Clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) and anticholinergic drugs are the mainstay treatment for neuropathic bladder (NB). However, there is not consensus about the time therapy should be started in pediatric patients.
AimTo analyze the impact of early start (first year of life) of CIC and anticholinergic treatment on long-term renal and bladder function. Our hypothesis is that those children who start conservative treatment in the first year of life have better outcome in terms of bladder and renal function and less need of surgical procedures, compared to those who started treatment later in life.
Patients and methodRetrospective study of pediatric patients with NB treated in our hospital (1995–2005) dividing them for comparison in two groups: group 1 started treatment in the first year of life and group 2 between 1 and 5 years old. Collected data included: date of CIC and anticholinergic initiation, presence of VUR or UHN, renal function, UTIs, renal scars, bladder behavior, surgery and urinary continence.
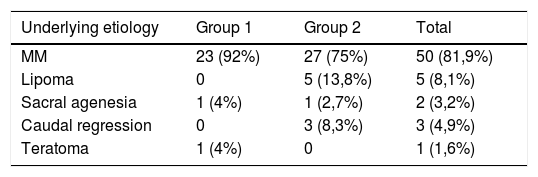
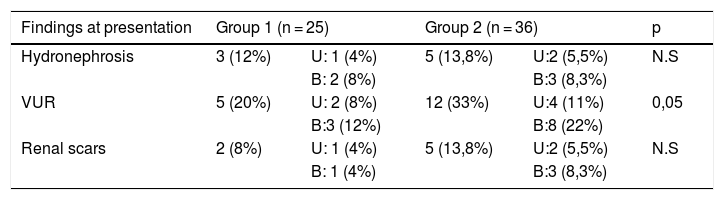
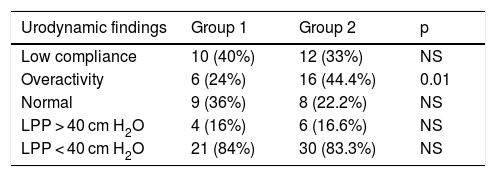
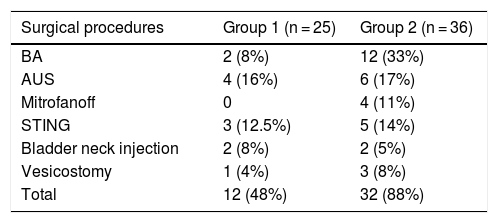
ResultsSixty-one patients were included, 25 in group 1 and 36 in group 2. Initially vesico-ureteral reflux (VUR) and overactive bladders were more frequent in group 2. In group 1 one overactive bladder changed to low compliant and in group 2, one normal bladder and 4 overactive bladders changed. At the end of follow-up there were 11 low compliant bladders in group 1 and 17 in group 2. However, in group 1, only 2 patients required bladder augmentation (BA) while in group 2, 12 patients needed it. At the end of the study only 2 patients in group 2 had slight renal insufficiency.
ConclusionsPatients who started conservative treatment in the first year of life have better long-term outcome in terms of UTI, renal scars and surgical procedures. Even if they initially had low compliant bladders, these patients require less BA.
El cateterismo limpio intermitente (CI) y el tratamiento anticolinérgico son la base del tratamiento conservador de la vejiga neuropática (VN); sin embargo, todavía no hay acuerdo sobre la edad a la que debería iniciarse dicha terapia.
ObjetivoEl objetivo de nuestro estudio fue analizar la influencia del inicio precoz (primer año de vida) del tratamiento anticolinérgico y el CI en la evolución a largo plazo de la función renal y vesical. Nuestra hipótesis es que los niños que iniciaron el tratamiento conservador en el primer año de vida tienen mejor pronóstico en términos de función renal y vesical, así como menos necesidad de tratamiento quirúrgico que aquellos que iniciaron el tratamiento a edades más avanzadas.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio retrospectivo de los pacientes con VN tratados en nuestro servicio (1995–2005) dividiéndolos para su comparación en dos grupos: grupo 1 incluye a aquellos que iniciaron el tratamiento conservador en el primera año de vida, y grupo 2, a aquellos que lo iniciaron entre el primer y el quinto año. Se revisaron las historias clínicas recogiendo datos sobre: edad de inicio del CI y tratamiento anticolinérgico, presencia de reflujo vésico-ureteral (RVU) o ureterohidronefrosis (UHN), función renal, presencia de cicatrices renales, infección del tracto urinario (UTI), presencia de cicatrices renales, comportamiento vesical, necesidad de intervención quirúrgica y continencia urinaria.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 61 pacientes: 25 en el grupo 1 y 36 en el grupo 2. Al inicio del estudio, la presencia de RVU e hiperactividad vesical eran más frecuentes en el grupo 2. En el grupo 1, un paciente con vejiga hiperactiva cambió a vejiga de baja acomodación, y en el grupo 2 un paciente con vejiga de acomodación normal y 4 con vejigas hiperactivas cambiaron a vejigas de baja acomodación. Al final del seguimiento, 11 pacientes del grupo 1 y 17 del grupo 2 tenían vejigas de baja acomodación; sin embargo, en el grupo 1 sólo dos pacientes precisaron una ampliación vesical (BA) y en el grupo 2 la precisaron 12 pacientes. Al final del estudio, solo dos pacientes del grupo 2 tenían una insuficiencia renal leve.
ConclusionSin pacientes que iniciaron el tratamiento conservador en el primer año de vida tienen mejor pronóstico a largo plazo en cuanto a la presencia de infecciones, cicatrices renales o necesidad de intervención quirúrgica. Incluso aquellos pacientes que inicialmente presentaban vejigas de baja acomodación tienen menor necesidad de ampliación vesical.