El tislelizumab, un anticuerpo monoclonal dirigido contra la proteína 1 de muerte programada (PD-1), ha demostrado una actividad antitumoral prometedora en el cáncer urotelial. Este estudio se diseñó para evaluar la eficacia y la seguridad de tislelizumab en el cáncer urotelial en un entorno real.
MétodosEl presente es un estudio retrospectivo de vida real realizado en el Liaoning Cancer Hospital & Institute (China). Los pacientes elegibles eran adultos de ≥ 18 años. Los pacientes recibieron 200 mg tislelizumab en monoterapia por vía intravenosa cada tres semanas hasta la progresión de la enfermedad, la toxicidad intolerable o la suspensión del tratamiento por cualquier otro motivo. Las variables de interés fueron la tasa de respuesta objetiva (TRO), la tasa de control de la enfermedad (TCE), la supervivencia libre de progresión (SLP), la supervivencia global (SG) y la seguridad.
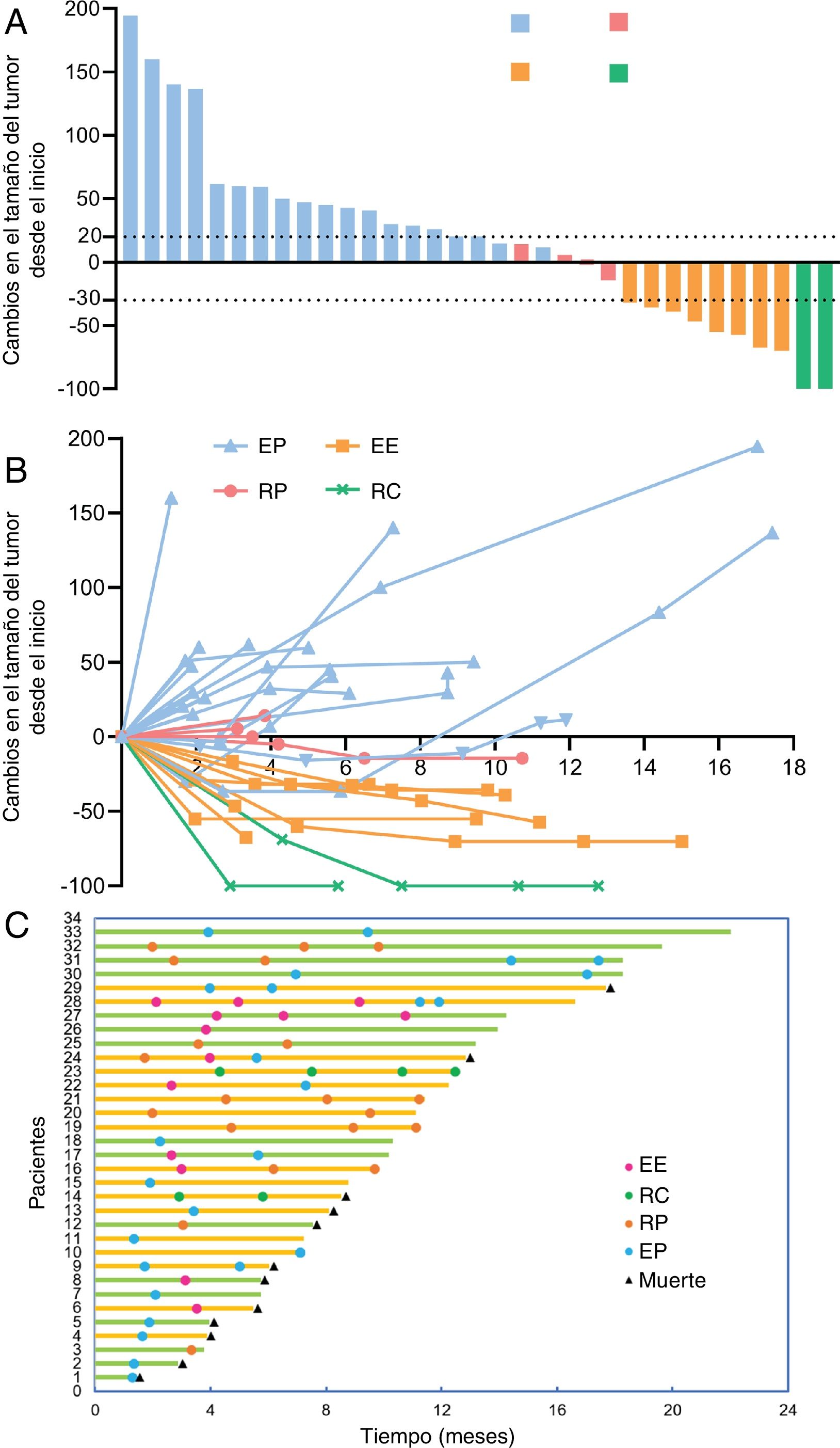
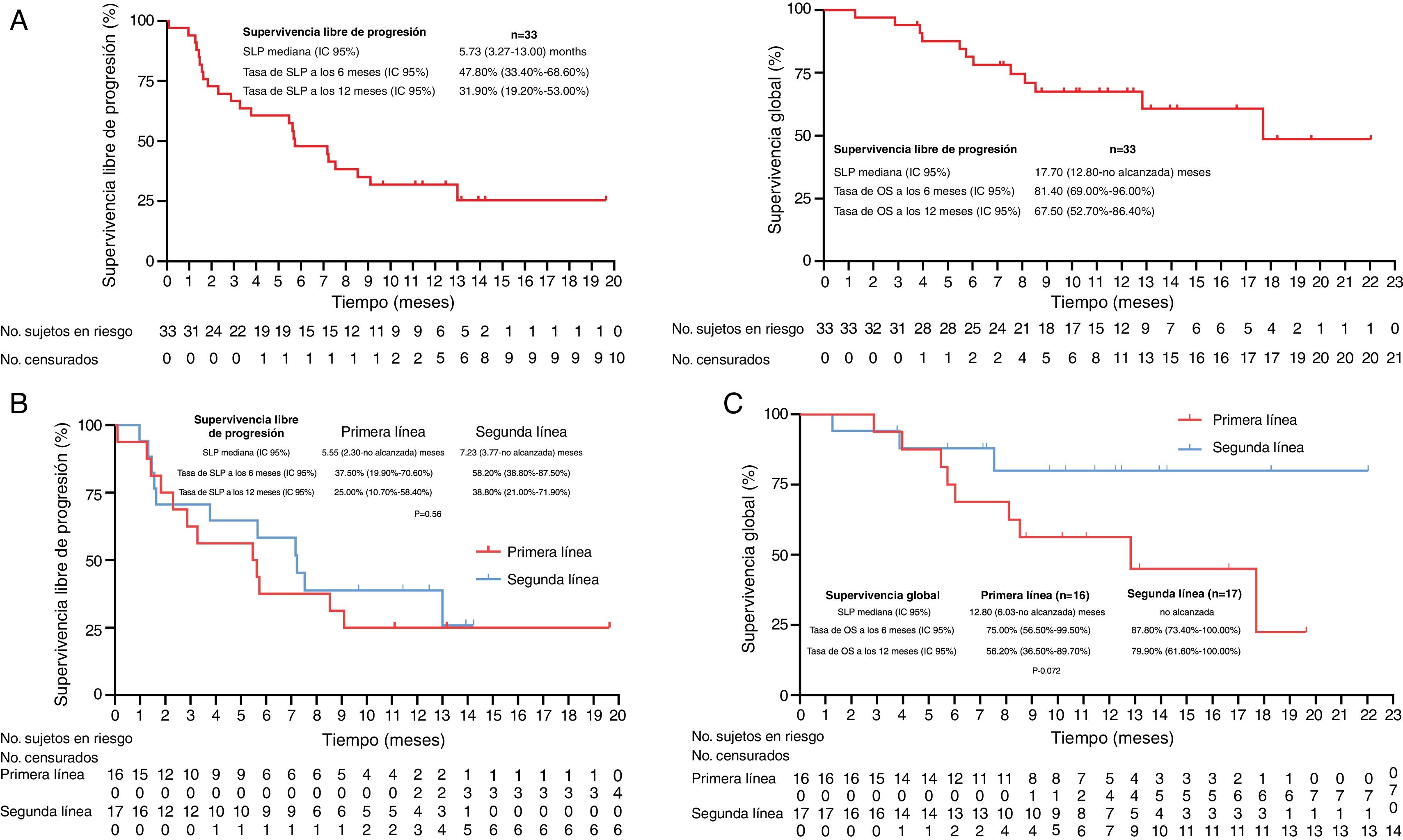
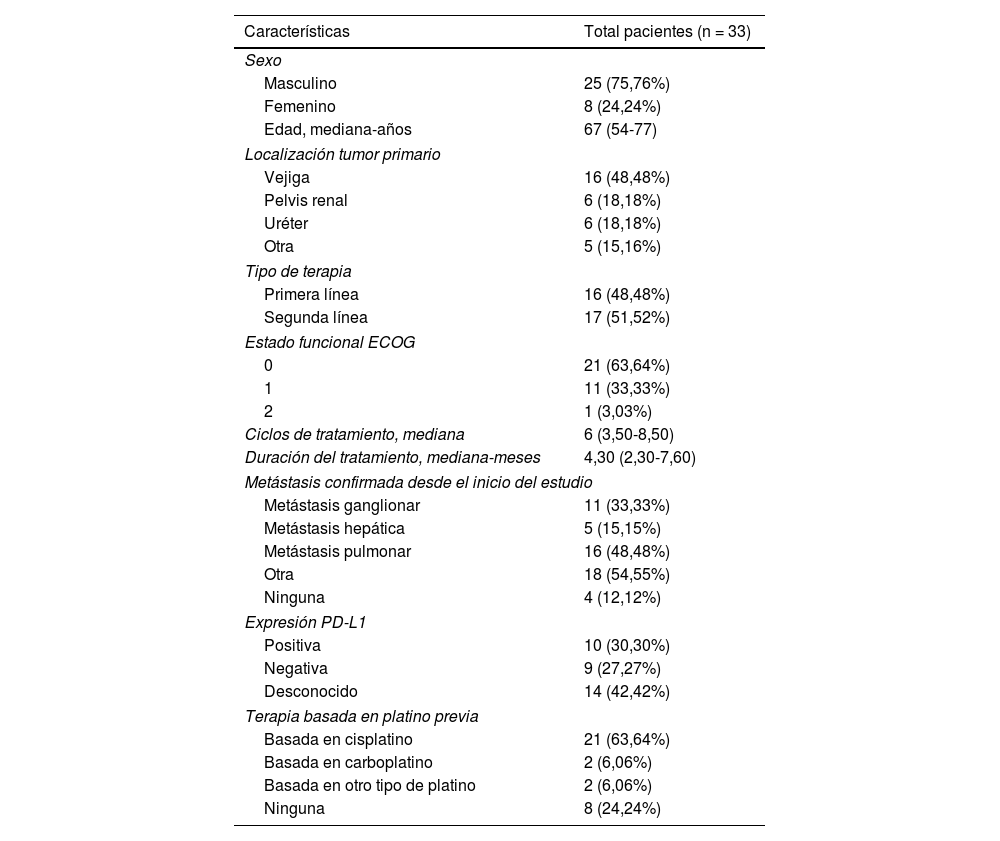
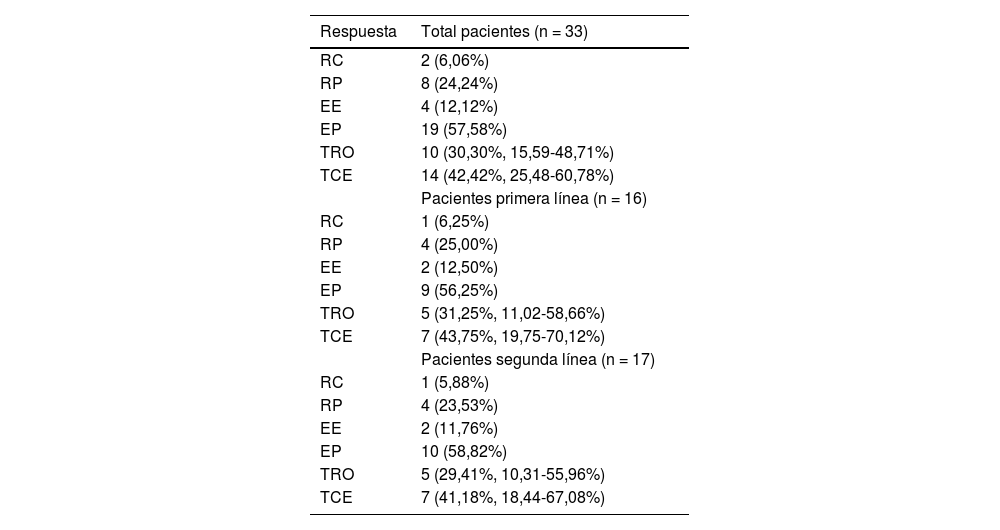
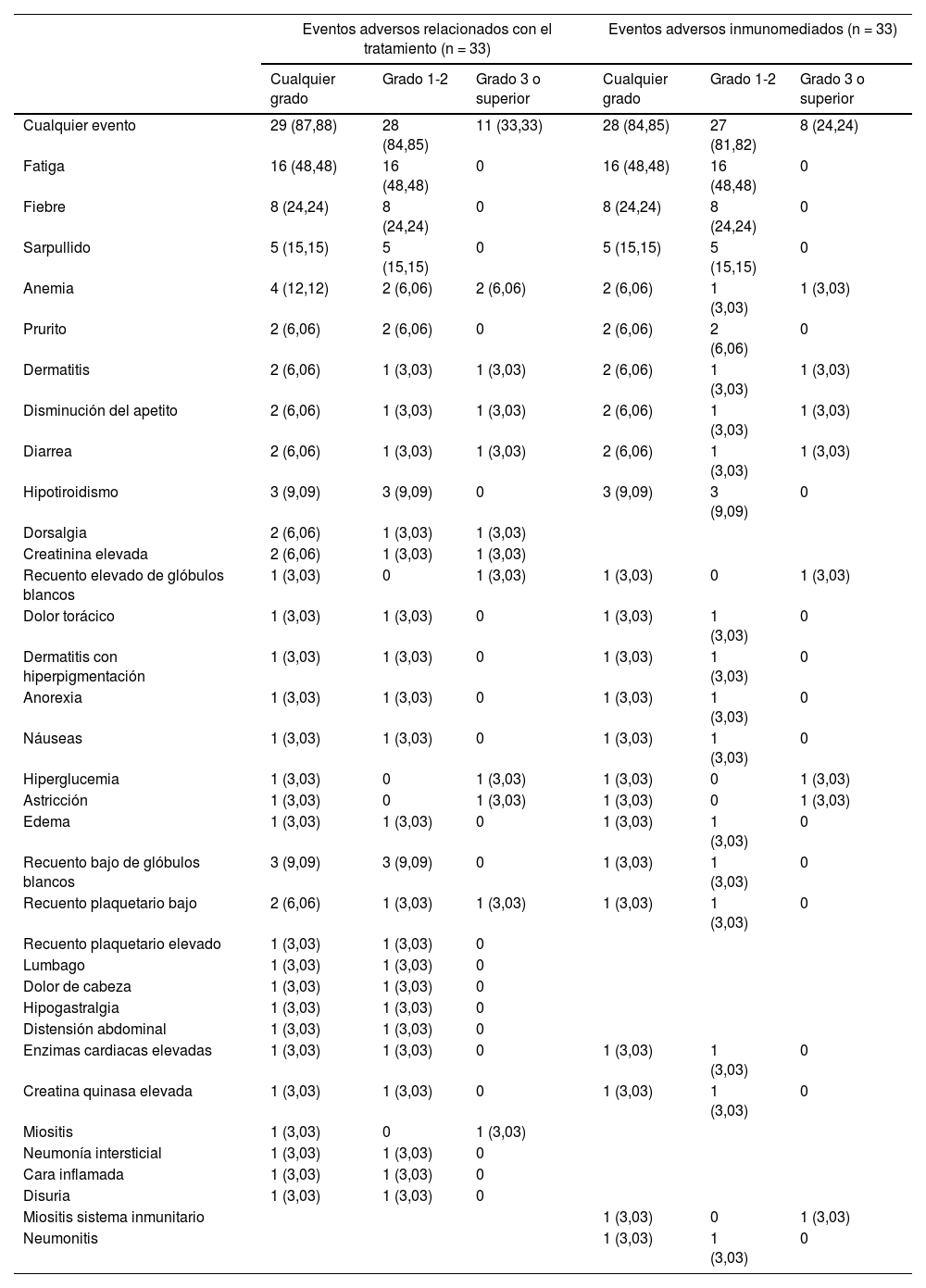
ResultadosUn total de 33 pacientes fueron inscritos entre marzo de 2020 y diciembre de 2022. La mediana de seguimiento fue de 10,17 (RIQ 5,73-12,47) meses. De los 33 pacientes, la TRO y la TCE fueron de 30,30% (IC 95%: 15,6-48,7%) y de 42,42% (IC 95%: 25,48-60,78%), respectivamente. La mediana de SLP fue de 5,73 (IC 95%: 