To evaluate the outcomes of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) compared to those of open (ORP) and laparoscopic (LRP) surgery. The interest lies fundamentally in the quality-of-life (QoL) evaluation, postoperative recovery, and personal satisfaction of patients with the intervention (PS) beyond oncological and functional outcomes.
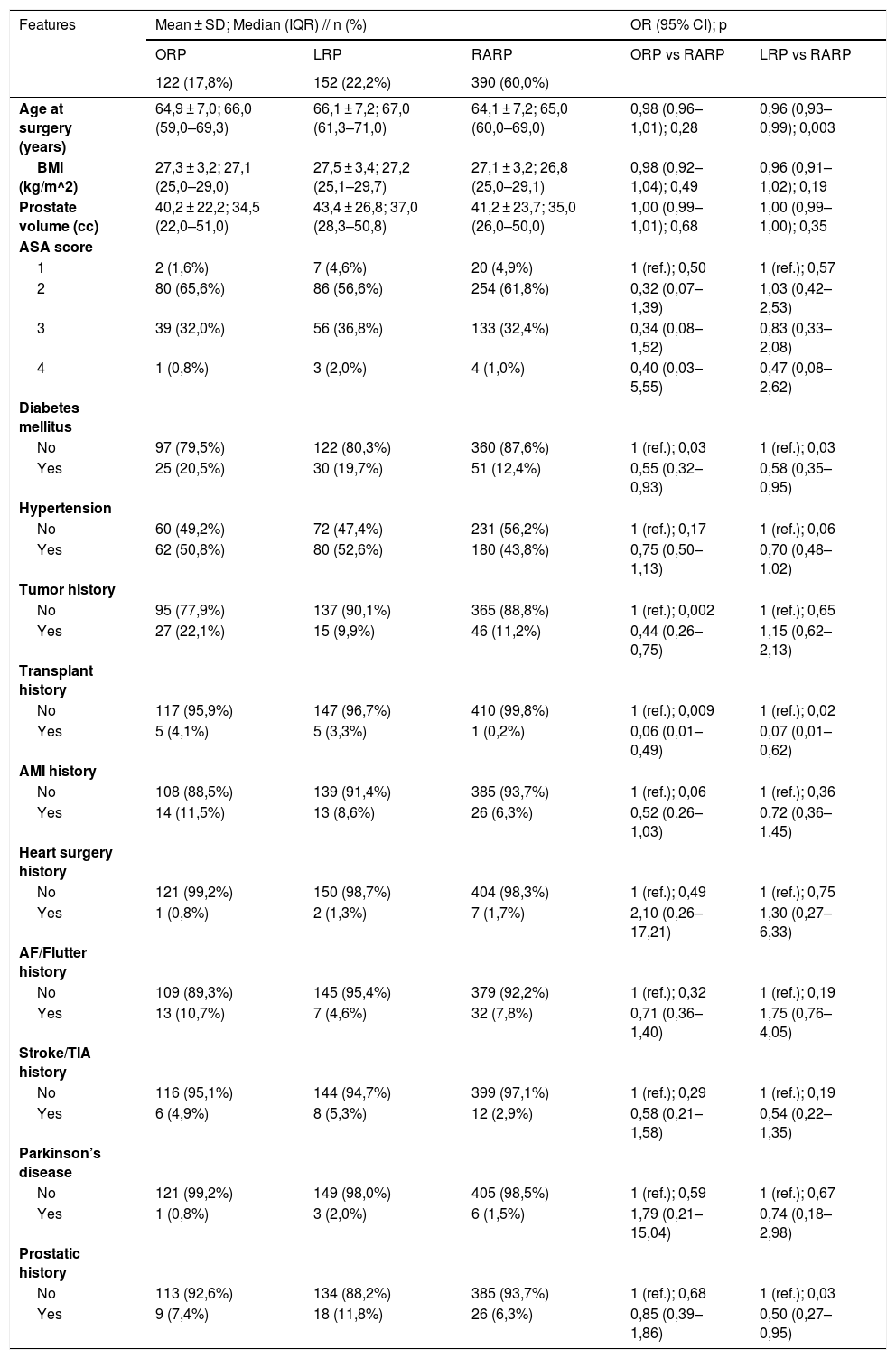
MethodsSix hundred eighty-five RPs were performed in our center between 2011–2018 (17,8% ORP, 22,2% LRP and 60% RARP). Patients were prospectively assessed through follow-up until April 2020 and a multiple questionnaire at 12-months post-RP that included ICIQ-SF, SHIM, IPSS, IQL and questions about pain, postoperative recovery and PS. Also baseline and postoperative patient- and treatment-related data were collected, and binomial logistic regressions were performed for the 1 vs.1 comparisons (ORP vs. RARP and LRP vs. RARP).
