To assess the ability of multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) to detect prostate cancer in patients with prior negative transrectal prostate biopsy (TPB).
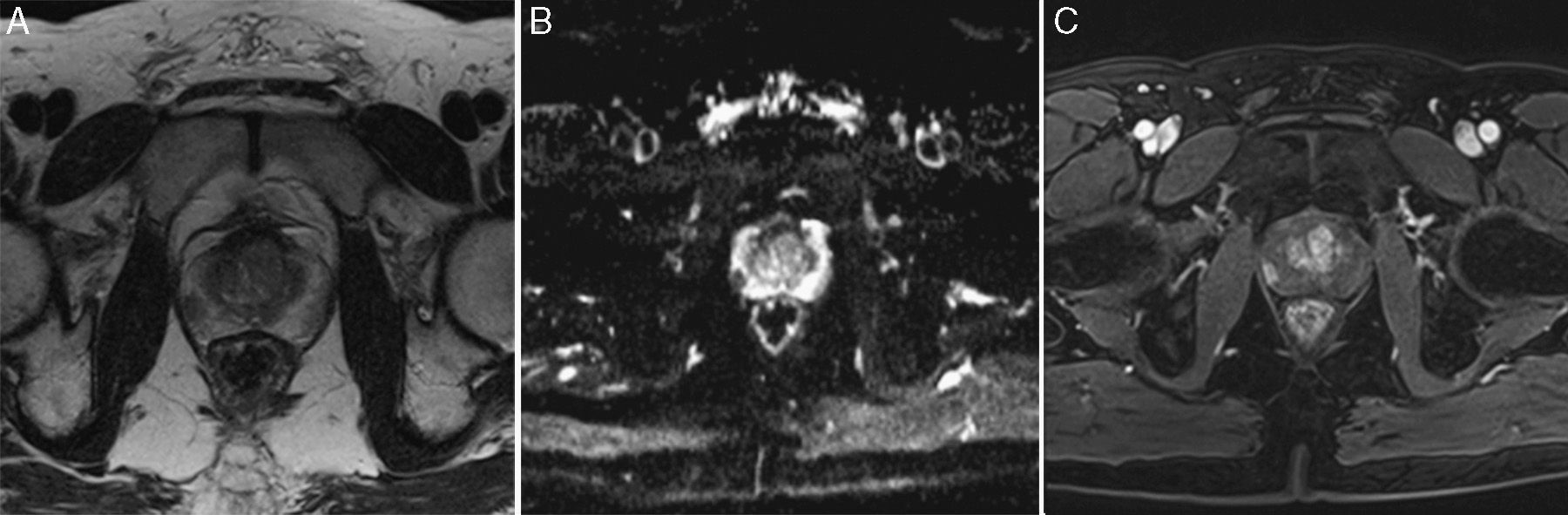
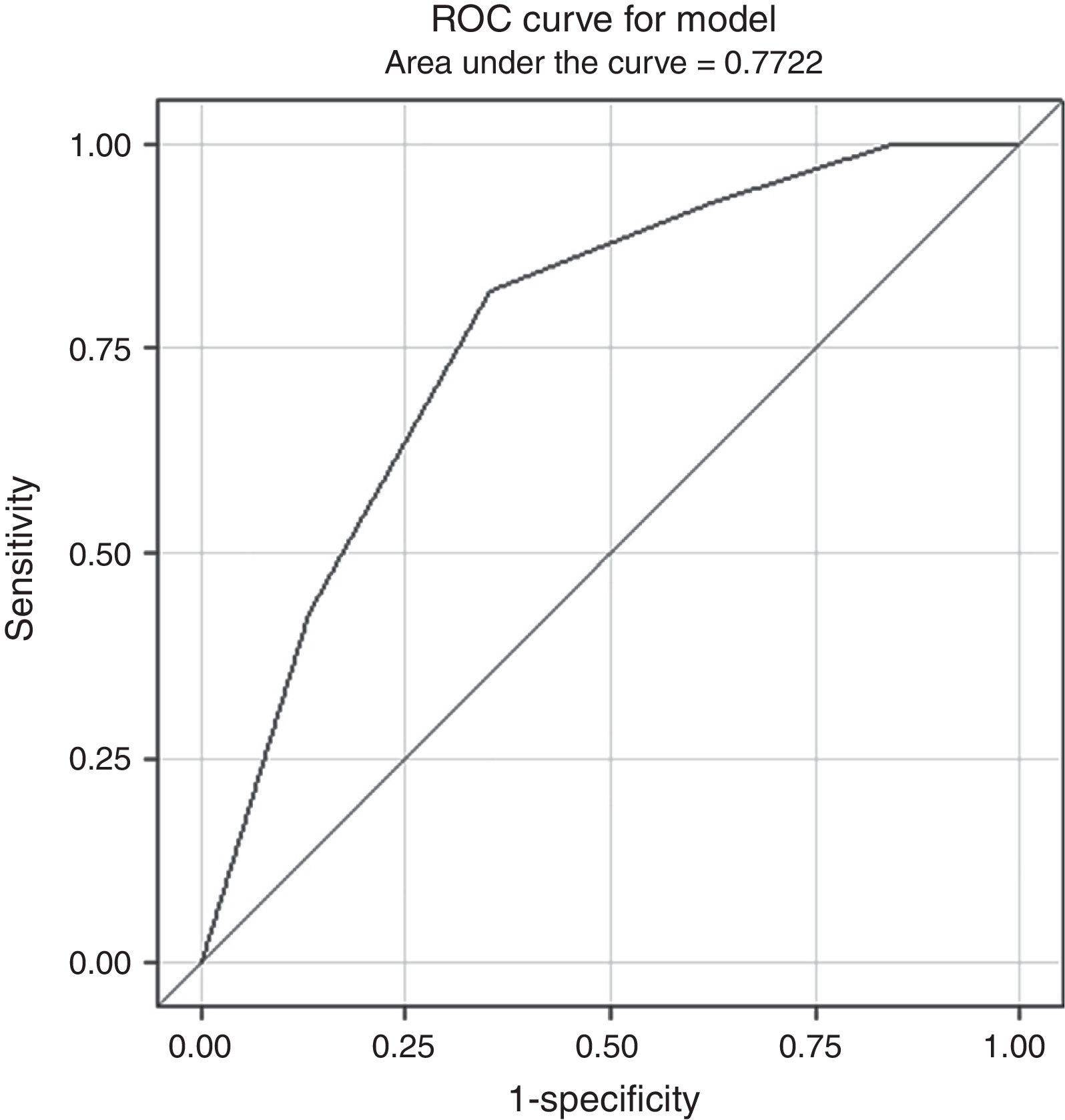
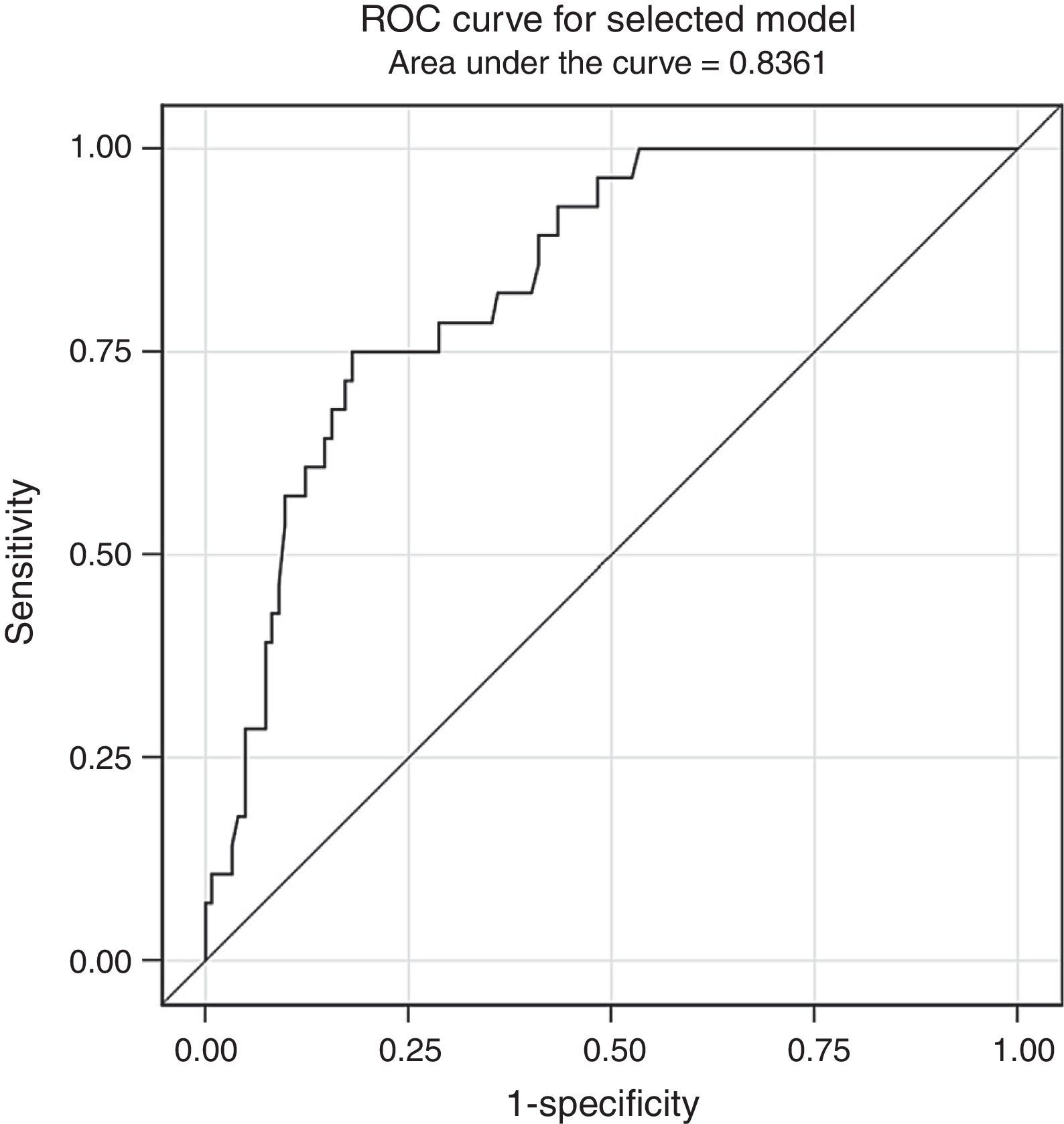
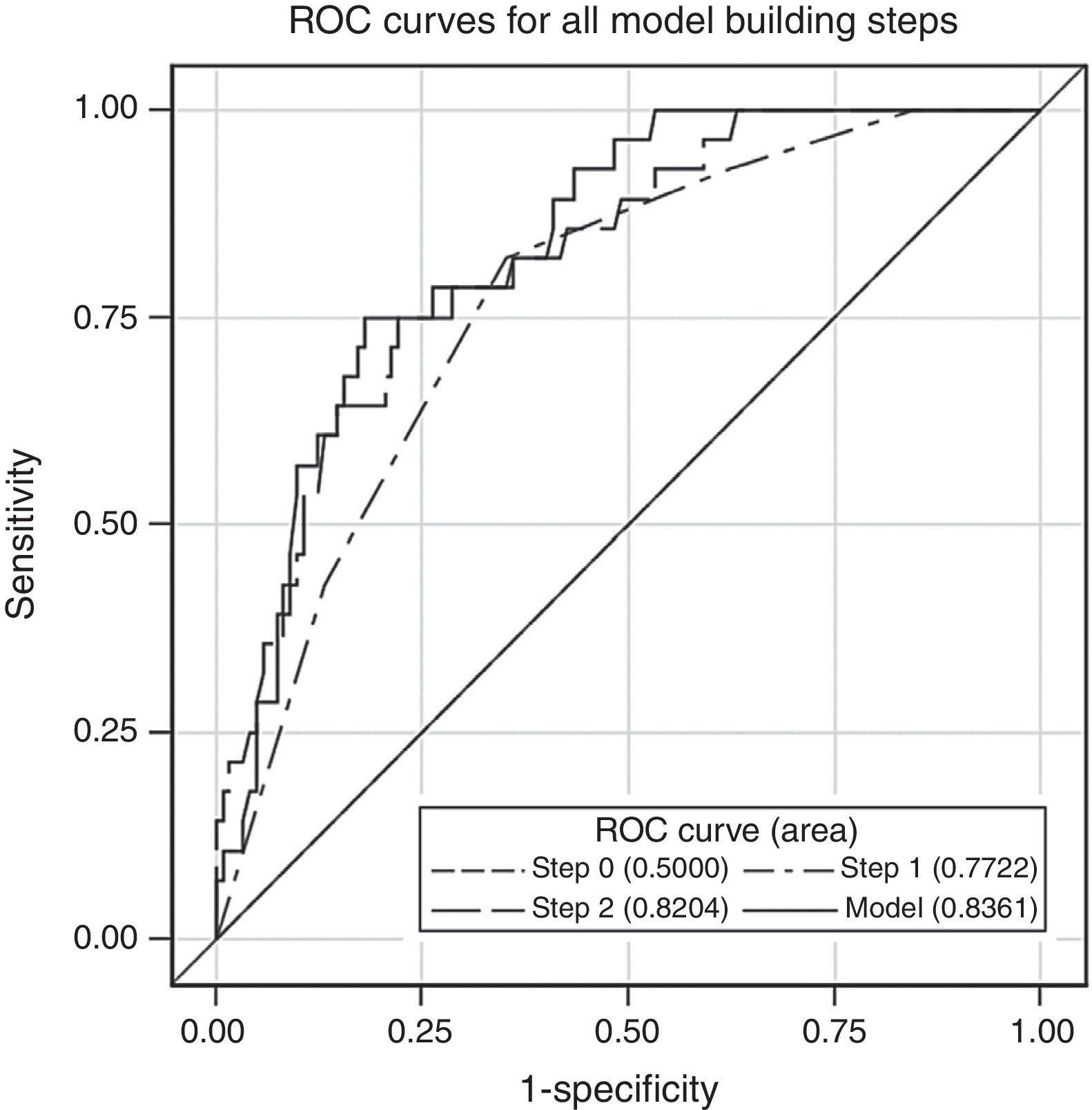
Materials and methodsmpMRI (TSE-T2-w, DWI and DCE sequences) was performed on 1.5T (Magnetom Avanto; Siemens Healthcare Solutions) in 150 patients suspicious of prostate cancer and with negative TPB. European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) criteria were used (score 1: clinically significant disease is highly unlikely to be present; score 2: clinically significant cancer is unlikely to be present; score 3: clinically significant cancer is equivocal; score 4: clinically significant cancer is likely to be present; score 5: clinically significant