Recientemente se ha generalizado el uso del sistema vesical imaging-reporting and data (VI-RADS). Nos propusimos validar el rendimiento diagnóstico del VI-RADS para diferenciar el cáncer vesical músculo-iinvasivo (CVMI) del cáncer vesical no músculo-invasivo (CVNMI) en un contexto de práctica clínica real.
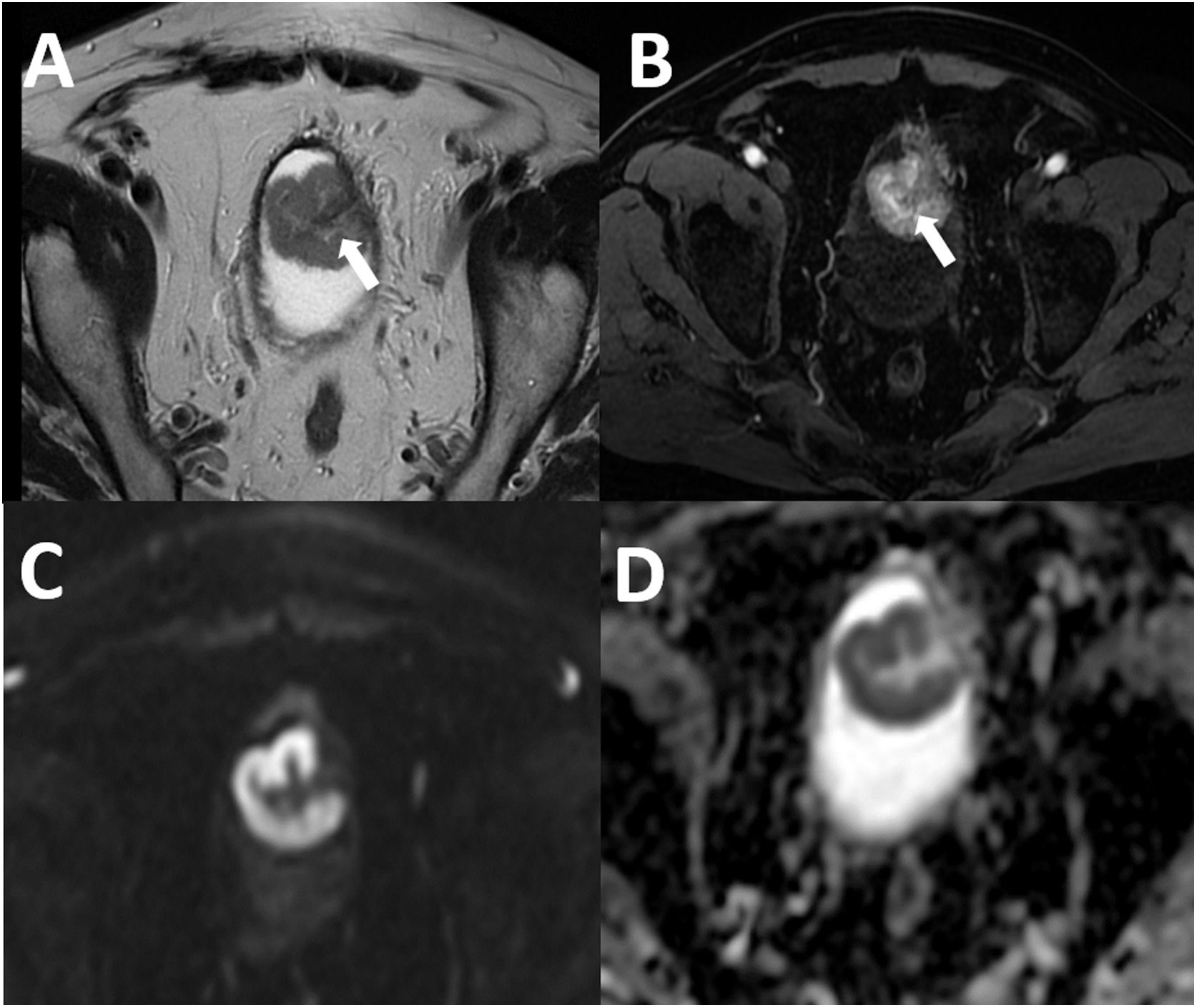
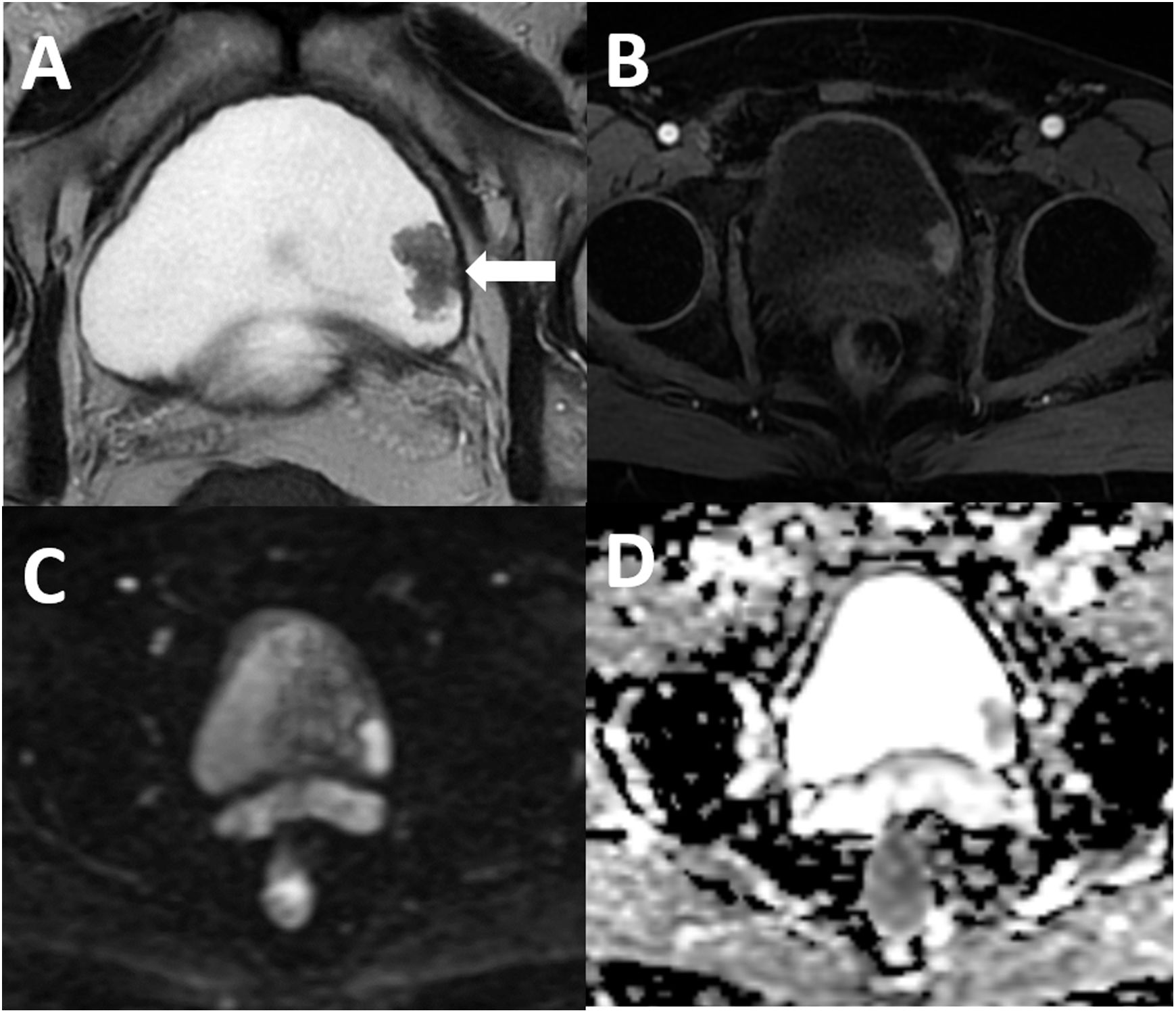
MétodosEntre diciembre de 2019 y febrero de 2022 se revisaron los pacientes con sospecha de cáncer vesical primario. Se incluyeron los pacientes con un protocolo de RM multiparamétrica adecuado para VI-RADS antes de cualquier tratamiento invasivo. La estadificación local de los pacientes se realizó mediante resección transuretral, segunda resección o cistectomía radical como tratamiento de referencia. Dos expertos en radiología genitourinaria cegados a los datos clínicos e histopatológicos evaluaron las imágenes de RM multiparamétrica de forma independiente y retrospectiva. Se analizó el rendimiento diagnóstico de ambos radiólogos y la concordancia entre lectores.
