Journal Information
Vol. 47. Issue 8.
Pages 471-473 (October 2023)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 47. Issue 8.
Pages 471-473 (October 2023)
Editorial
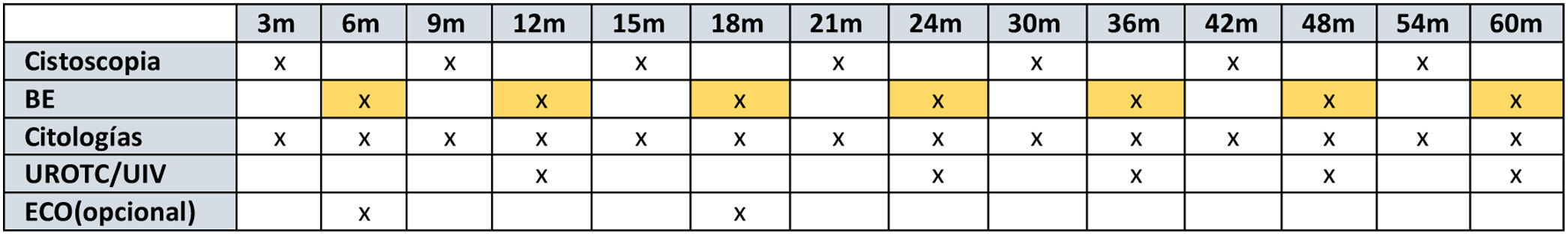
Bladder Epicheck® for surveillance in high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Initial experience and follow-up proposal
Experiencia inicial y propuesta de seguimiento del tumor de vejiga no músculo infiltrante de alto riesgo mediante el uso de Bladder Epicheck®
Visits
23
J. Caño Velasco
, L. Polanco Pujol, J.C. Moreno Cortés, A. Lafuente Puentedura, C. Hernández Fernández
Corresponding author
Servicio de Urología, Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, Spain
This item has received
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Actas Urológicas Españolas (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail