Daily practice requires quick, simple and accessible methods to appropriately assess the urinary excretion of solutes in diagnostic or follow-up evaluations of children with renal lithiasis.
ObjectivesThe objective of this study was to correlate urine elimination of substances related to renal lithiasis that depend on the volume of excreted urine in a unit of time with other parameters that are calculated by measuring the concentration of these substances in blood and urine, such as urinary ratios, fractional excretions and excretion rates.
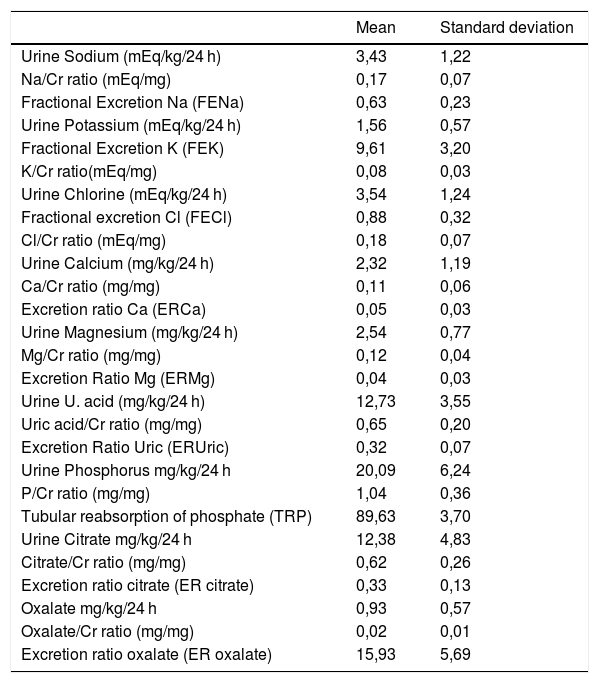
Materials and methodsThe study included 401 healthy children aged 3–14 years (187 boys and 214 girls), mean age 8,78 ± 3,40 years. The analysis was carried out by Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
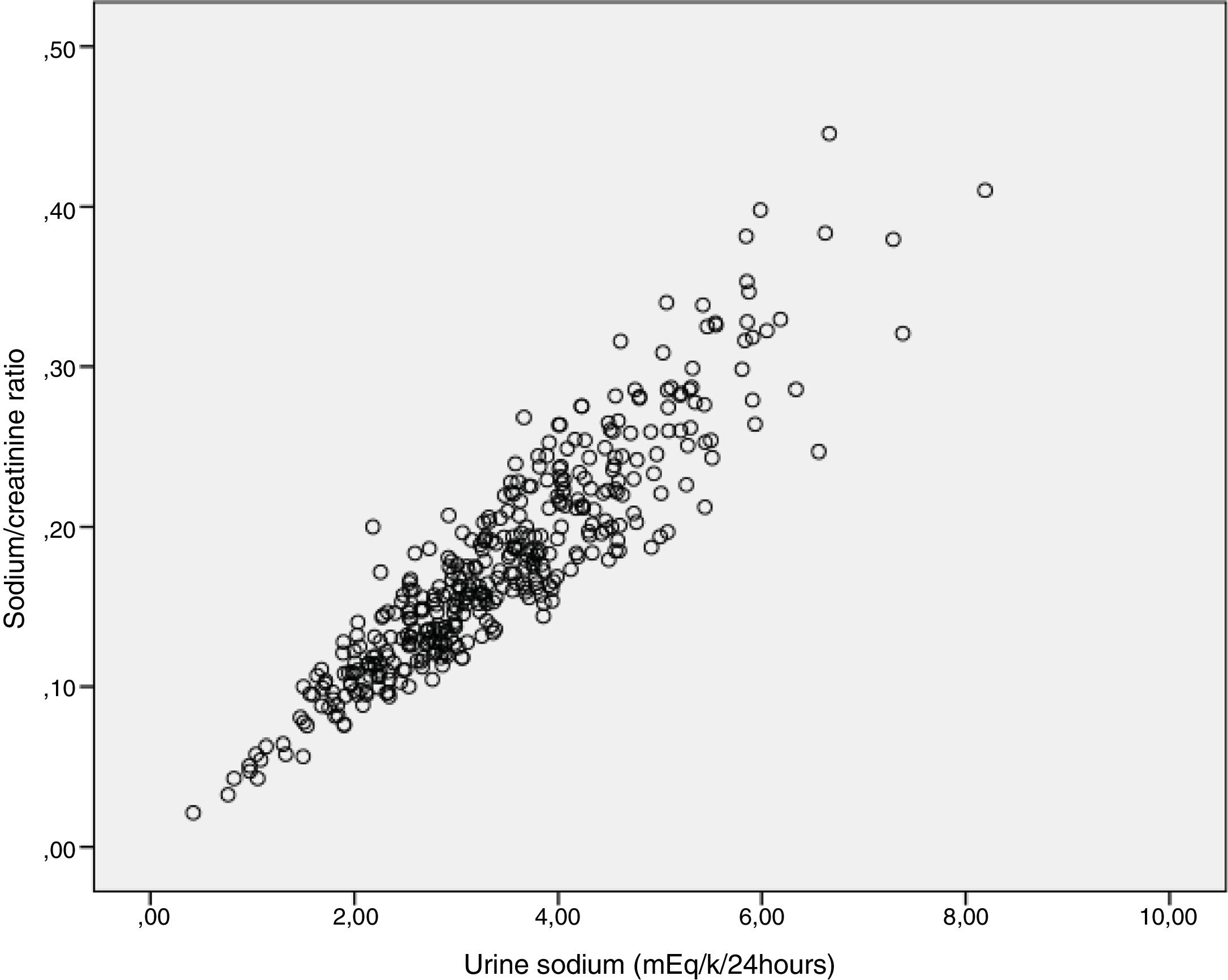
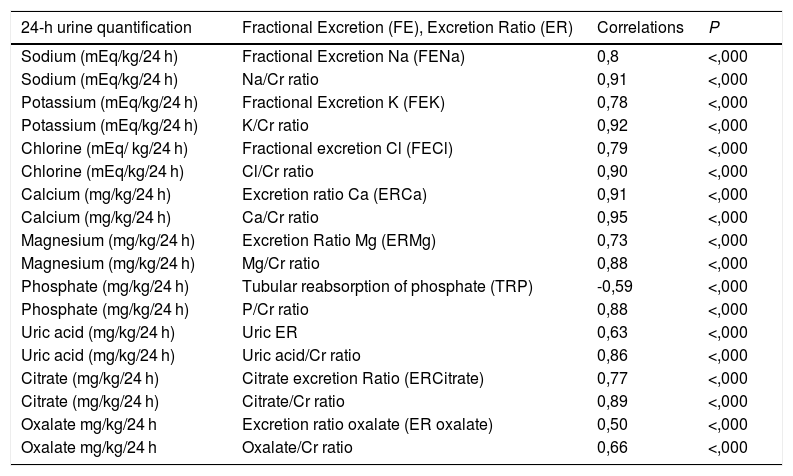
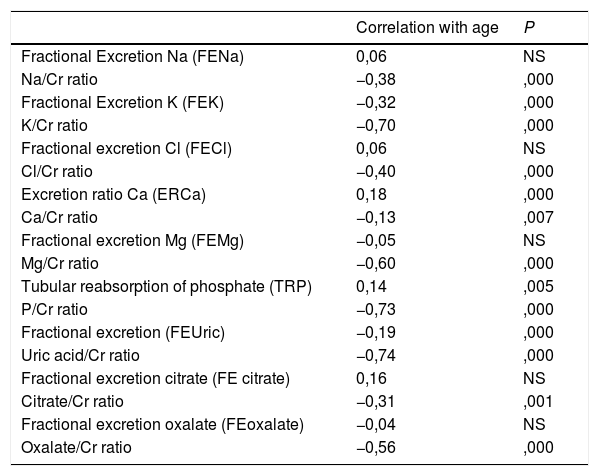
ResultsThere was significant correlation between the elimination of sodium, potassium and chlorine in 24-h urine sample and the urinary ratios and fractional excretions of these ions.
