La vejiga hiperactiva (VH) es un trastorno frecuente que aumenta con la edad y afecta a la calidad de vida de los pacientes. Las guías recomiendan los programas de modificación de la conducta como tratamiento de primera línea, aunque la fisioterapia también se ha utilizado con éxito, seguridad y bajo coste. La fisioterapia clínica está utilizando la electroestimulación transcutánea del nervio tibial (ETNT) y la electroestimulación vaginal (EV). Este estudio tuvo como objetivo evaluar si la combinación de EV con ETNT es más exitosa que la monoterapia con ETNT para el tratamiento de las mujeres con VH.
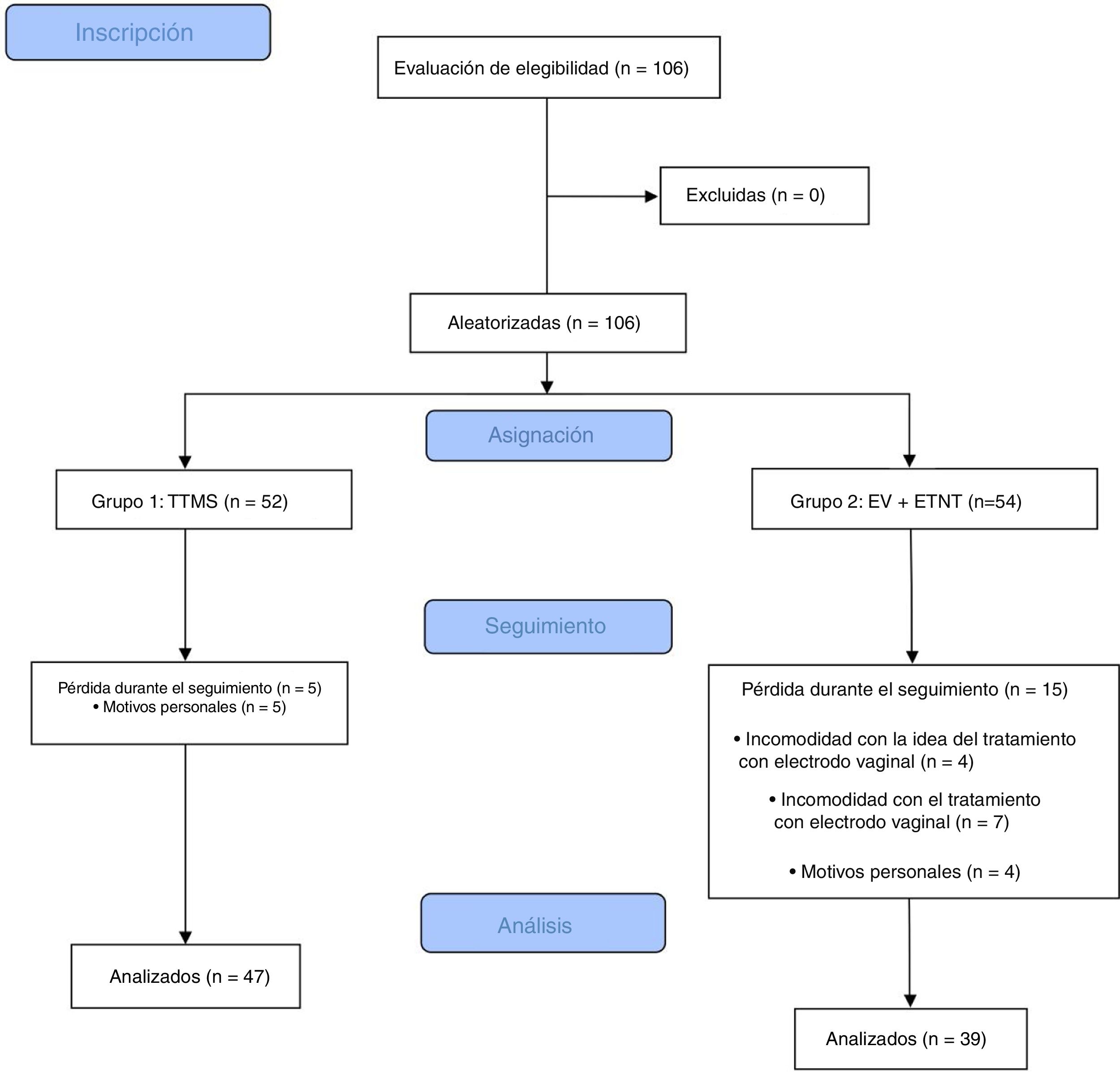
Pacientes y métodosEn total, 106 mujeres mayores de 18 años diagnosticadas con VH o incontinencia urinaria mixta con síntomas típicos de VH se dividieron aleatoriamente en 2 grupos: grupo 1: ETNT (n = 52); grupo 2: ETNT + EV (n = 54). El diario miccional de 3 días, la fuerza muscular del suelo pélvico (escala de Ortiz), el cuestionario de salud de King y el cuestionario de VH se evaluaron antes y después del tratamiento. La variable principal fue la frecuencia urinaria y una reducción de ≥ 3 micciones/día se consideró como clínicamente relevante. Se usaron modelos lineales mixtos para la comparación de los 2grupos.
