Inflammatory markers have prognostic value in various tumors due to the role of inflammatory phenomena at different stages of tumor development. The aim of this study is to demonstrate the prognostic value of these markers, as well as other clinical and analytical variables in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
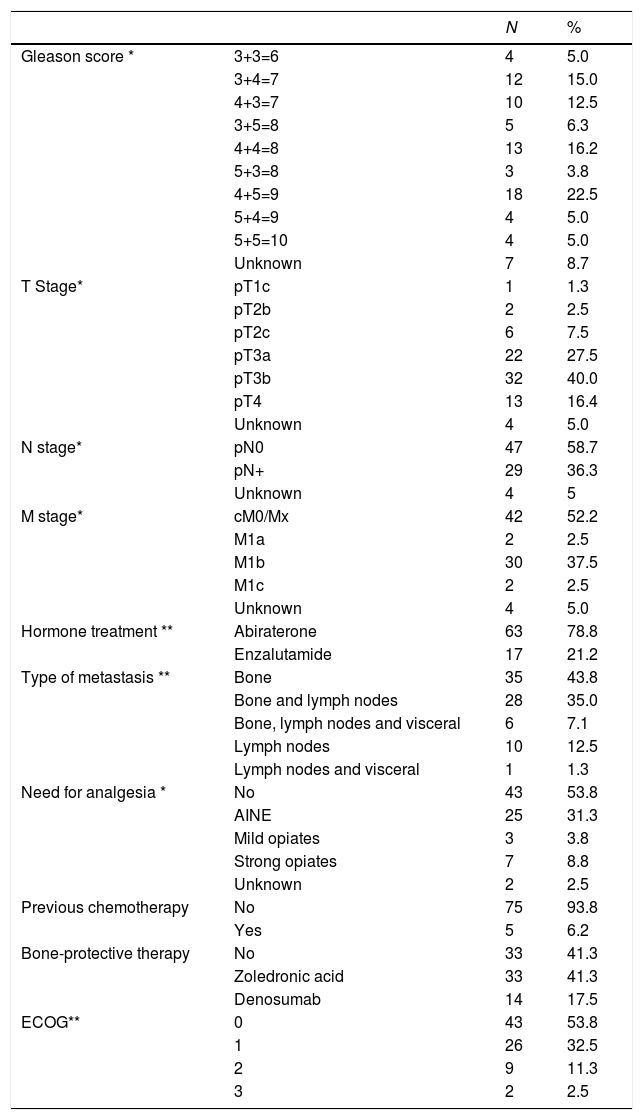
Material and methodsProspective cohort study carried out on 80 patients diagnosed with mCRPC. Clinical and analytical data were collected, and the following inflammatory markers were estimated: Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC), Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Total Platelet Count (TPC), Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Lymphocyte-Monocyte Ratio (LMR) and Systemic Inflammation Index (SII). The values of albumin, hemoglobin (Hb), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were also determined.
