Prostate cancer (PC) treatment in early stages is radical prostatectomy (RP) or external radiotherapy (ER). There is some uncertainty regarding the development of new ER induced malignant tumors or second primary tumor (SPT), a fact influencing the choice of therapy. The purpose of this study is to determine the best therapeutic alternative for localized PC, in regards to incidence and time of development.
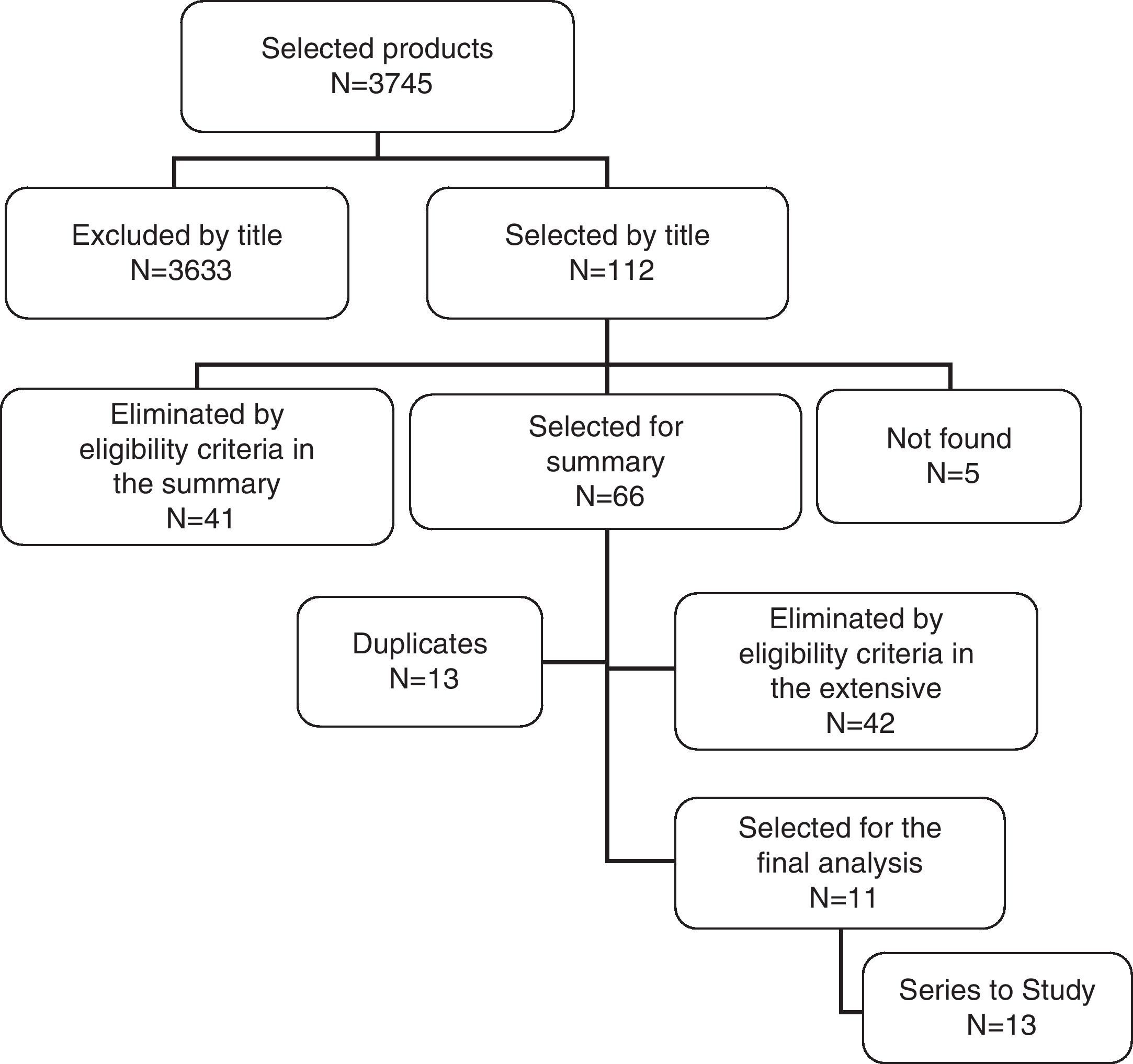
Material and methodsA systematic review of the literature is proposed by means of evaluation of studies conducted with localized PC and treated with RP or ER, published between 1990 and 2010. The Mega searchers used were Cochrane Library and Trip Database, and the databases used were MEDLINE, OVID, Science Direct, SciELO and LiLACS, using MeSH terms and free words. The studies selected were analyzed using the MINCIR score of methodological quality (MQ) to compare articles with different design. The variables were considered to be number of patients treated, localization of lesions, global incidence of STP and MQ of the studies. Averages, medians and weighted averages (WA) were calculated. The study groups were compared using the 95% confidence intervals of the medians.
