The optical trocar access (OTA) is a modified closed technique that aims to minimize the risk of vascular or bowel injuries while reducing the likelihood of gas leakage. A learning curve (LC) effect for OTA has been invoked with n = 30 procedures being considered as a threshold to define expertise. We aim to evaluate the impact of the LC within the first thirty cases of OTA performed by a trainee.
MethodsThis is a prospective randomized study on 60 patients elected to laparoscopic gynecological surgery. Patients were randomized to have OTA insertion by a junior surgeon or by an expert. LC was evaluated by: 1) insertion time; number of: 2) corrections by the senior; 3) times the tip of the trocar stopped in the preperitoneal layer; 4) mistakes of skin incision; 5) times the tip of the trocar ends under the omentum; 6) complications. To analyze the LC within the first 30 cases, procedures were stratified in 3 groups (cases 1−10; 11−20; 21−30) for both trainee and expert and LC variables were compared.
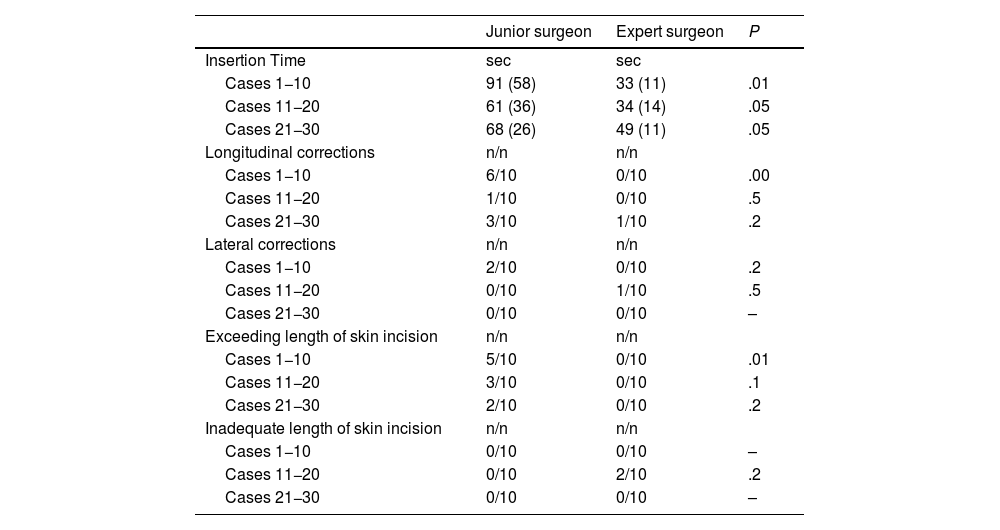
ResultsOverall, mean OTA insertion time was 56 s. No major intra- and post-operative complications were recorded. Mean insertion time was statistically significantly longer for the trainee compared to the expert within the first 10 cases (91 vs 33 s respectively, P = .01). For cases 11−20 and 21−30, time advantage of the senior surgeon is less evident (P = .05). The number of times the tip of the trocar stopped in the preperitoneal layer was similar between groups, as well as times the tip of the trocar ends under the omentum.
ConclusionsOTA is a fast and simple way to achieve the pneumoperitoneum and first trocar insertion as a single step. The current series confirms the effectiveness of the technique since the beginning of the LC.
El acceso con trocar óptico (ATO) es una técnica modificada de laparoscopia cerrada cuyo objetivo es minimizar el riesgo de lesiones vasculares o intestinales y reducir la posible fuga de gas. Se ha analizado el efecto de la curva de aprendizaje (CA) para el ATO, considerando n = 30 procedimientos como umbral para definir un nivel aceptable de experticia. Nuestro objetivo es evaluar el impacto de la CA en los primeros treinta casos de ATO realizados por un aprendiz.
MétodosSe trata de un estudio prospectivo aleatorizado en 60 pacientes planificadas para cirugía ginecológica laparoscópica. Las pacientes fueron seleccionadas aleatoriamente para el ATO realizado por un cirujano sin entrenamiento previo en la técnica o por un cirujano experto. La CA se evaluó mediante: 1) tiempo hasta lograr el acceso; 2) número de correcciones hechas por el experto; 3) número de veces en que la punta del trocar se detuvo en la capa preperitoneal; 4) errores al realizar la incisión en la piel; 5) veces en que la punta del trocar termina bajo el epiplón; 6) complicaciones. Para analizar el CA en los 30 primeros casos, se estratificaron los procedimientos en 3 grupos (casos 1−10; 11−20; 21−30) tanto para el aprendiz como para el experto y se compararon las variables de la CA.
ResultadosDe forma global, el tiempo medio de inserción para el ATO fue de 56 segundos. No se registraron complicaciones intraoperatorias ni postoperatorias graves. El tiempo medio de inserción fue estadísticamente más largo para el aprendiz en comparación con el experto en los 10 primeros casos (91 s frente a 33 s respectivamente, P =,01). En los casos 11−20 y 21−30, la ventaja de tiempo del cirujano experto se hizo menos evidente (P =,05). El número de veces que la punta del trocar se detuvo en la capa preperitoneal fue similar entre los grupos, así como las veces que la punta del trocar llegó por debajo del epiplón.
ConclusionesLa técnica de ATO es rápida y reproducible para realizar el neumoperitoneo y la inserción del primer trocar en un solo paso. La serie actual confirma la eficacia de la técnica desde el inicio de la CA.