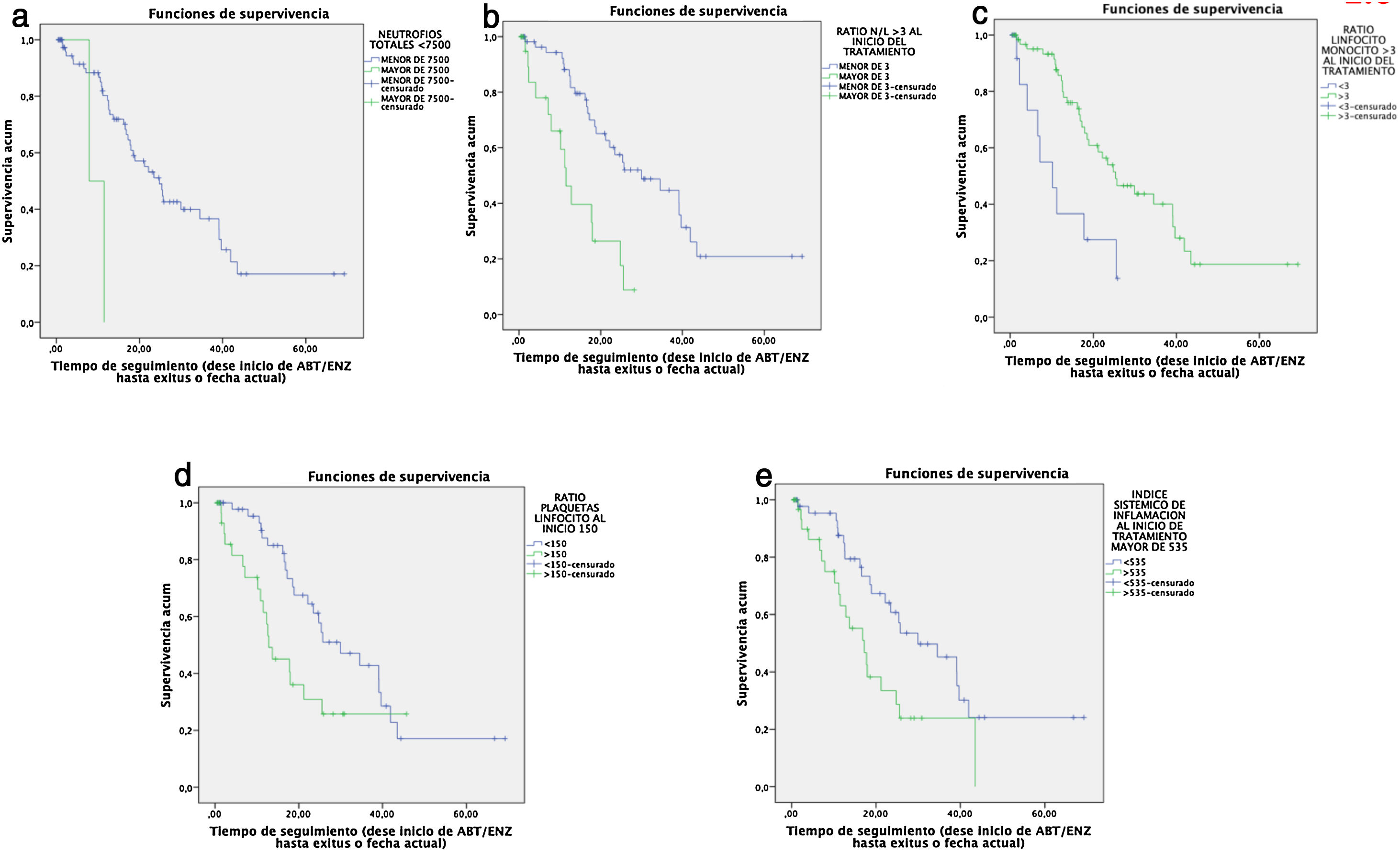
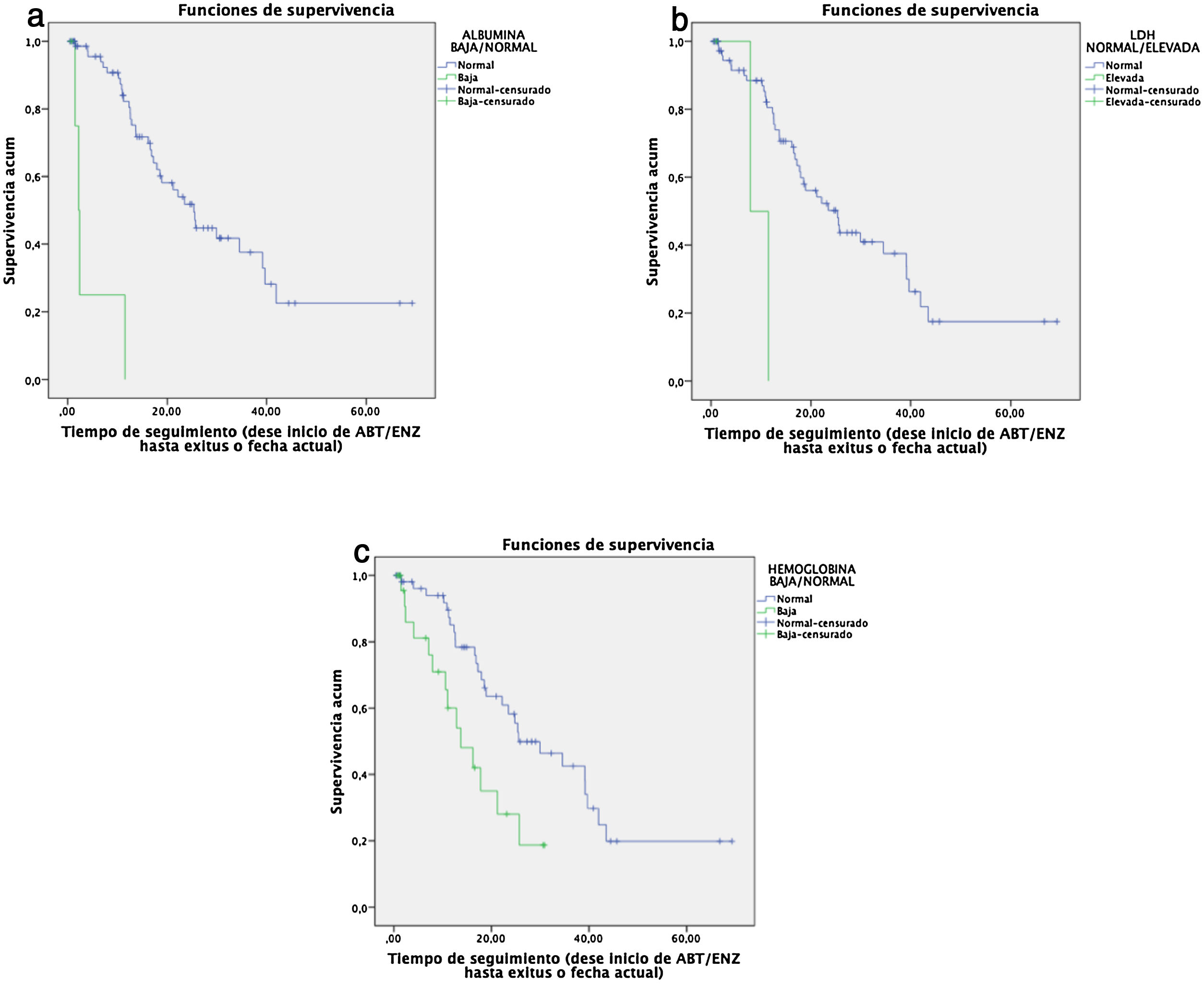
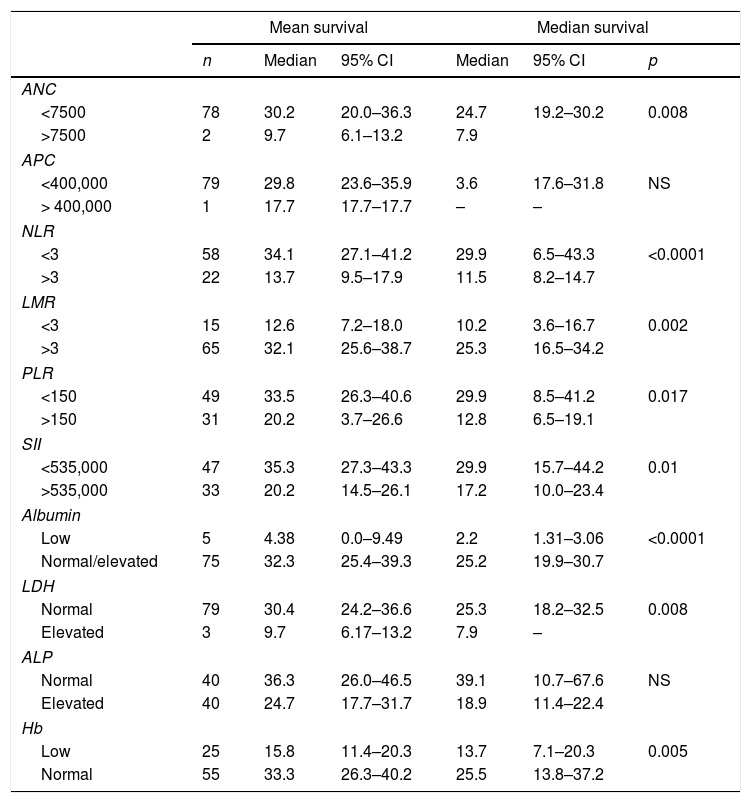
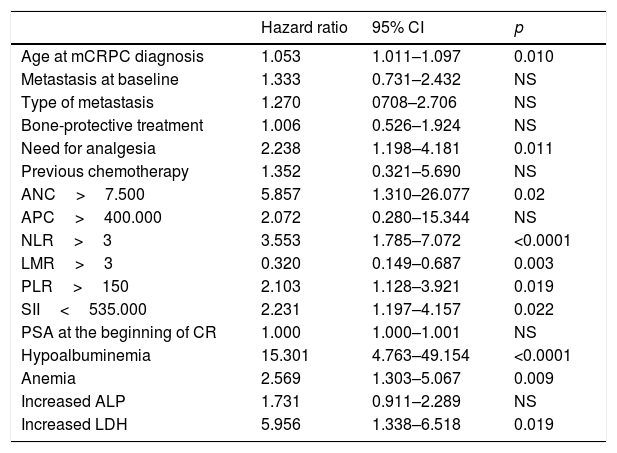
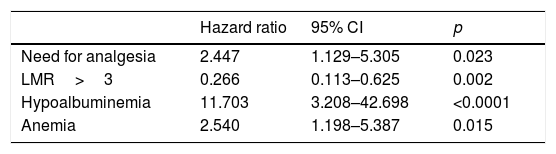
ResultsPatients with ANC>7500, NLR>3, PLR>150, LMR>3 and/or SII>535,000, presented significantly lower median survival time than the remaining patients, and TPC was the only marker which did not show a significant association. Moreover, NLR, PLR and SII were inversely correlated with survival time. Patients with hypoalbuminemia, anemia, and elevated LDH values had significantly lower median survival time. Albumin and hemoglobin were directly correlated to overall survival time. The need for analgesia was also associated with shorter survival.
ConclusionThe values of certain inflammatory markers are associated with shorter survival time in patients with mCRPC, and their use in clinical practice can be considered to evaluate the prognosis and estimate survival.
Los marcadores inflamatorios tienen valor pronóstico en diferentes tumores por la intervención de los fenómenos inflamatorios de las diferentes etapas del desarrollo tumoral. El objetivo de este estudio es demostrar el valor pronóstico de estos marcadores, así como de otras variables clínicas y analíticas en pacientes con cáncer de próstata metastásico resistente a la castración (CPRCm).
Material y métodosEstudio de cohortes prospectivo realizado en 80 pacientes diagnosticados de CPRCm. Se recogieron datos clínicos y analíticos, estimándose los siguientes marcadores inflamatorios: recuento total de neutrófilos (RTN), ratio neutrófilo/linfocito (RN/L), recuento total de plaquetas (RTP), ratio plaquetas/linfocito (RP/L), ratio linfocito/monocito (RL/M) e índice sistémico de inflamación (ISI). igualmente se determinaron los valores de albúmina, hemoglobina (Hb), fosfatasa alcalina (FA) y lactato deshidrogenasa (LDH).
ResultadosLos pacientes con RTN>7500, RN/L>3, RP/L>150, RL/M>3 y/o ISI>535.000, presentaron una mediana de supervivencia significativamente menores que el resto de pacientes, siendo el RTP el único marcador que no mostró asociación significativa. Además, la RN/L, RP/L y el ISI se correlacionaron inversamente con el tiempo de supervivencia. Los pacientes con hipoalbuminemia, anemia y valores elevados de LDH presentaron medianas de supervivencia significativamente menores. La albumina y la hemoglobina presentaron a su vez una correlación directa con el tiempo total de supervivencia. La necesidad de analgesia también se asoció con una menor supervivencia.
ConclusiónLos valores de determinados marcadores inflamatorios se asocian con menor supervivencia en pacientes con CPRCm, pudiendo considerarse su uso en la práctica clínica para evaluar el pronóstico y estimar la supervivencia.