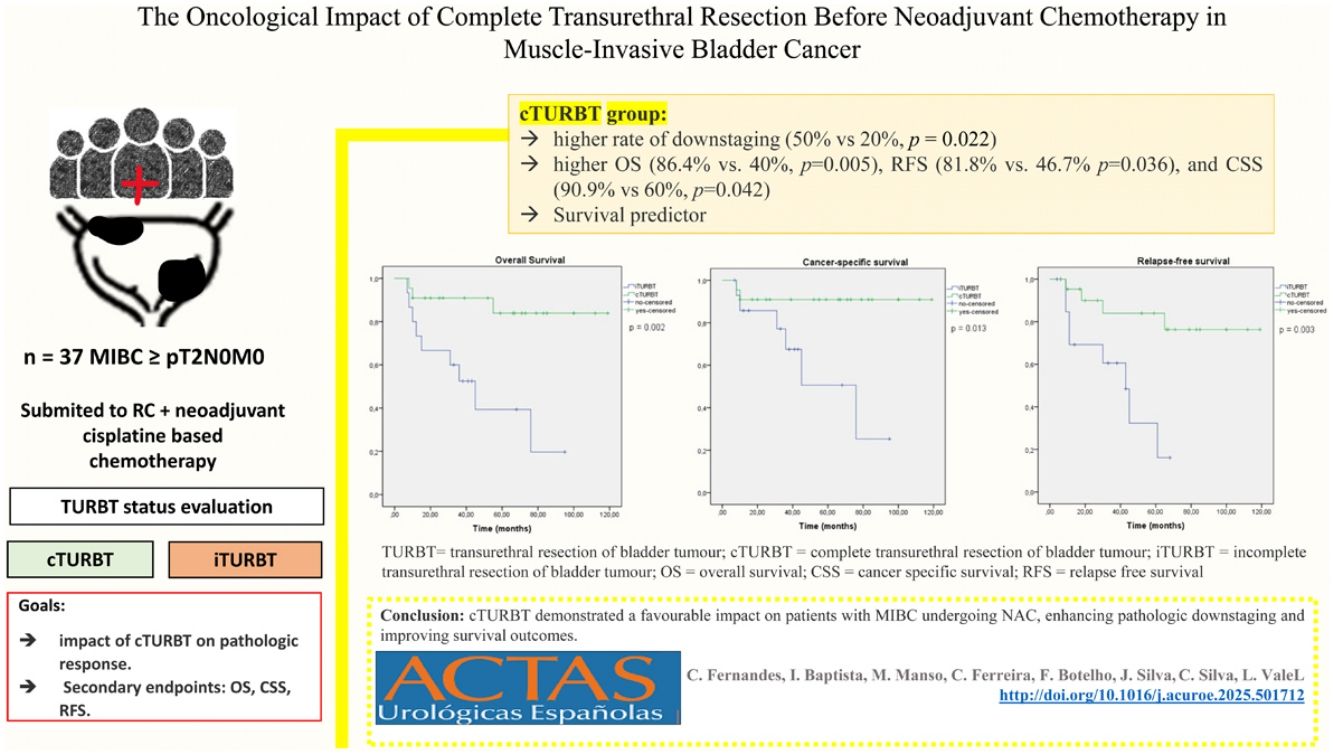
To assess the impact of cTURBT on pathologic response. Secondary endpoints involved survival and oncologic outcomes.
MethodsTertiary centre data from patients with MIBC submitted to NAC and radical cystectomy between March 2010 and November 2022 was retrospectively analysed. Patients with complete resection (cTURBT) before NAC were compared to those with incomplete (iTURBT).
ResultsThirty-seven patients were included in this study. NAC regime was identical between groups. cTURBT group demonstrated a higher rate of downstaging than the iTURBT group (50% vs 20%, p = 0.022). During the mean 49-month follow-up period, overall survival (86.4% vs. 40%, p=0.005), relapse-free survival (81.8% vs. 46.7% p=0.036), and cancer-specific survival (90.9% vs 60%, p=0.042) were higher in the cTURBT group. Furthermore, we observed significantly fewer relapses, higher survival rates, and lower oncological-related deaths in patients who exhibited downstaging.
ConclusioncTURBT demonstrated a favourable impact on patients with MIBC undergoing NAC, enhancing pathologic downstaging and improving survival outcomes. Our results can be confounded by cTURBT being a proxy for less aggressive disease.
Evaluar el impacto de la resección transuretral del tumour vesical completa (RTUVc) en la respuesta patológica. Los criterios de valoración secundarios fueron la supervivencia y los resultados oncológicos.
MétodosSe analizaron de forma retrospectiva los datos de pacientes con cáncer vesical músculo invasor (CVMI) sometidos a quimioterapia neoadyuvante (QNA) y cistectomía radical en un centro terciario entre marzo de 2010 y noviembre de 2022. Se compararon los resultados de los pacientes que sometidos a RTUVc antes de QNA con los de los pacientes sometidos a una resección incompleta (RTUVi).
ResultadosUn total de 37 pacientes fueron incluidos en este estudio. El esquema de QNA fue igual para todos los grupos. El grupo RTUVc demostró mayores tasas de reducción del estadio que el grupo RTUVi (50% frente a 20%, p=0,022). Durante el periodo medio de seguimiento de 49 meses, la supervivencia global (86,4% frente a 40%, p=0,005), la supervivencia libre de recidiva (81,8% frente a 46,7%, p=0,036) y la supervivencia específica del cáncer (90,9% frente a 60%, p=0,042) fueron superiores en el grupo RTUVc. Además, observamos un número significativamente menor de recidivas, tasas de supervivencia más elevadas y una menor mortalidad por cáncer en los pacientes que presentaban un descenso del estadio.
ConclusiónLa RTUVc demostró un impacto favorable en los pacientes con CVMI sometidos a QNA, aumentando las tasas de reducción del estadio patológico y mejorando los resultados de supervivencia. Nuestros resultados pueden generar confusión por el hecho de que la RTUVc sea un indicador indirecto de enfermedad menos agresiva.