El objetivo del estudio fue analizar el impacto de la pandemia por COVID-19 en la presentación y el manejo de la enfermedad litiásica.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo comparativo de los procedimientos (urgentes y electivos) por litiasis durante los primeros 8 meses de la pandemia (01/03/2020 al 31/10/2020), comparándose con el mismo periodo de 2019, y entre olas. Las pruebas utilizadas fueron la prueba exacta de Fisher, la t de Student, la chi-cuadrado y la U de Mann-Whitney.
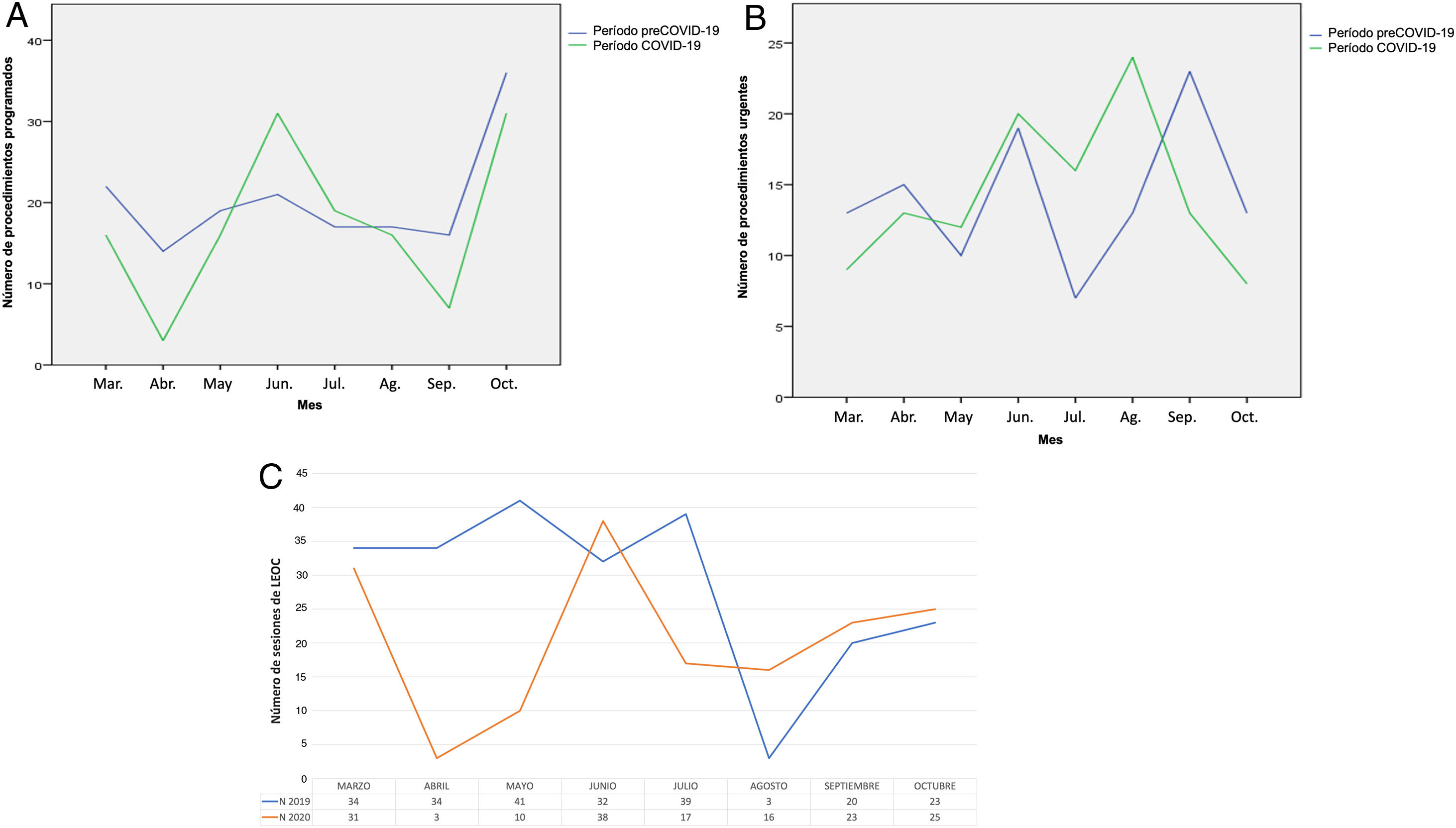
ResultadosSe analizaron 530 procedimientos. El número total de procedimientos quirúrgicos por enfermedad litiásica fue similar entre los 2 periodos. En cuanto a la cirugía electiva, se identificó un aumento en la tasa de complicaciones en el periodo de pandemia, pero no se observaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en cuanto a tipos de procedimientos realizados y necesidad de tratamientos complementarios. El patrón de presentación del cólico renoureteral complicado fue diferente durante la pandemia, con un mayor número de días desde el inicio de los síntomas hasta la consulta y una mayor proporción de pacientes con fracaso renal agudo. Asimismo, se detectó un aumento significativo de los niveles de creatinina en la primera ola, así como un incremento en el número de procedimientos urgentes tras la primera ola debido al retraso en el tratamiento y diagnóstico de la enfermedad litiásica.
ConclusionesLa pandemia por COVID-19 ha impactado negativamente en el tratamiento urgente y electivo de la litiasis. Se deben aprender lecciones sobre el manejo de la litiasis en este contexto para evitar complicaciones graves y mejorar los estándares de atención.
The aim was to determine the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on urolithiasis presentation and management.
MethodsIn this retrospective study, we comparatively evaluated urgent and elective procedures due to urolithiasis during the early 8 months of the COVID-19 pandemic (March 1, 2020, to October 31, 2020) compared to the same period a year before, and between waves. Fisher's exact test, Student's t-test, chi-square test and Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare the patients’ characteristics and outcomes between the 2 periods and waves.
ResultsFive hundred and thirty procedures were included. The overall numbers of surgical procedures due to urolithiasis were similar between pre-pandemic and pandemic periods. Regarding elective surgery, our data draw attention to the increased complication rate in the pandemic times, but no statistically significant differences in terms of types of procedures and need for complementary treatments were observed. We noted that patterns of presentation of complicated renal colic were different during COVID-19 pandemic, with a higher number of days after the onset of symptoms and a higher proportion of patients presenting acute kidney injury. Furthermore, a significant increase of creatinine levels at presentation in first wave was detected, and a growth in the number of urgent procedures after the first wave was noted, owing to the delay in urolithiasis treatment and diagnosis.
ConclusionsThe COVID-19 pandemic has negatively affected both urgent and elective management of urolithiasis. Lessons about the management of urolithiasis in this context should be learned to avoid fatal complications and improve standards of care.