cancer is highly likely to be present). PSA measurement (total and free), digital rectal examination (DRE), transrectal ultrasound (TRU) and a second TPB (at least 14 cylinders) were performed in all patients. Variables were submitted for independent blind analysis. The accuracy of each test was measured. Stepwise selection model for prediction of prostate cancer in second TPB was developed.
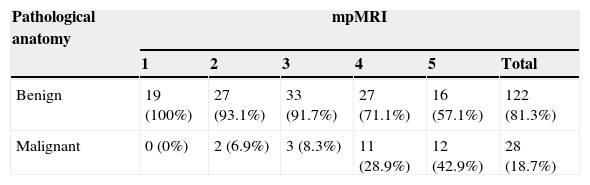
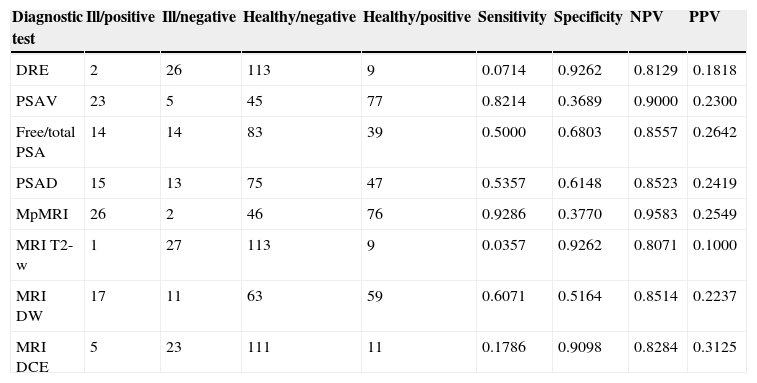
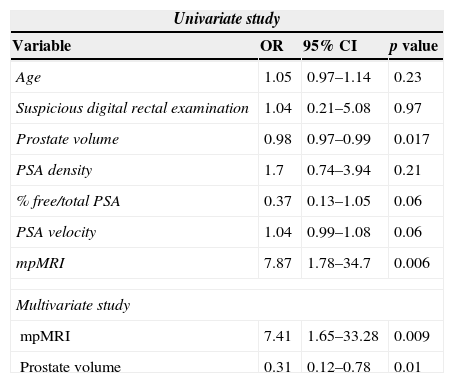
ResultsMean age was 66.2±5 years (51–77), mean PSA 11.3±9.6ng/mL (0.9–75) and mean prostatic volume 82.2±42 (20–250) cc. DRE was suspicious in 11 (7.3%) patients. The mean number of cylinders per patient sampled in second TRB was 17.6±2.7(14–22). Second TRB was positive in 28 patients (18.7%). mpMRI was positive (score 3–5) in 102 (68%), test sensibility was 92.9% and the NPV was 95.8%. The