The aim of this study is to evaluate and compare erection function (EF) after Excision and Primary Anastomosis Urethroplasty (EPAU) and Buccal Mucosal Graft Urethroplasty (BMGU) in bulbar urethral stricture.
MethodsPatients who underwent urethroplasty were identified retrospectively. The criteria for inclusion in the study were determined as being over 18 years old and under 70 years old, being sexually active. Exclusion criteria are; preoperative severe erectile dysfunction, stricture outside the bulbar urethra, psychosocial incompatibility, urethral stricture related to pelvic fracture, follow-up time less than a year. As the primary endpoint, the International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5) was determined as a comparison of EF in the preoperative and third, sixth and twelfth months after surgery. The secondary endpoint was the evaluation of the effects of demographic data, stricture and treatment characteristics on EF.
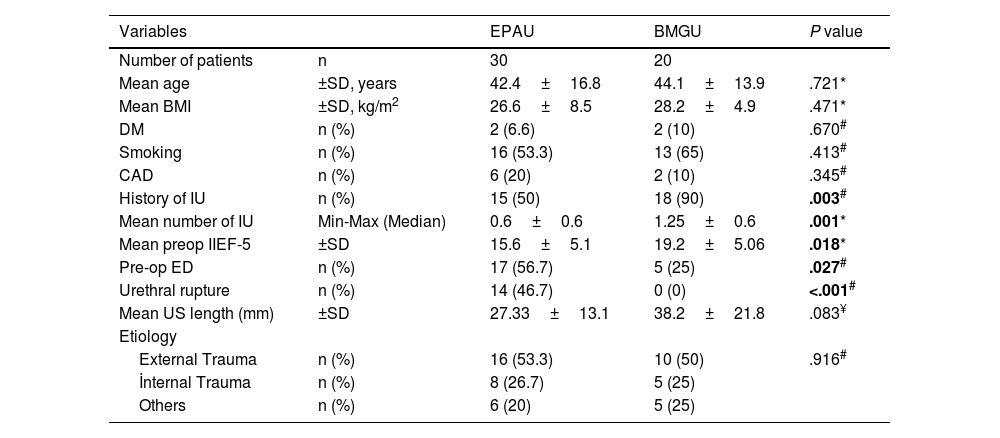
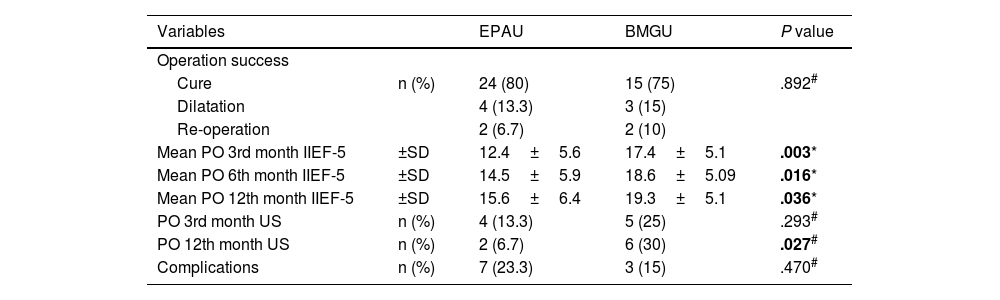
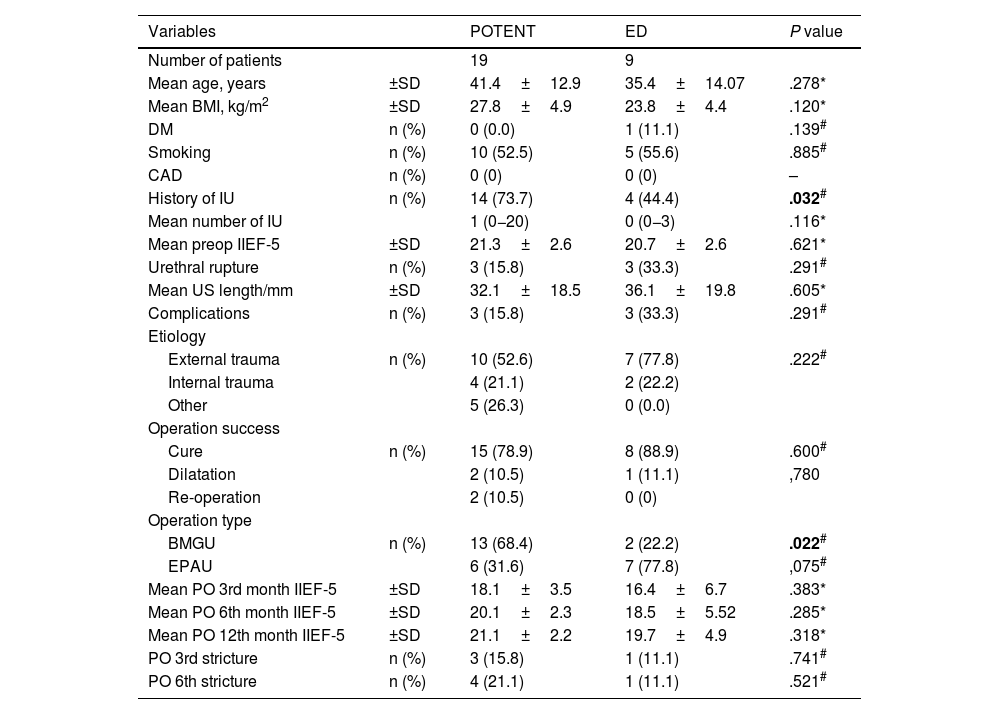
ResultsFifty patients were identified considering the inclusion/exclusion criteria. It was observed that there were 30 patients who underwent EPAU and 20 patients who underwent BMGU. At the third month after surgery, EF showed a statistically significant decrease in the EPAU group. In both patient groups, it was observed that the early negative effects after the operation in EF started to improve in the sixth month and returned to the baseline level by the first year.
ConclusionEPAU and BMGU techniques have a similar effect on EF in the medium and long term. Both methods can be used safely and effectively in the appropriate patient group.
El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar y comparar la función eréctil (FE) tras la uretroplastia por escisión y anastomosis primaria (UEAP) y la uretroplastia con injerto de mucosa oral (UIMO) en la estenosis de uretra bulbar.
MétodosSe identificaron retrospectivamente los pacientes sometidos a uretroplastia. Se determinaron como criterios de inclusión en el estudio la edad entre 18 años y 70 y ser sexualmente activo. Los criterios de exclusión fueron la disfunción eréctil grave preoperatoria, estenosis distinta de la uretra bulbar, incompatibilidad psicosocial, estenosis uretral relacionada con fractura pélvica y tiempo de seguimiento inferior a un año. Como criterio de valoración primario, se utilizó el IIEF-5 (International Index of Erectile Function-5) para la comparación de la FE en el preoperatorio y en el tercer, sexto y duodécimo mes tras la intervención quirúrgica. El criterio de valoración secundario fue el efecto de los datos demográficos, las características de la estenosis y del tratamiento sobre la FE.
ResultadosTras aplicar los criterios de inclusión/exclusión se identificaron 50 pacientes. De ellos, 30 fueron sometidos a UEAP y 20 a UIMO. Al tercer mes de la intervención, la FE mostró una disminución estadísticamente significativa en el grupo UEAP. En ambos grupos de pacientes se observó una mejoría de los efectos negativos postoperatorios sobre la EF en el sexto mes, recuperando su nivel basal a los 12 meses.
ConclusiónLas técnicas UEAP y UIMO tienen un efecto similar sobre la FE a medio y largo plazo, y ambas pueden utilizarse con seguridad y eficacia en el grupo de pacientes adecuado.