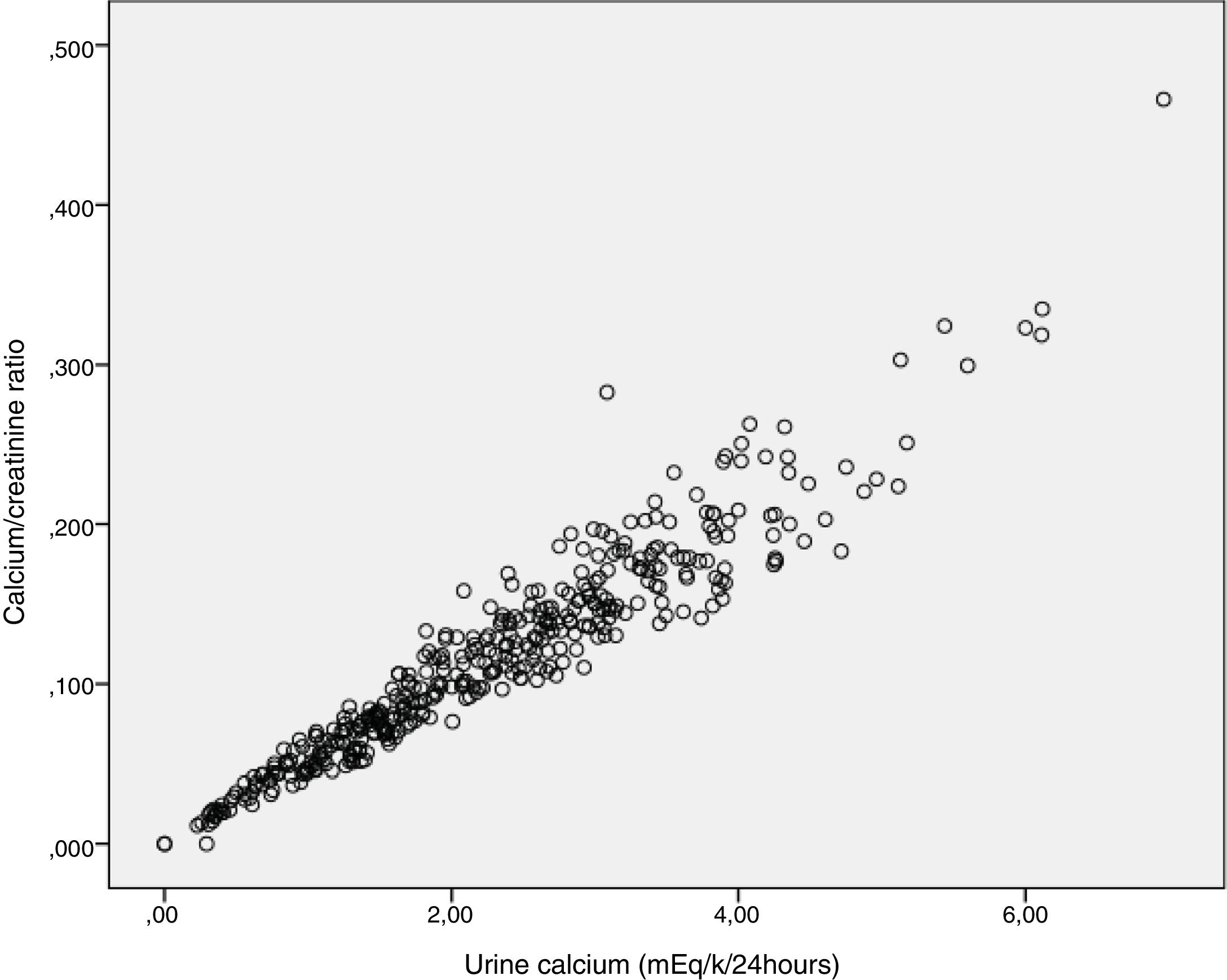
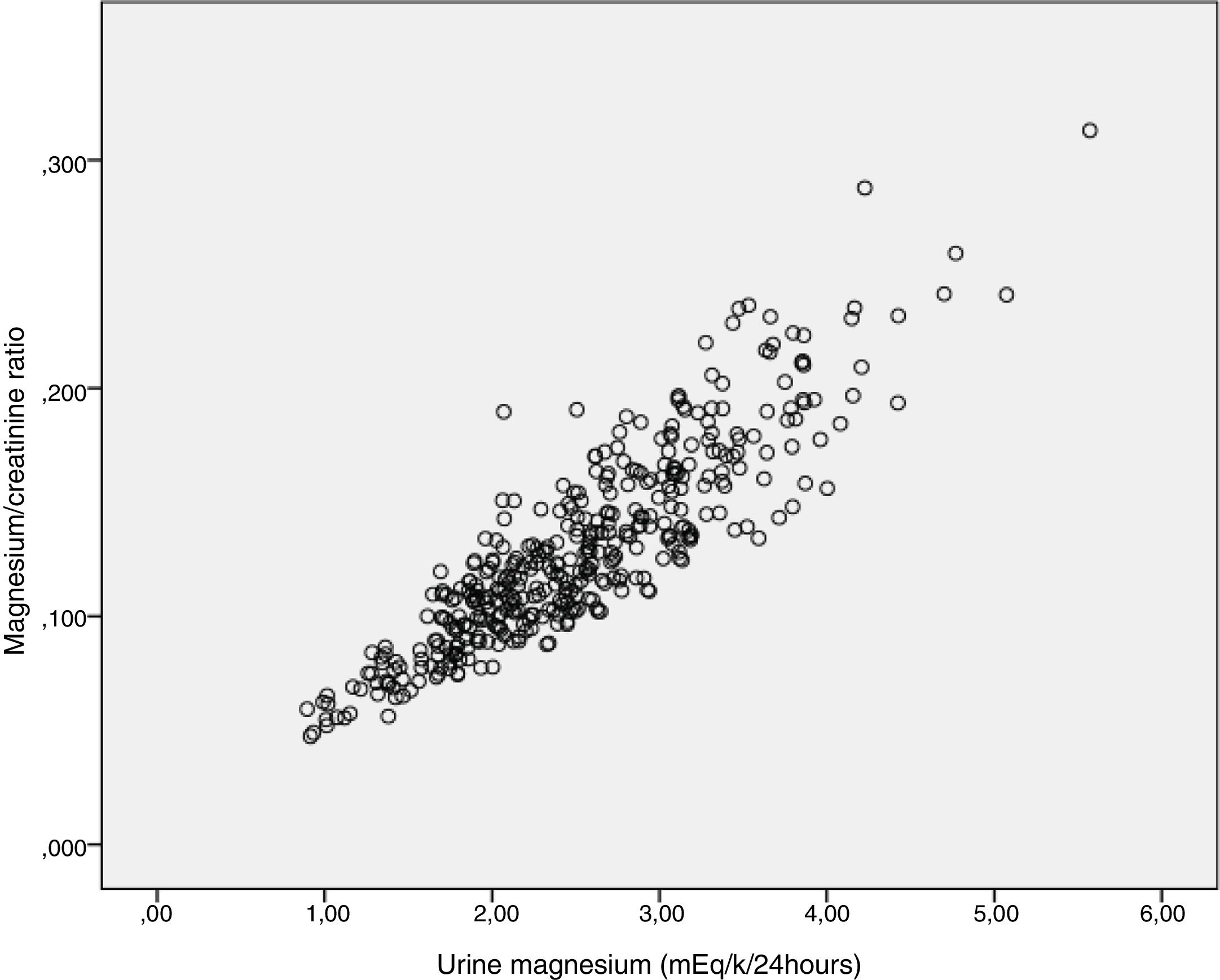
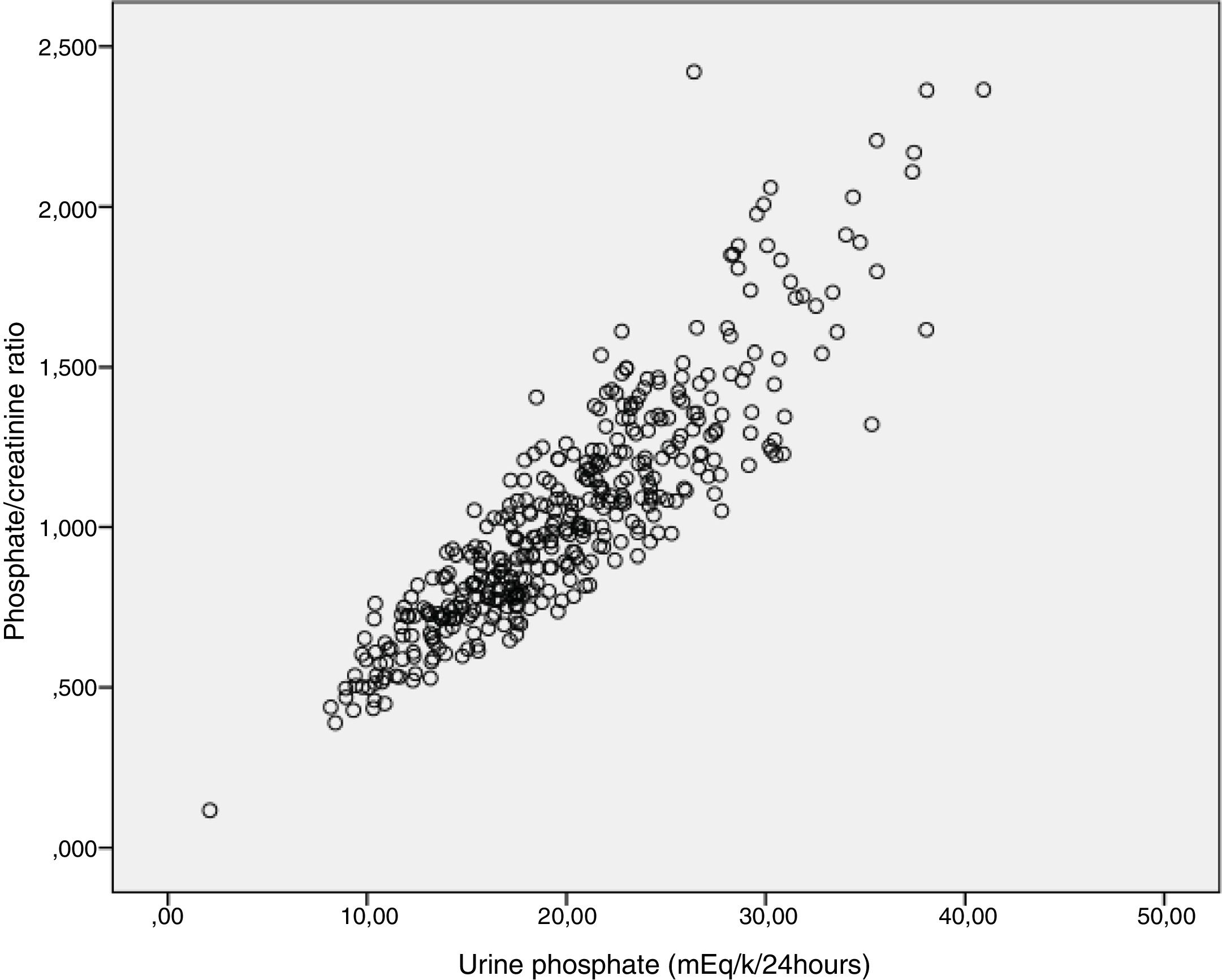
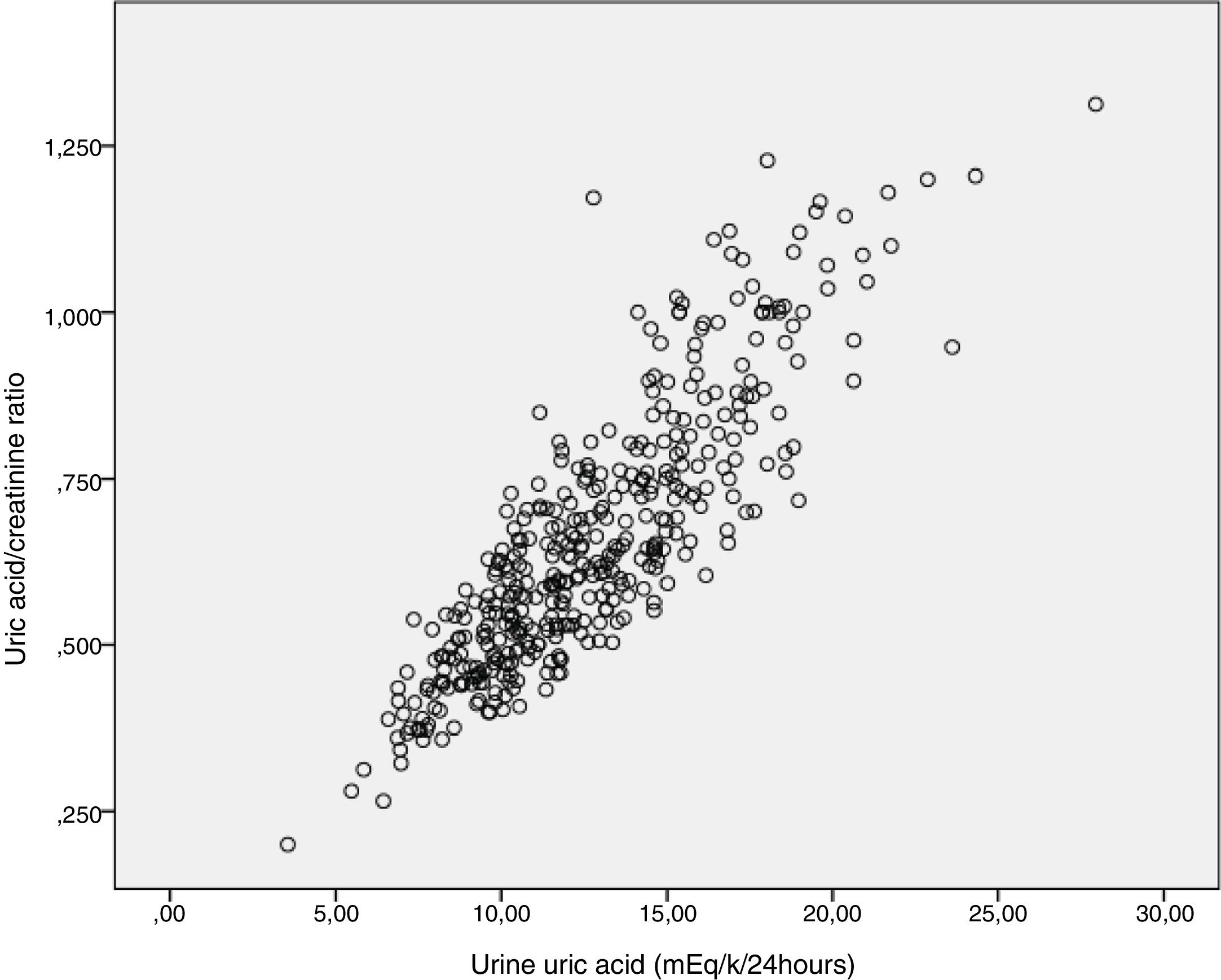
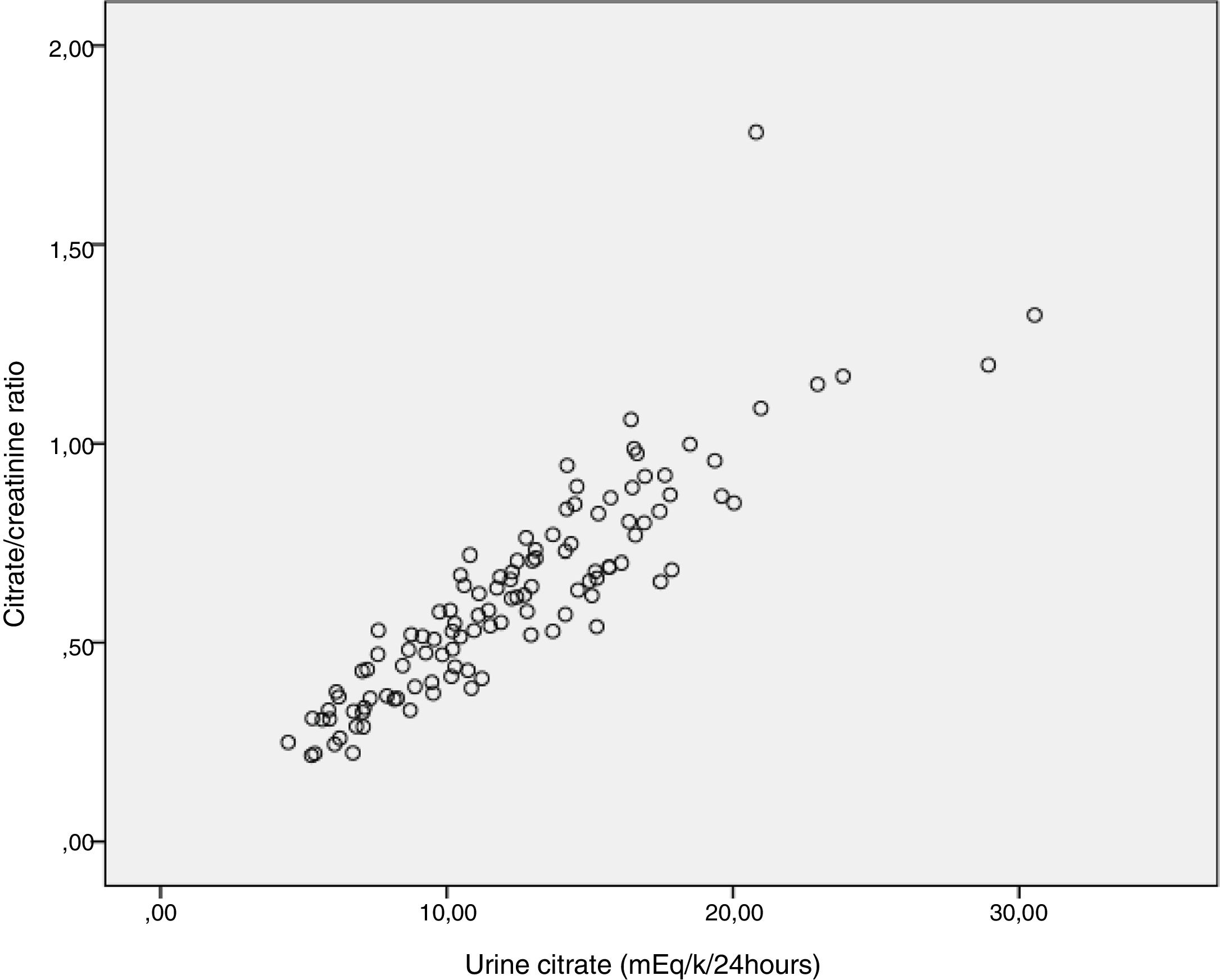
Urinary ratios and rates of excretion of calcium, uric acid, phosphate, magnesium, citrate and oxalate were highly correlated with the determinations of these substances in 24-h collections.
ConclusionsThese equations provide relevant information for the study of the etiology