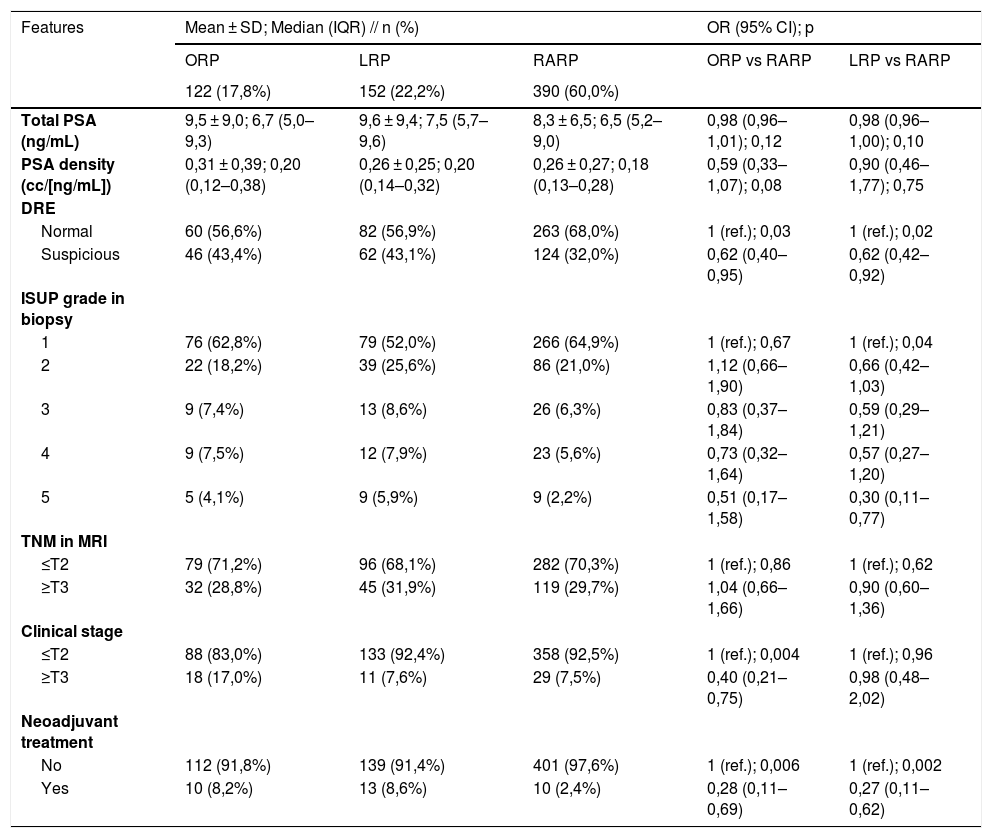
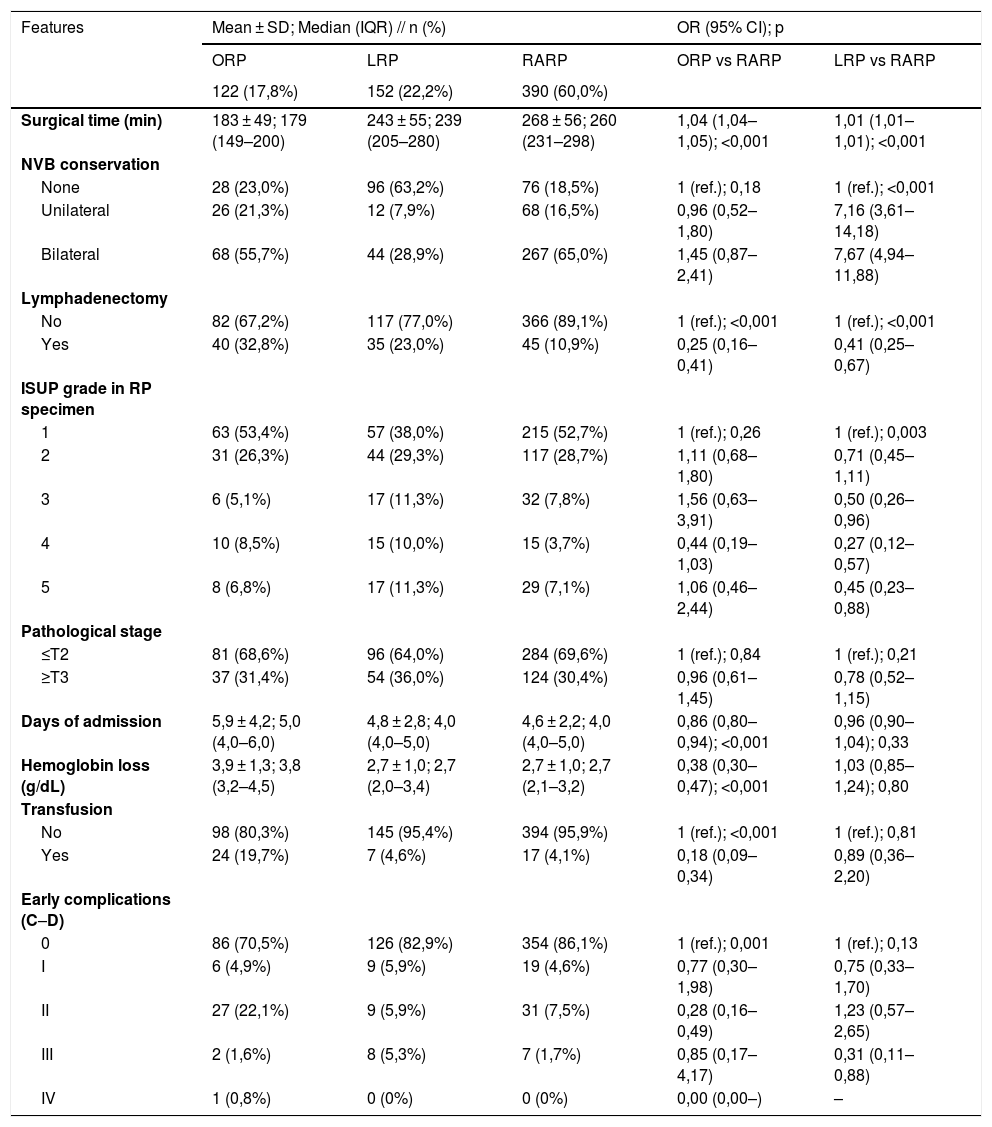
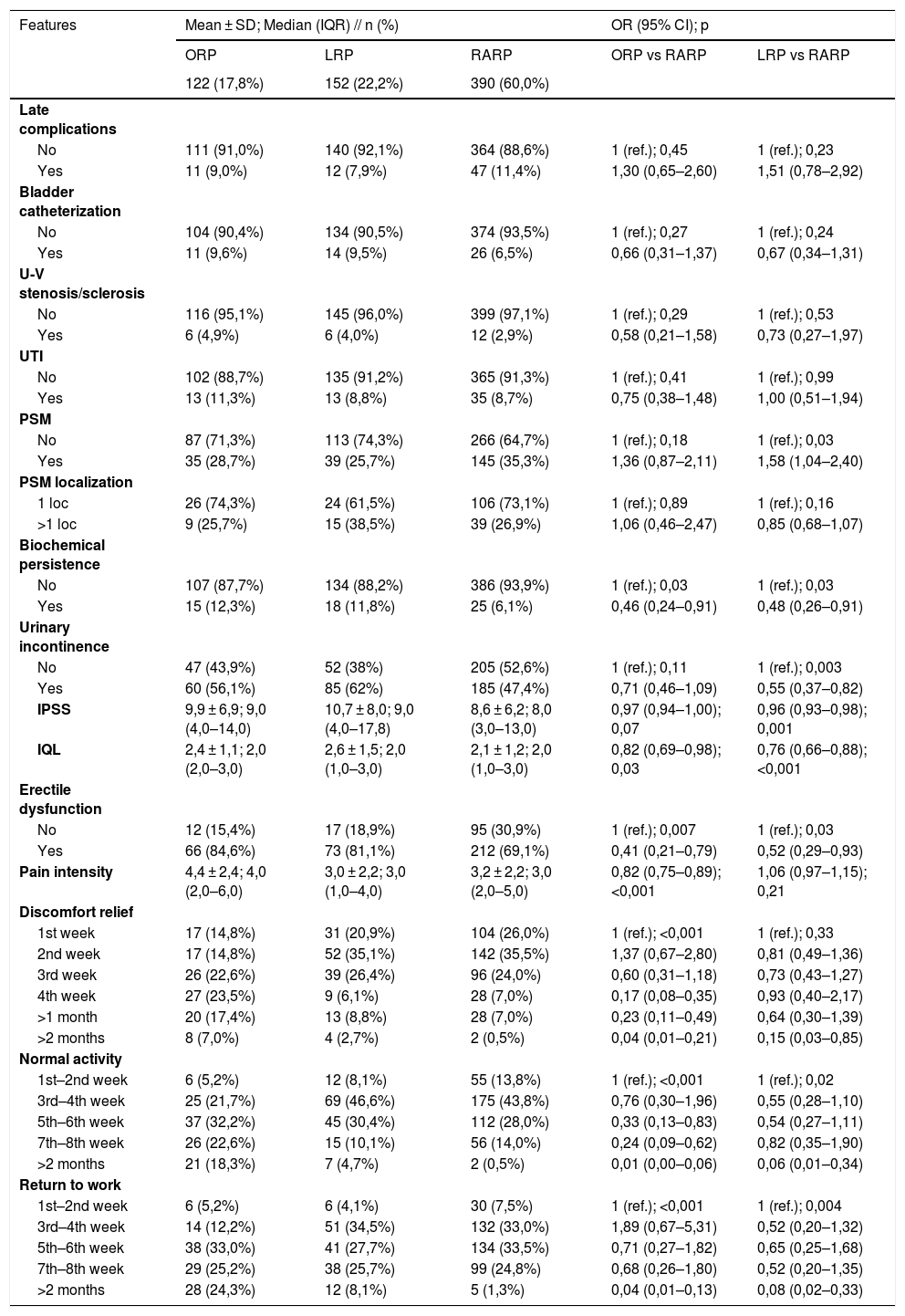
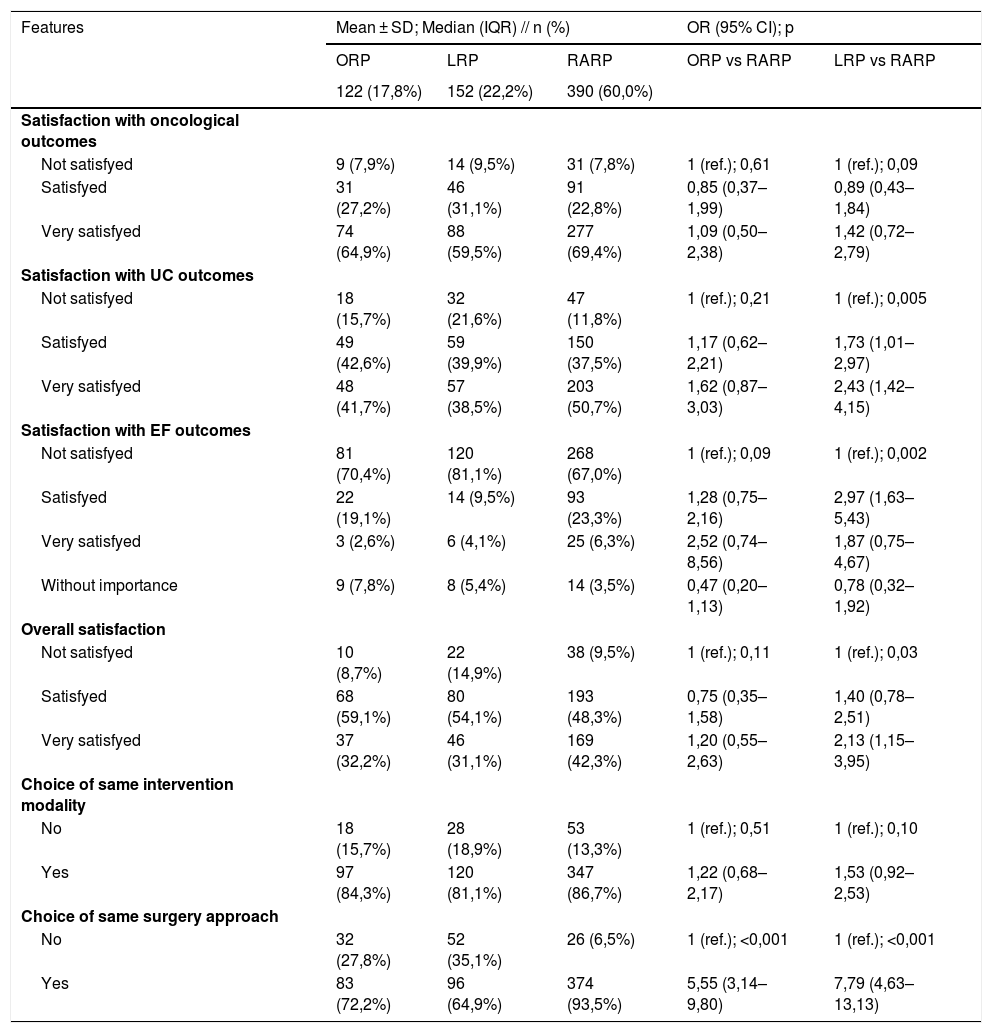
ResultsRARP patients have overall fewer comorbidities, less tumor aggressiveness, more operative time requirements and more positive surgical margins than ORP and LRP patients. Nevertheless, RARP outperforms ORP in: hospital stay (days) (OR 0,86; 95% CI: 0,80–0,94), hemoglobin loss (OR 0,38; 95% CI: 0,30–0,47), transfusion rate (OR 0,18; 95% CI: 0,09–0,34), early complications (p = 0,001), IQL (OR 0,82; 95% CI: 0,69–0,98), erectile function (OR 0,41; 95% CI: 0,21–0,79), pain control (OR 0,82; 95% CI: 0,75–0,89), postoperative recovery (p < 0,001) and choice of a different approach (OR 5,55; 95% CI: 3,14–9,80). RARP is superior to LRP in: urinary continence (OR 0,55; 95% CI: 0,37–0,82), IPSS (OR 0,96; 95% CI: 0,93–0,98), IQL (OR 0,76; 95% CI: 