Realizamos este metaanálisis para evaluar la precisión diagnóstica de los microARN (miARN) circulantes para el diagnóstico precoz del cáncer de próstata (CaP).
MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica sistemática (actualizada al 18 de febrero de 2021) en PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, base de datos Wanfang y China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) para identificar los estudios elegibles. La sensibilidad (SEN), la especificidad (SPE), la razón de verosimilitud positiva (PLR), la razón de verosimilitud negativa (NLR), la razón de probabilidades de diagnóstico (DOR) y el área bajo la curva (AUC) de la curva característica de funcionamiento del receptor (SROC) se agruparon tanto para el análisis general como para el de subgrupos. La metarregresión y el análisis de subgrupos se realizaron para explorar la heterogeneidad y se utilizó el gráfico en embudo de Deek para evaluar el sesgo de publicación.
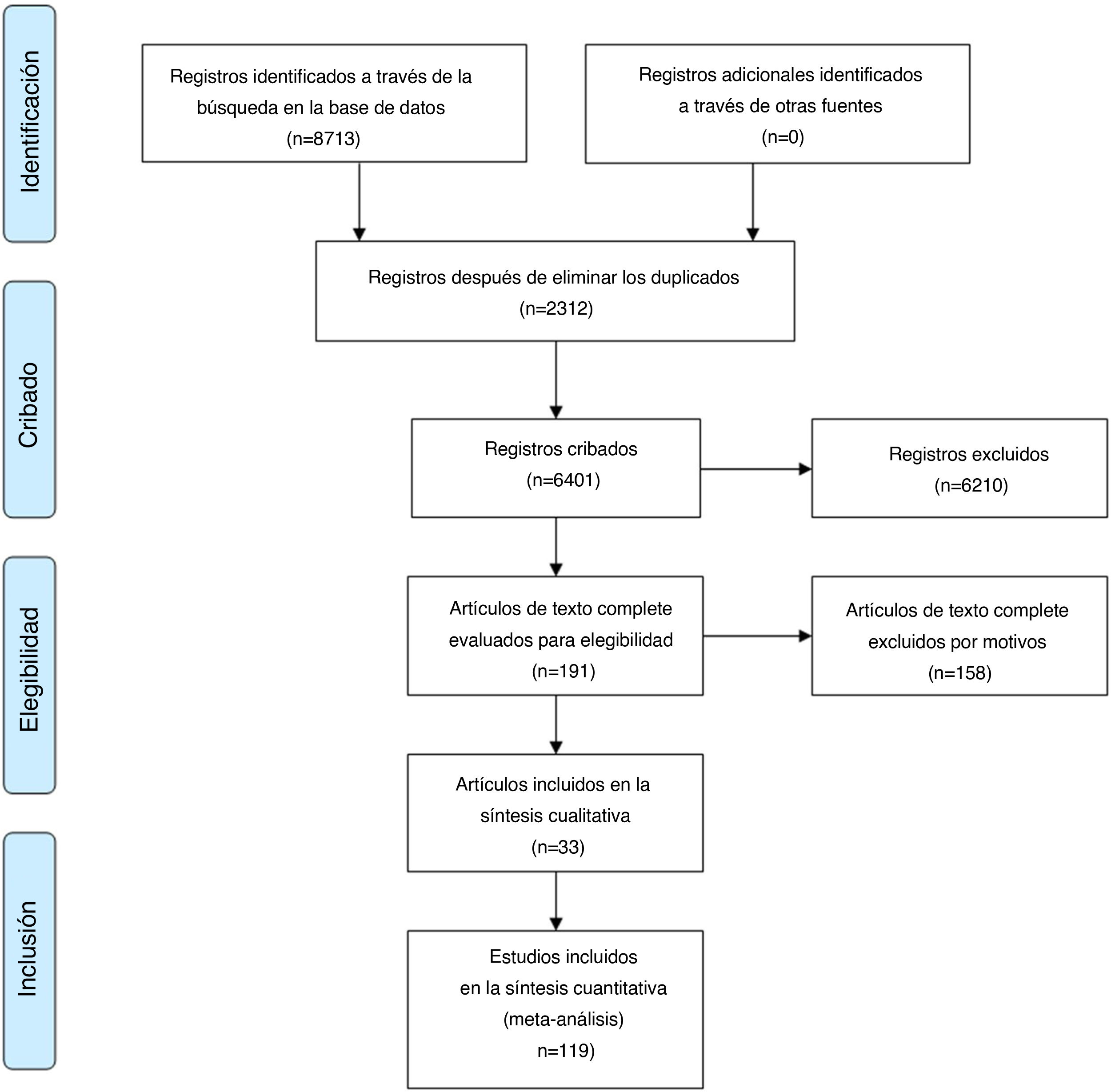
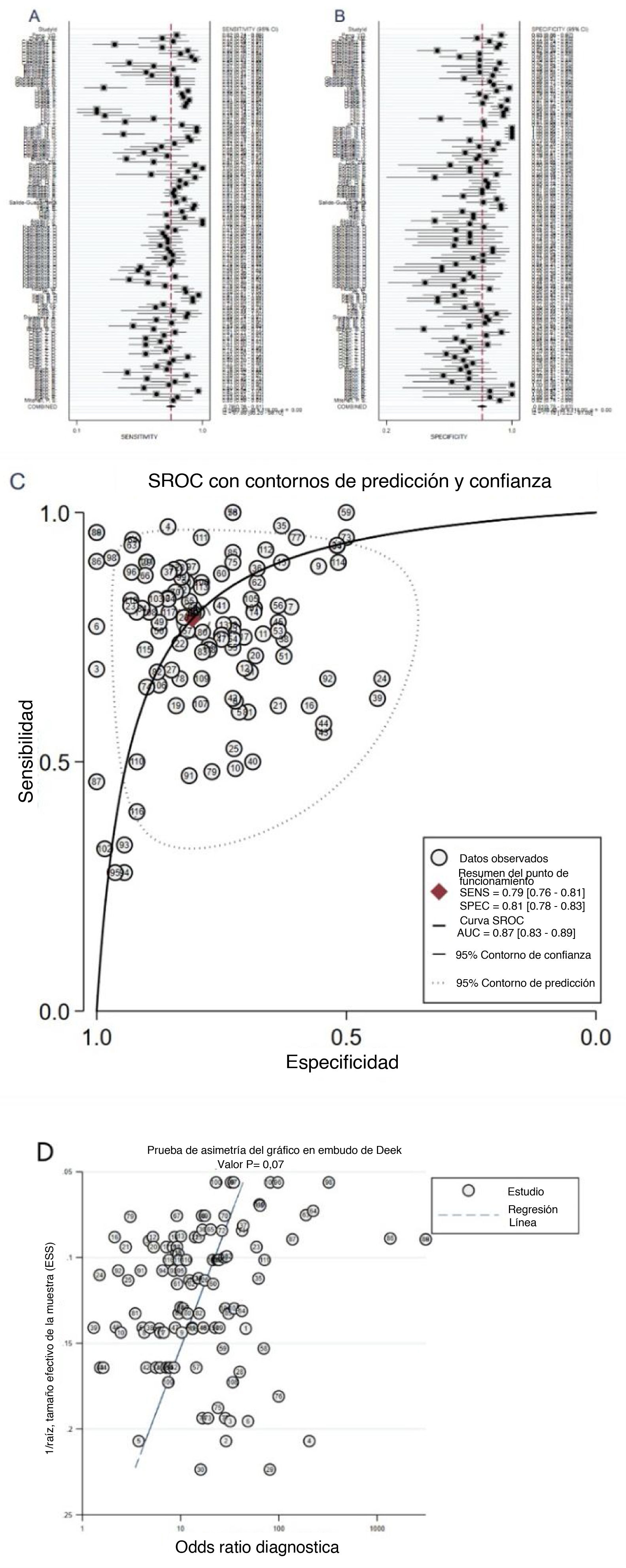
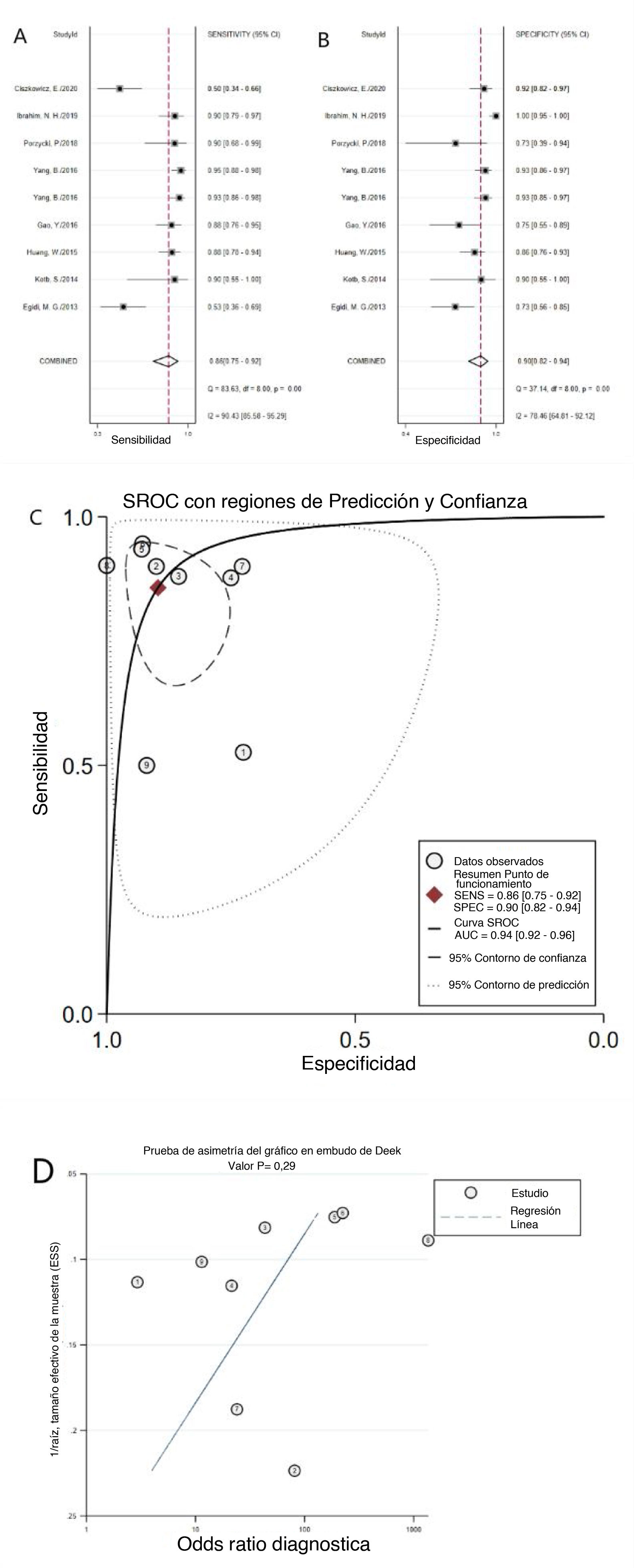
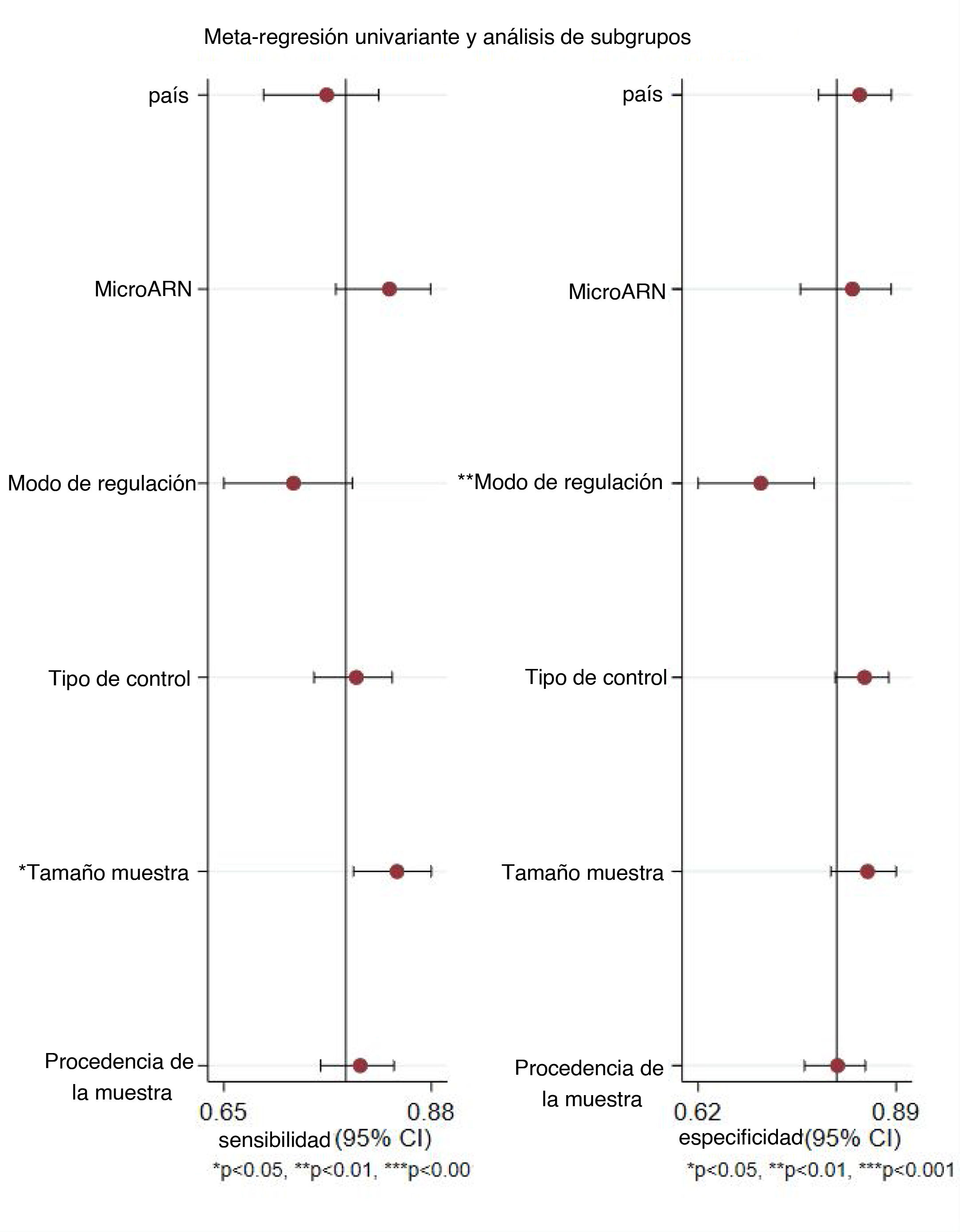
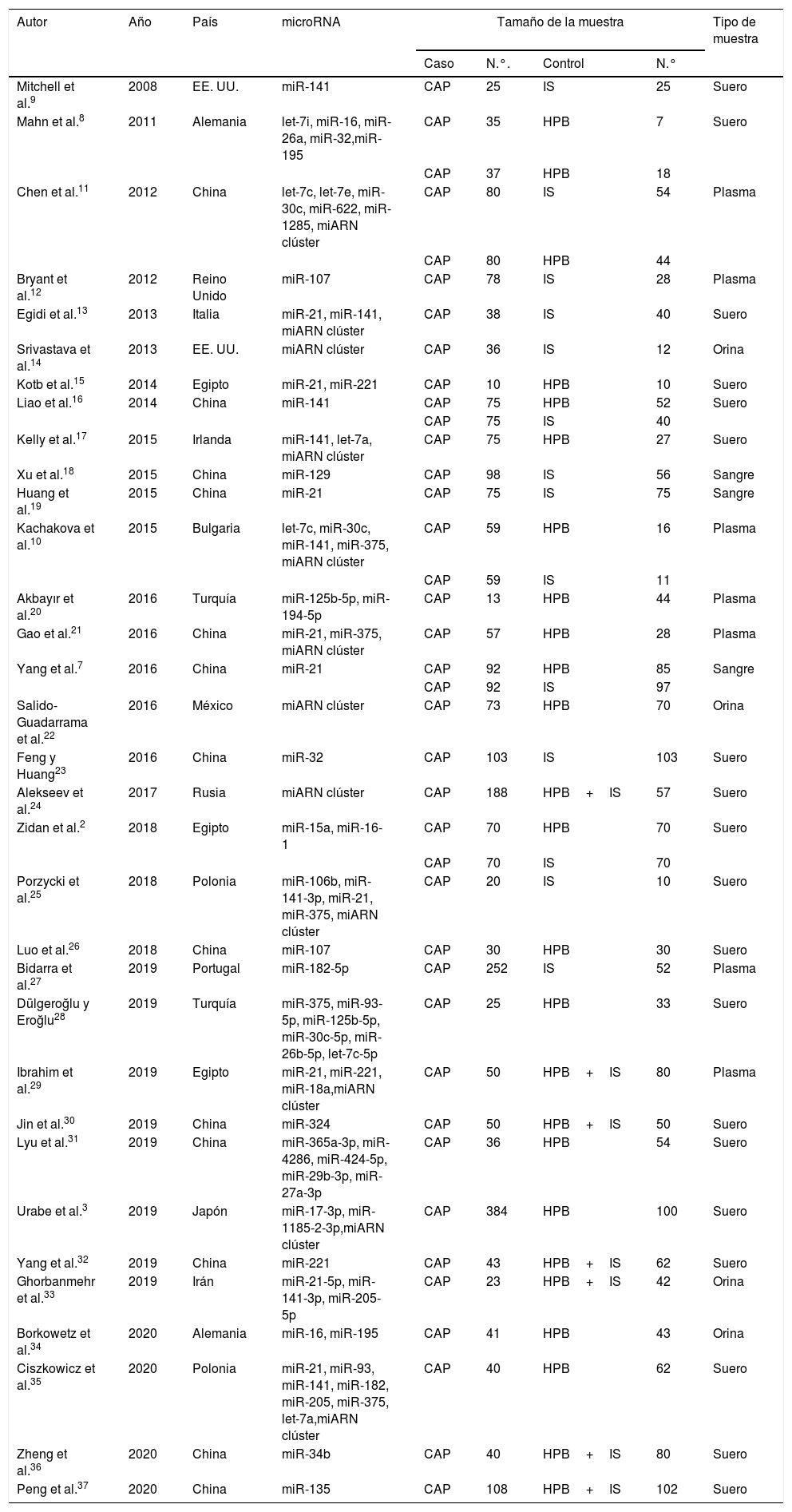
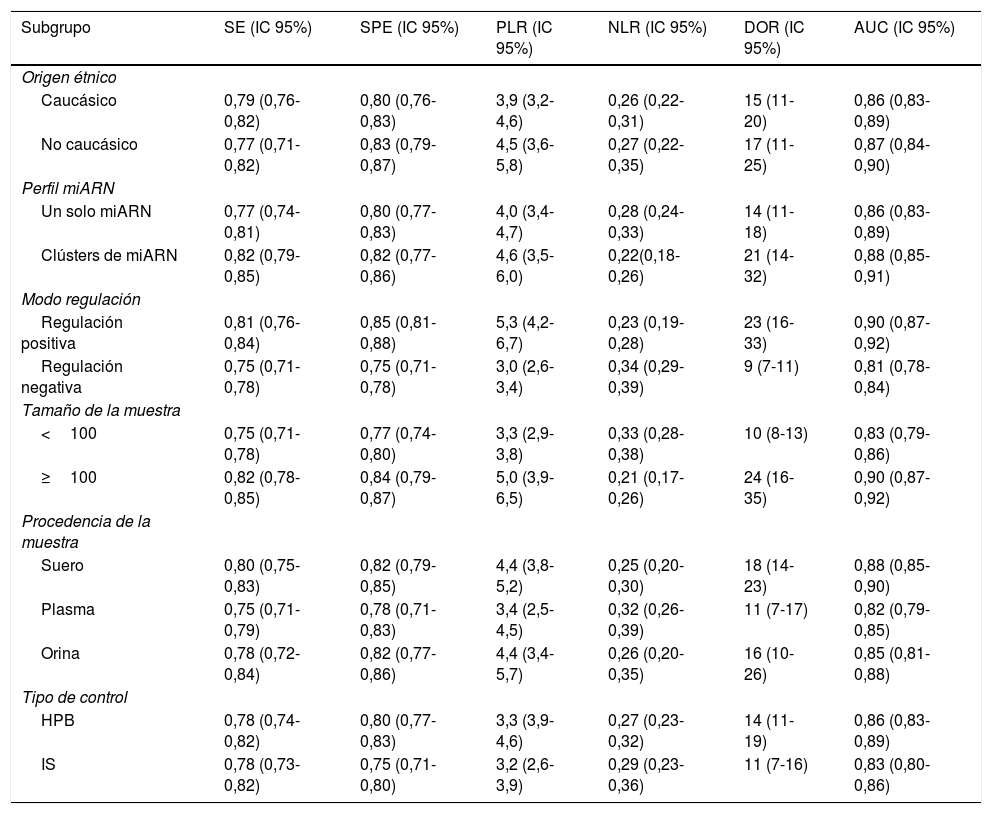
ResultadosCiento diecinueve estudios de 33 artículos pertenecientes a 8.703 pacientes con CaP y 4.914 controles se incluyeron en nuestro metaanálisis. La SEN, la SPE, la PLR, la NLR, la odds ratio diagnóstica y el AUC para el análisis general fueron 0,79, 0,81, 4,1, 0,26, 16 y 0,87, respectivamente. La SEN, la SPE, la PLR, la NLR, la odds ratio diagnóstica y el AUC agrupadas de miR-21 en el diagnóstico del CaP fueron 0,86, 0,90, 8,3, 0,16, 52 y 0,94, respectivamente. El análisis de subgrupos sugirió que el miARN sérico regulado al alza con un tamaño de muestra grande