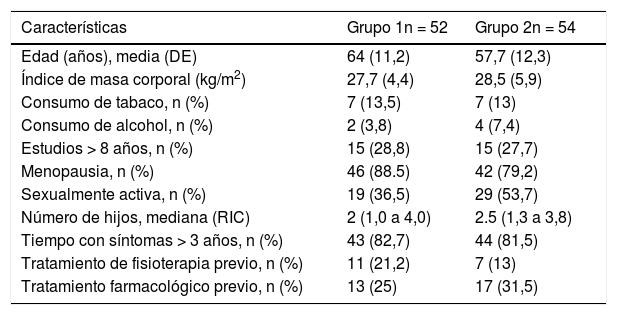
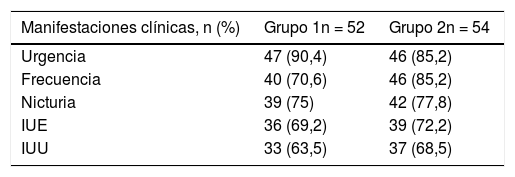
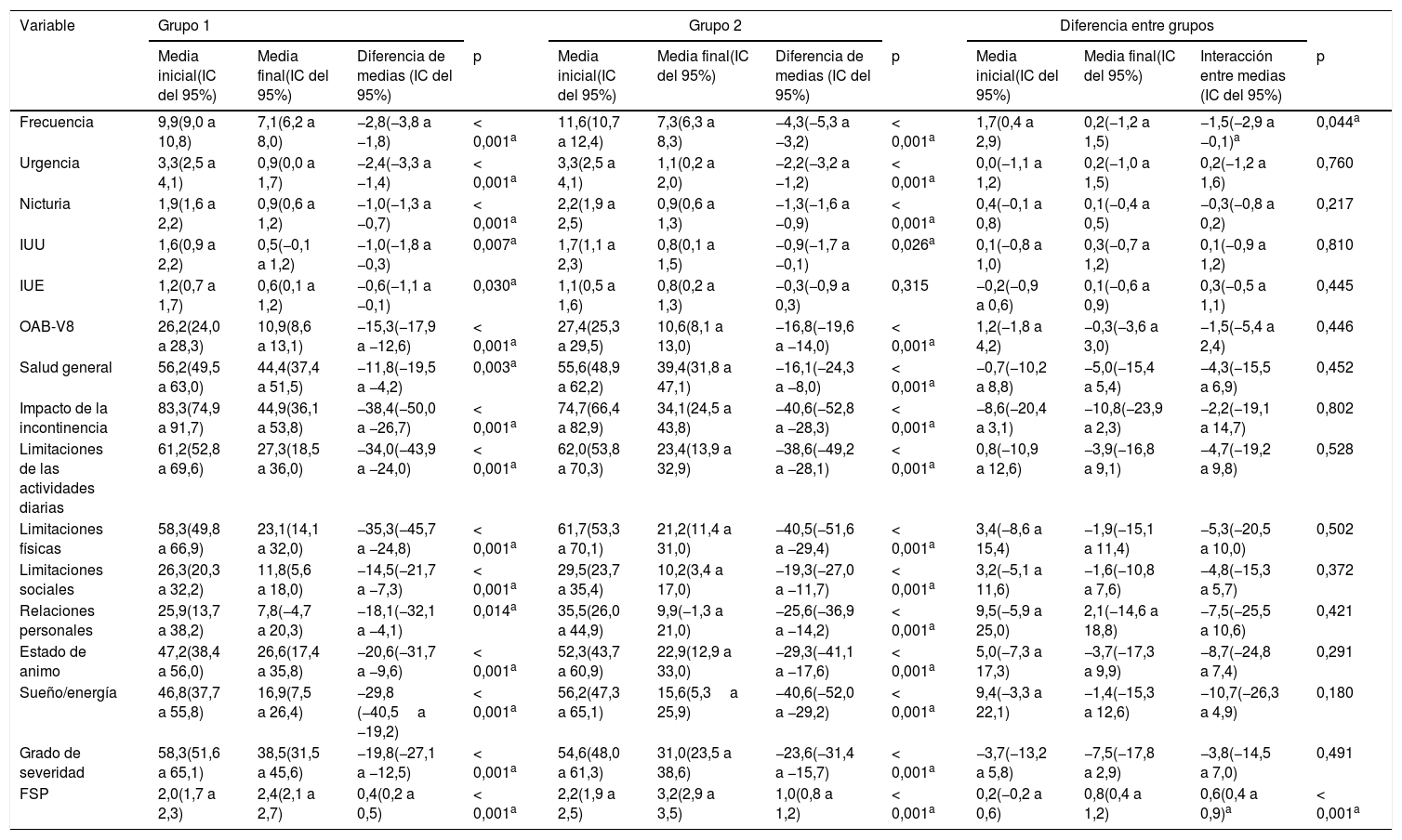
ResultadosInicialmente, los grupos fueron similares en edad, índice de masa corporal, número de embarazos, tiempo de aparición de VH y prevalencia de síntomas de VH. Después del tratamiento se observó una reducción en la frecuencia urinaria de 1,5 micciones en el grupo 2; a pesar de ser estadísticamente significativa, esta no fue clínicamente relevante.
ConclusionesLa combinación de EV con ETNT no hizo que el tratamiento para la VH fuese más efectivo que la monoterapia con ETNT.
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a prevalent disorder that increases with age and impairs patients’ quality of life. Guidelines recommend behavior modifications as the first-line treatment; however, physiotherapy has also been used with success, safety, and low cost. Transcutaneous tibial nerve electrical stimulation (TTNS) and vaginal electrical stimulation (VS) are being used in clinical physiotherapy practice. This study aimed to verify whether the addition of VS to TTNS is more beneficial than TTNS alone for women with OAB.
Patients and methodsIn all, 106 women aged >18 years diagnosed with OAB or mixed urinary incontinence with prevalent OAB symptoms were randomly divided into 2 groups: Group 1: TTNS (n = 52); Group 2: TTNS + VS (n = 54). The 3 day voiding diary, pelvic floor muscle strength (Ortiz Scale), King's Health Questionnaire, and Overactive Bladder Questionnaire were assessed before and after treatment. Urinary frequency was considered the primary outcome, and a reduction of ≥ 3 micturitions/day was considered clinically relevant. Mixed linear models were used to compare the 2groups.
ResultsInitially, the groups were similar in age, body mass index, number of pregnancies, time of OAB onset, and prevalence of OAB symptoms. After treatment, a reduction in urinary frequency of 1.5 micturitions was observed in Group 2, which was not clinically relevant despite being statistically significant.
ConclusionsThe addition of VS to TTNS for the treatment of OAB was not more effective than TTNS as a single therapy.