0,66–0,88), erectile function (OR 0,52; 95% CI: 0,29–0,93), postoperative recovery (p = 0,02 and 0,004), PS (p = 0,005; 0,002; and 0,03) and choice of a different approach (OR 7,79; 95% CI: 4,63–13,13).
ConclusionsThe findings of our study globally endorse a positive effectiveness of RARP over ORP and/or LRP, both on functional issues, postoperative recovery, QoL and PS. Oncologic results should still be improved.
Evaluar los resultados de la prostatectomía radical asistida por robot (PRAR), y compararlos con los de la cirugía abierta (PRA) y laparoscópica (PRL). El interés no sólo radica en los resultados oncológicos y funcionales de la serie, sino en la evaluación de la calidad de vida (QoL), la recuperación postoperatoria, y la satisfacción personal de los pacientes con la intervención (PR), fundamentalmente.
MétodosSe realizaron 685 PR en nuestro centro entre 2011–2018 (17,8% PRA, 22,2% PRL y 60% PRAR). Los pacientes fueron evaluados prospectivamente mediante seguimiento hasta abril de 2020, y con la realización un cuestionario múltiple a los 12 meses post-PR, que incluía ICIQ-SF, SHIM, IPSS, IQL y preguntas sobre el dolor, la recuperación postoperatoria y la satisfacción del paciente (SP). También se recogieron datos basales y postoperatorios relacionados con el paciente y el tratamiento, y se realizaron regresiones logísticas binomiales para las comparaciones 1 vs. 1 (PRA vs. PRAR y PRL vs. PRAR).
ResultadosLos pacientes tratados con PRAR tienen en general menos comorbilidades, menos agresividad tumoral, un requerimiento de mayor tiempo operatorio y un numero mayor de márgenes quirúrgicos positivos que los pacientes tratados con PRA y PRL. Sin embargo, la PRAR supera a la PRA en: días de estancia hospitalaria (OR 0,86; IC 95%: 0,80–0,94), disminución de hemoglobina (OR 0,38; IC 95%: 0,30–0,47), tasas de transfusión (OR 0,18; IC 95%: 0,09–0,34), complicaciones tempranas (p = 0,001), IQL (OR 0,82; IC 95%: 0,69–0,98), función eréctil (OR 0,41; IC 95%: 0,21–0,79), manejo del dolor (OR 0,82; IC 95%: 0,75–0,89), recuperación postoperatoria (p < 0,001) y elección de un abordaje diferente (OR 5,55; IC 95%: 3,14–9,80). La PRAR es superior a la PRL en: continencia urinaria (OR 0,55; IC 95%: 0,37–0,82), IPSS (OR 0,96; IC 95%: 0,93–0,98), IQL (OR 0,76; IC 95%: 0,66–0,88), función eréctil (OR 0,52; IC 95%: 0,29–0,93), recuperación postquirúrgica (p = 0,02 y 0,004), PS (p = 0,005; 0,002; y 0,03) y elección de un abordaje diferente (OR 7,79; IC 95%: 4,63–13,13).
ConclusionesLos hallazgos de nuestro estudio respaldan la efectividad de la PRAR sobre la PRL y/o la PRA de manera global, tanto en factores funcionales, como en la recuperación postoperatoria, la QoL y la PS. Los resultados oncológicos aún deben ser mejorados.