3,27-13,00) meses, con una tasa de SLP a 12 meses de 31,90% (IC 95%: 19,20-53,00%). La mediana de SG fue de 17,7 (IC 95%: 12,80-no alcanzada) meses, con una tasa de SG a 12 meses de 67,50% (IC 95%: 52,70-86,40%); 11 (33,33%) y ocho (24,24%) pacientes experimentaron eventos adversos relacionados con el tratamiento (EAt) y eventos adversos inmunomediados de grado ≥ 3, respectivamente. No se produjo ninguna muerte relacionada con el tratamiento.
ConclusiónLa excelente eficacia y la toxicidad controlable de tislelizumab en el cáncer urotelial localmente avanzado o metastásico sugieren que puede ser una opción terapéutica prometedora para esta población.
Tislelizumab, a monoclonal antibody against programed death protein-1 (PD-1), has shown encouraging antitumor activity in urothelial cancer. This study was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of tislelizumab in urotelial cancer in a real-world setting.
MethodsThe study was a real-world retrospective study undertaken at Liaoning Cancer Hospital & Institute, China. Eligible patients were ≥18 years. Patients received 200-mg tislelizumab monotherapy intravenously every 3 weeks until the disease progressed to intolerable toxicity. Outcomes included an objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and safety.
ResultsBetween March 2020 and December 2022, 33 patients were enrolled. The median follow-up was 10.17 (IQR 5.73-12.47) months. Of all 33 patients, ORR and DCR were 30.30% (95% CI 15.6-48.7%) and 42.42% (95% CI 25.48-60.78%), respectively. The median PFS was 5.73 (95% CI 3.27-13.00) months, with a 12-month PFS rate of 31.90% (95% CI 19.20-53.00%). The median OS was 17.7 (95% CI 12.80-not reach) months, with a 12-month OS rate of 67.50% (95% CI 52.70-86.40%). Eleven (33.33%) and 8 (24.24%) experienced ≥grade 3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and immune-related Aes, respectively. No treatment-related deaths occurred.
ConclusionThe excellent efficacy and controllable safety of tislelizumab in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer suggest that it may be a promising therapeutic option for this population.