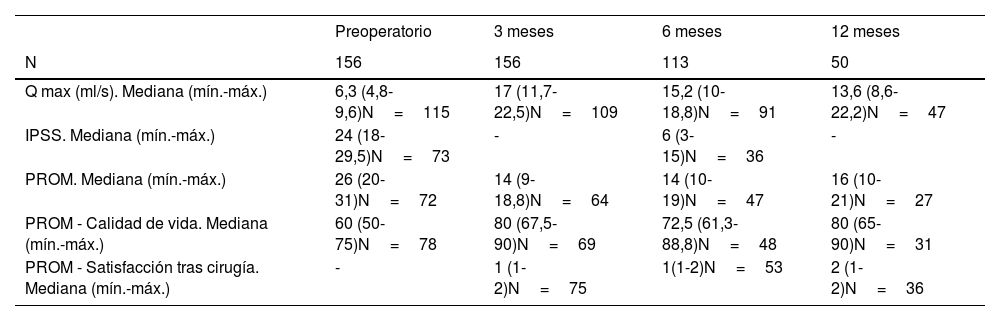
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo multicéntrico en pacientes diagnosticados de estenosis uretral y tratados con balón Optilume® en la práctica clínica habitual. Se recogieron datos de flujometría, cuestionarios (PROM e IPSS) y cistoscopia antes de la cirugía y tras 3, 6 y 12 meses después del procedimiento, según práctica habitual. Se consideró éxito quirúrgico la ausencia de necesidad de manipulación uretral posterior y un Qmax>10ml/s.
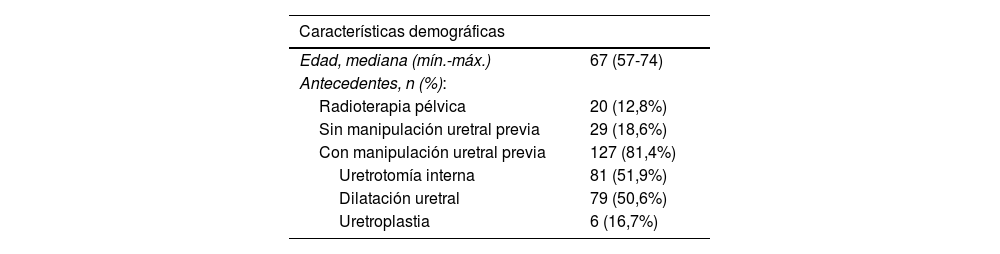
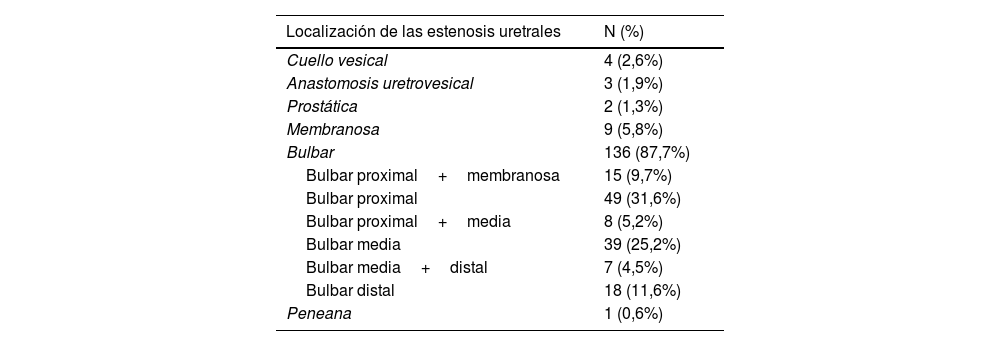
ResultadosSe incluyeron 238 pacientes tratados con Optilume® entre mayo de 2021 y abril de 2024 en 12 hospitales españoles. Se analizaron 156 con seguimiento mínimo de 3 meses. Mediana de longitud de las estenosis: 1,5cm (0,5-5,3), principalmente en uretra bulbar (87,7%). Un 12,8% tenía antecedentes de radioterapia pélvica. Manipulación uretral previa en el 81,4% de casos. Se registraron complicaciones postoperatorias en el 14,2% de pacientes. La tasa de éxito del tratamiento fue del 73,8%, con una mediana de seguimiento de 8 meses (5-12). No se identificaron factores predictivos de recurrencia de estenosis. Las tasas de recidiva fueron mayores en estenosis localizadas en uretra posterior frente a uretra anterior (42,9% vs. 24,6%, p=0,126). No se observaron diferencias significativas entre pacientes con y sin manipulación uretral previa.
ConclusiónEl balón de dilatación uretral Optilume® es un tratamiento seguro y efectivo a corto plazo en nuestra práctica clínica habitual.
The Optilume® paclitaxel-coated urethral dilatation balloon is an alternative to conventional endoscopic treatments that combines mechanical dilatation with local delivery of paclitaxel.
ObjectiveTo describe the success rate and analyze the safety of the device in real clinical practice. To evaluate possible predictors of treatment failure.
Material and methodsRetrospective multicenter study in patients diagnosed with urethral stricture and treated with an Optilume® balloon in routine clinical practice. Data were collected from flowmetry, questionnaires (PROM and IPSS) and cystoscopy before surgery, and 3, 6 and 12 months after the procedure, according to standard practice. Surgical success was defined as the absence of subsequent urethral manipulation and a Qmax>10ml/s.
Results238 patients treated with Optilume® in 12 Spanish hospitals between May 2021 and April 2024 were included in the study. Of these, 156 who had a minimum follow-up of 3 months, were analyzed. Median stricture length: 1.5cm (0.5 - 5.3), mainly in bulbar urethra (87.7%). Of the total, 12.8% of patients had a history of pelvic radiotherapy, and 81.4% had undergone prior urethral manipulation. Postoperative complications were reported in 14.2% of the total. The treatment success rate was 73.8%, with a median follow-up of 8 months (5-12). No predictors of stricture recurrence were identified. Recurrence rates were higher in strictures located in the posterior versus anterior urethra (42.9% vs. 24.6%, p=0.126). No significant differences were observed between patients with and without prior urethral manipulation.
ConclusionTreatment with Optilume® has been shown to be safe and effective in short-term routine clinical practice.