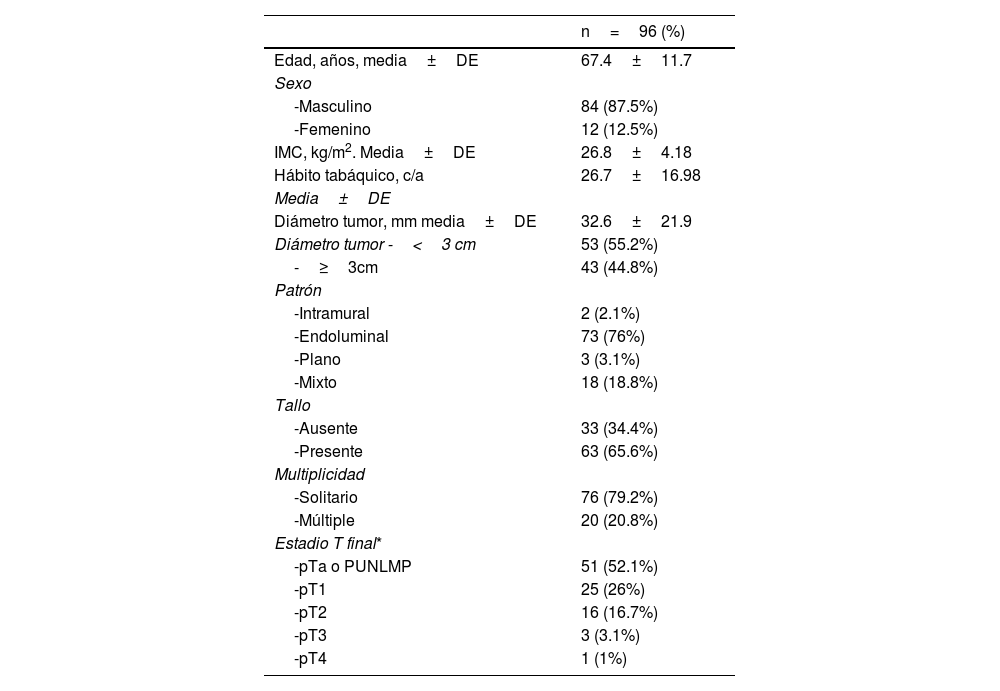
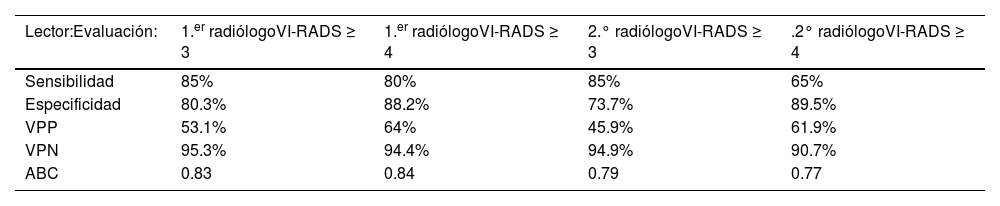
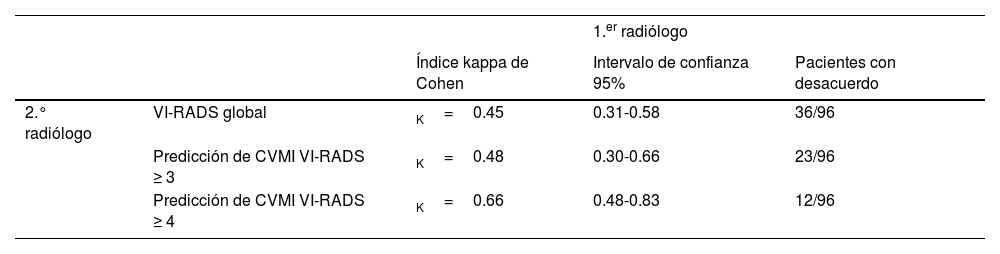
ResultadosDe los 96 pacientes, 20 (20,8%) tenían CVMI y 76 (79,2%) tenían CVNMI. La exactitud diagnóstica del CVMI fue alta para los dos radiólogos. El primer radiólogo tenía un área bajo la curva (ABC) de 0,83 y 0,84, una sensibilidad de 85% y 80% y una especificidad de 80,3% y 88,2% para VI-RADS≥3 y≥4, respectivamente. El segundo radiólogo tenía un área bajo la curva (ABC) de 0,79 y 0,77, una sensibilidad del 85% y el 65% y una especificidad del 73,7% y el 89,5% para VI-RADS≥3 y≥4, respectivamente. La concordancia de la puntuación VI-RADS global entre los dos radiólogos fue moderada (K=0,45).
ConclusiónEl sistema VI-RADS tiene un alto poder diagnóstico para diferenciar el CVMI de CVNMI antes de la resección transuretral. La concordancia entre los radiólogos es moderada.
Preoperative Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) becomes widespread. We aimed to validate the diagnostic performance of VI-RADS in differentiating muscle-invasive (MIBC) from non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) in a real-world setting.
MethodsBetween December 2019 and February 2022 suspected primary bladder cancer patients were reviewed. Those with proper multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) protocol for VI-RADS before any invasive treatment were included. Patients were locally staged according to transurethral resection, second resection, or radical cystectomy as the reference standard. Two experienced genitourinary radiologists who were blinded to clinical and histopathological data evaluated the mpMRI images independently and retrospectively. The diagnostic performance of both radiologists and the interreader agreement were analyzed.
ResultsAmong 96 patients, 20 (20.8%) had MIBC, and 76 (79.2%) had NMIBC. Both radiologists had great diagnostic performance in diagnosing MIBC. The first radiologist had an area under curve (AUC) of 0.83 and 0.84, the sensitivity of 85% and 80%, and the specificity of 80.3% and 88.2% for VI-RADS≥3 and≥4, respectively. The second radiologist had an area under curve (AUC) of 0.79 and 0.77, the sensitivity of 85% and 65%, and the specificity of 73.7% and 89.5% for VI-RADS≥3 and≥4, respectively. The overall VI-RADS score agreement between the two radiologists was moderate (K=0.45).
ConclusionVI-RADS is diagnostically powerful in differentiating MIBC from NMBIC prior to transurethral resection. The agreement between radiologists is moderate.