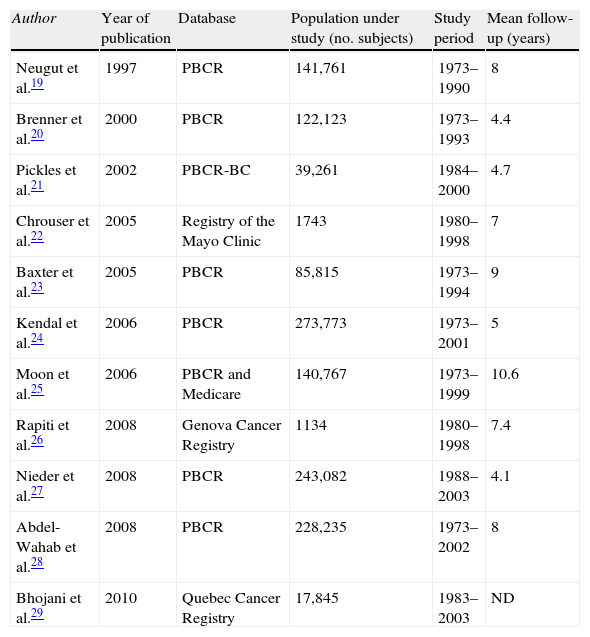
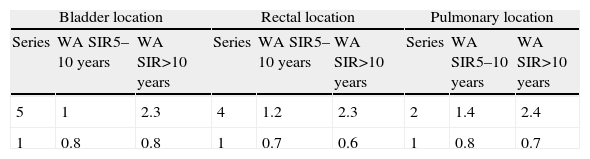
ResultsEleven articles fulfilled the screening criteria (retrospective cohorts and case series); providing 13 series for the study. The average of MQ was 14.7 points (13 and 16 points). The most frequent localizations of STP were bladder, rectum and long. The WA of the global incidence of STP for the series was 3.6% (4.1% for ER and 2.2% RP).
ConclusionThe information existing did not make it possible to demonstrate an association between the appearance of STP and therapies for localized PC, even though there was a superior tendency in irradiated patients.
El tratamiento del cáncer prostático (CP) en estadios precoces es la prostatectomía radical (PR) o la radioterapia externa (RE). Existe incertidumbre respecto del desarrollo de nuevos tumores malignos o segundo tumor primario (STP) inducidos por RE, hecho gravitante en la elección de la terapia. El objetivo de este estudio es determinar la mejor alternativa terapéutica para CP localizado, en lo que respecta a la incidencia y tiempo de desarrollo de STP.
Material y métodoSe plantea una revisión sistemática de la literatura mediante la evaluación de estudios realizados con CP localizado y tratado con PR o RE, publicados entre 1990 y 2010. Se utilizaron los Mega buscadores Cochrane Library y Trip Database, y las bases de datos MEDLINE, OVID, Science Direct, SciELO y LiLACS, empleando términos MeSH y palabras libres. Los estudios seleccionados fueron analizados utilizando el escore MINCIR de calidad metodológica (CM) para comparación de artículos con diferente diseño. Se consideraron las variables número de pacientes tratados, localización de lesiones, incidencia global de TSP y CM de los estudios. Se calcularon promedios, medianas y promedios ponderados (PP). Se compararon los grupos en estudio utilizando intervalos de confianza del 95% de las medianas.
Resultados11 artículos cumplieron los criterios de selección (cohortes retrospectivas y series de casos); aportando 13 series para el estudio. El promedio de CM fue 14,7 puntos (13 y 16 puntos). Las localizaciones más frecuentes de TSP fueron vejiga, recto y pulmón. El PP de la incidencia global de TSP para las series fue de 3,6% (4,1% para RE y 2,2% PR).
ConclusiónLa información existente no permite demostrar asociación entre aparición de TSP y las terapias para CP localizado, a pesar de que existe una tendencia superior en pacientes irradiados.