risk of prostate cancer diagnosis in second TPB is modified by: PSA velocity >0.75 (OR 1.04 [0.99–1.08]; p=0.06), free/total ratio PSA <15% (OR 0.37 [0.13–1.05]; p=0.06), each cc. of prostate volume (OR 0.98 [0.97–1]; p=0.017) and mpMRI 3–5 (OR 7.87 [1.78–34.7]; p=0.006). Multivariate analysis reveals that mpMRI (OR 7.41 [1.65–33.28]; p=0.009) and prostatic volume (OR 0.31 [0.12–0.78]; p=0.01) are independent risk predictors of prostate cancer.
ConclusionsAccording to ESUR guidelines and in patients with prior negative prostate biopsy, mpMRI is a valuable tool for the prediction of prostate cancer in second TPB. Lower the prostate volume, the higher the reliability.
Evaluar el papel del estudio multiparamétrico mediante imagen por resonancia magnética (mpMRI) de próstata para detectar cáncer de próstata en pacientes con biopsia prostática transrectal (BPTR) negativa previa.
Material y métodosSe practicó una mpMRI (secuencias TSE-T2-w, DWI y DCE) de la próstata con equipo de 1.5T (Magnetom Avanto; Siemens Healthcare Solutions) a 150 pacientes con sospecha previa de cáncer de próstata y BPTR negativa. Se aplicaron criterios de European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) (1: muy posiblemente benigno, 2: posiblemente benigno, 3: dudoso, 4: posiblemente maligno, y 5: muy posiblemente maligno). A todos los pacientes se les realizó PSA (total y libre), tacto rectal (TR), ecografía transrectal (ETR) y segunda BPTR de, al menos, 14 cilindros. Las variables fueron analizadas de forma ciega independiente. Se estudió la exactitud de cada prueba y se evaluó un modelo de selección de variables stepwise para predecir cáncer en la segunda BPTR.
ResultadosLa edad media±desviación estándar fue 66,2±5 (51-77) años, el PSA 11,3±9,6 (0,9-75) ng/mL y el volumen prostático 82,2±42 (20-250) cc. El TR fue sospechoso en 11(7,3%) pacientes. La segunda BPTR muestreó 17,6±2,7 (14-22) cilindros por caso y resultó positiva en 28 (18,7%) pacientes. La mpMRI se consideró positiva (3-5) en 102 (68%), siendo la sensibilidad de la prueba del 92,9% y el VPN del 95,8%. Modifican riesgo de cáncer en segunda BPTR: velocidad de PSA>0,75 (OR 1,04 [0,99-1,08]); p=0,06), PSA libre/total < 15% (OR 0,37 [0,13-1,05]; p=0,06), cada cc de volumen prostático (OR 0,98 [0,97-1]; p=0,017) y mpMRI 3-5 (OR 7,87 [1,78-34,7]; p=0,006). El análisis multivariante reveló que mpMRI (OR 7,41 [1,65-33,28]; p=0,009) y volumen prostático (OR 0,31 [0,12-0,78]; p=0,01) definen riesgo de cáncer de forma independiente.
ConclusionesLa mpMRI según criterios ESUR es una herramienta de gran valor para predecir la presencia de cáncer en la segunda BPTR en pacientes con biopsia previa negativa y resulta más fiable en próstatas de menor volumen.