The clinical symptoms in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) are directly proportional to prostate volume. We aimed to show whom and when to intervene in a noninvasive way, correlating the patient's subjective symptoms with objective diagnostic tools.
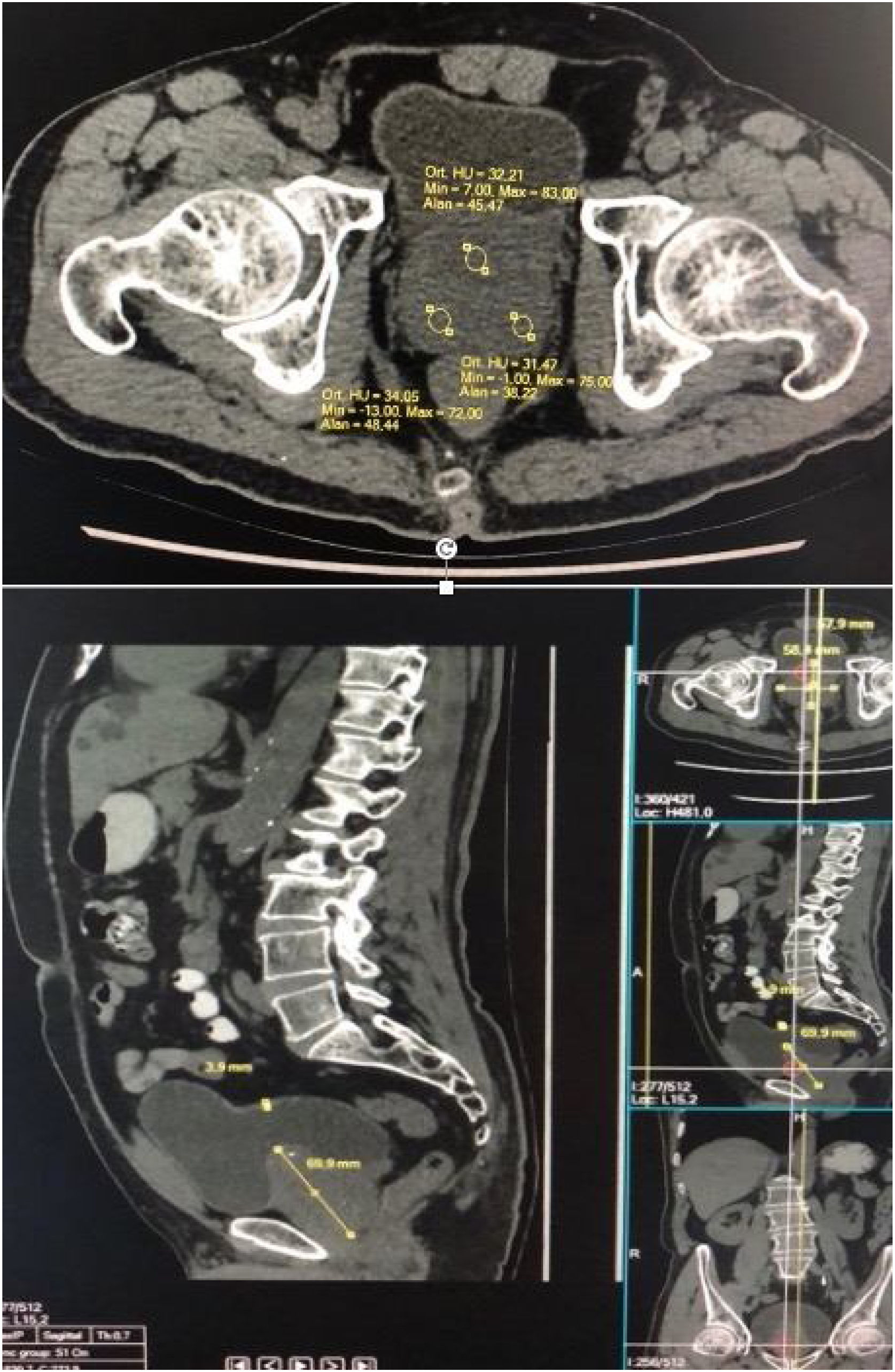
Material and methodInternational Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) was evaluated in patients who consulted the urology outpatient clinic for the first time with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Subsequently, PSA, urea, creatinine, complete urinalysis, uroflowmetry, urinary tract ultrasound and non-contrast lower abdominal computed tomography (CT) examinations were requested. Prostate central (transitional zone) zone and peripheral zone HU scores, prostatic urethral length and bladder wall Hounsfield units (HU) scores were recorded by using computed tomography (CT). The ellipsoid formula was used for ultrasonographic and tomographic measurements of prostate size (anteroposterior diameter × transverse diameter × longitudinal diameter × 0.52).
ResultsA statistically significant negative correlation was found between the prostate peripheral zone/central zone HU ratio and the maximum flow rate measured in the uroflowmetry test.
ConclusionThis is the first study in the literature to evaluate the correlation between voiding parameters such as Qmax, Qave and IPSS scores, and prostate and bladder wall HU scores obtained by computed tomography examination in BPH patients. A significant relationship has been detected between the peripheral zone/central zone HU ratio and Q max. Additional studies with larger patient populations could better clarify the contribution of HU in the diagnosis of BPH and treatment decision making of these patients.
Los síntomas clínicos en la hiperplasia prostática benigna (HBP) son directamente proporcionales al volumen de la próstata. Nuestro objetivo es definir el tipo de paciente que debe ser intervenido de forma no invasiva, así como el momento idóneo para esta intervención, correlacionando los síntomas subjetivos del paciente con las herramientas objetivas de diagnóstico.
Material y métodoSe utilizó el cuestionario International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) en los pacientes que acudieron por primera vez a la consulta externa de urología con síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI). A continuación, se solicitaron niveles de PSA, urea, creatinina, análisis de orina completos, uroflujometría, ecografía del tracto urinario y tomografía computarizada (TC) abdominal inferior sin contraste. Se registraron los valores de UH de la zona central (zona de transición) y de la zona periférica de la próstata, la longitud de la uretra prostática y los valores de UH de la pared vesical mediante tomografía computarizada (TC). Se utilizó la fórmula del elipsoide para las mediciones ultrasonográficas y tomográficas del tamaño de la próstata (diámetro anteroposterior × diámetro transversal × diámetro longitudinal × 0,52).
ResultadosSe halló una correlación negativa estadísticamente significativa entre la proporción de UH de la zona periférica de la próstata/zona central y el flujo máximo medido en la uroflujometría.
ConclusiónEste es el primer estudio de la literatura en evaluar la correlación entre los parámetros miccionales, como las puntuaciones de Qmax, Qave e IPSS, y las puntuaciones de UH de la próstata y la pared vesical obtenidas mediante tomografía computarizada en pacientes con HBP. Se ha detectado una relación significativa entre la proporción de UH de la zona periférica/zona central y Q máx. Estudios adicionales con poblaciones de pacientes más amplias podrían arrojar más luz sobre la contribución de las UH en el diagnóstico de la HBP y las decisiones del tratamiento de estos pacientes.