of renal lithiasis in children, as well as about compliance to dietary treatment. They also assess the effectiveness of the various treatments used in these patients, without having to resort to 24-h collections, which pose a considerable challenge in the pediatric age group.
En la práctica diaria es necesario disponer de métodos rápidos, sencillos y accesibles para valorar adecuadamente la excreción urinaria de solutos en los estudios destinados al diagnóstico o seguimiento de los niños con litiasis renal.
ObjetivosLos objetivos de este trabajo fueron relacionar la eliminación urinaria de los metabolitos vinculados con la litiasis renal que dependen del volumen de orina expulsada en una unidad de tiempo, con otros parámetros que se calculan midiendo la concentración de estas sustancias en sangre y en orina, entre los cuales se incluyen los cocientes urinarios, excreciones fraccionales e índices de excreción.
Material y métodosEl estudio incluyó 401 niños sanos de 3–14 años (187 niños y 214 niñas),con una edad media de 8,78 ± 3,40. El análisis se realizó mediante el coeficiente de correlación de Pearson.
ResultadosExistía una muy buena correlación, entre los valores de la eliminación cuantificada en orina de 24 horas de sodio, potasio y cloro con los Cocientes urinarios y las Excreciones Fraccionales de estos iones.
Los cocientes urinarios e Índices de excreción de calcio, ácido úrico, fosfato, magnesio, citrato y oxalato mostraron una excelente correlación con las determinaciones de estas sustancias en orina de 24 horas.
ConclusionesEstas ecuaciones proporcionan una información muy útil en el estudio de la etiología de la litiasis renal en los niños, así como en la adherencia al tratamiento dietético. También valora la eficacia de los distintos tratamientos utilizados en estos pacientes, sin tener que recurrir a la orina minutada que presenta grandes dificultades en pediatría.