podría llevar a cabo una mejor precisión diagnóstica de los pacientes con CaP. Además, no se encontró sesgo de publicación.
ConclusionesEl miARN circulante, especialmente el miR-21, puede utilizarse como un biomarcador no invasivo prometedor en el diagnóstico precoz del CaP.
This meta-analysis has been conducted to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of circulating microRNAs for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer (PCA).
MethodsA systematic literature search was performed (updated to February 18, 2021) in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Wanfang database and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) to identify eligible studies. The pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under curve (AUC) of the summary receiver-operating characteristic (SROC) curve were calculated for both overall and subgroup analysis. The meta-regression and subgroup analysis were performed to explore heterogeneity and Deeks’ funnel plot was used to assess publication bias.
ResultsOne hundred nineteen studies from 33 articles owned 8703 PCA patients and 4914 controls were included in our meta-analysis. The overall sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio and area under the curve were 0.79, 0.81, 4.1, 0.26, 16 and 0.87, respectively. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the curve of miR-21 in diagnosis of PCA were 0.86, 0.90, 8.3, 0.16, 52 and 0.94, respectively. Subgroup analysis suggested that the upregulated miRNA of serum type with large sample size could carry out a better diagnostic accuracy of PCA patients. Moreover, publication bias was not found.
ConclusionsCirculating microRNA, especially miR-21, can be used as a promising noninvasive biomarker in the early diagnosis of PCA.