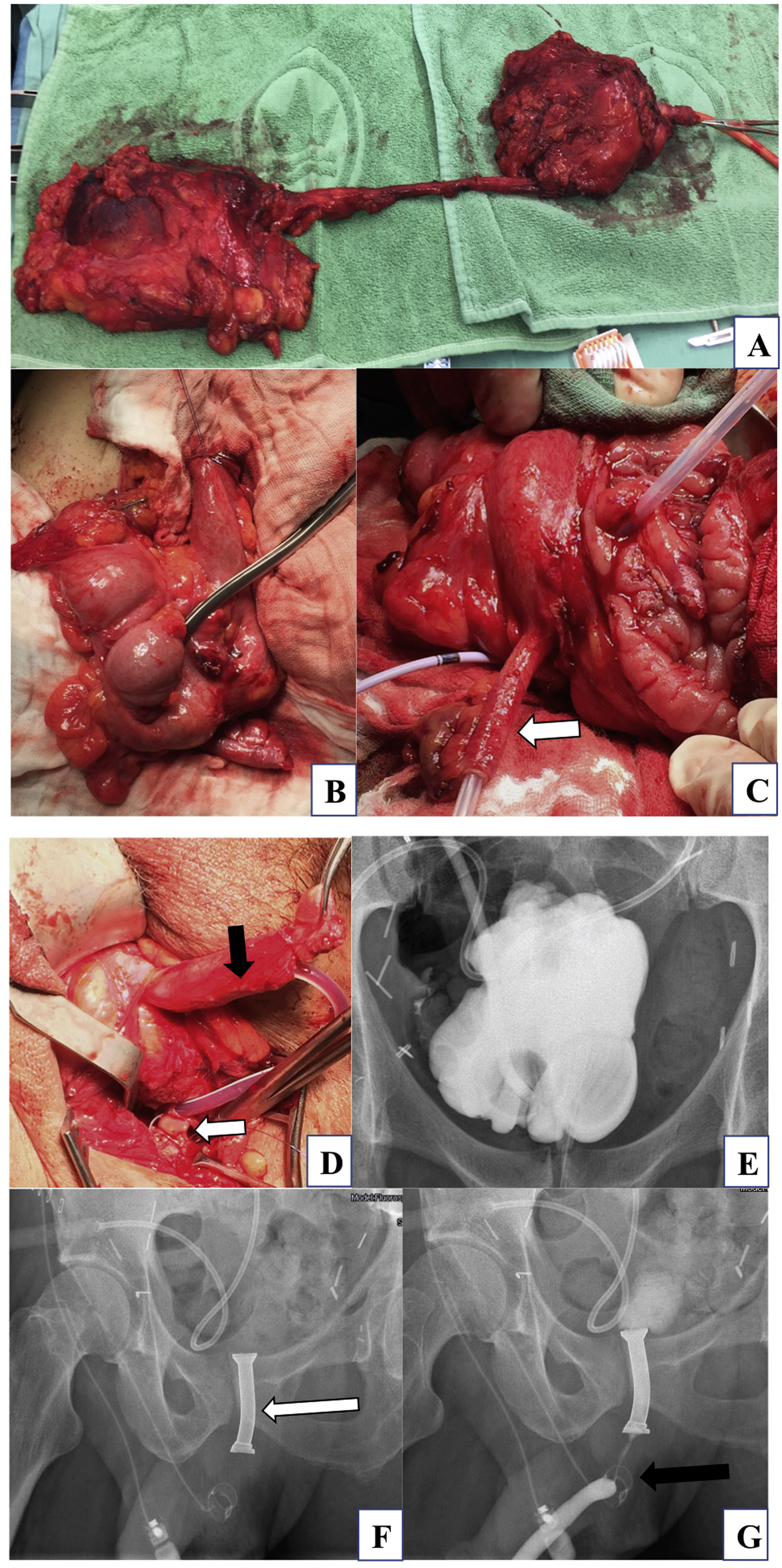
The authors describe the technique of orthotopic bladder replacement with an ileocecal pouch and unaltered appendix used as an orthotopic urethral substitute. Additional procedures with regard to the bothersome voiding symptoms will be described.
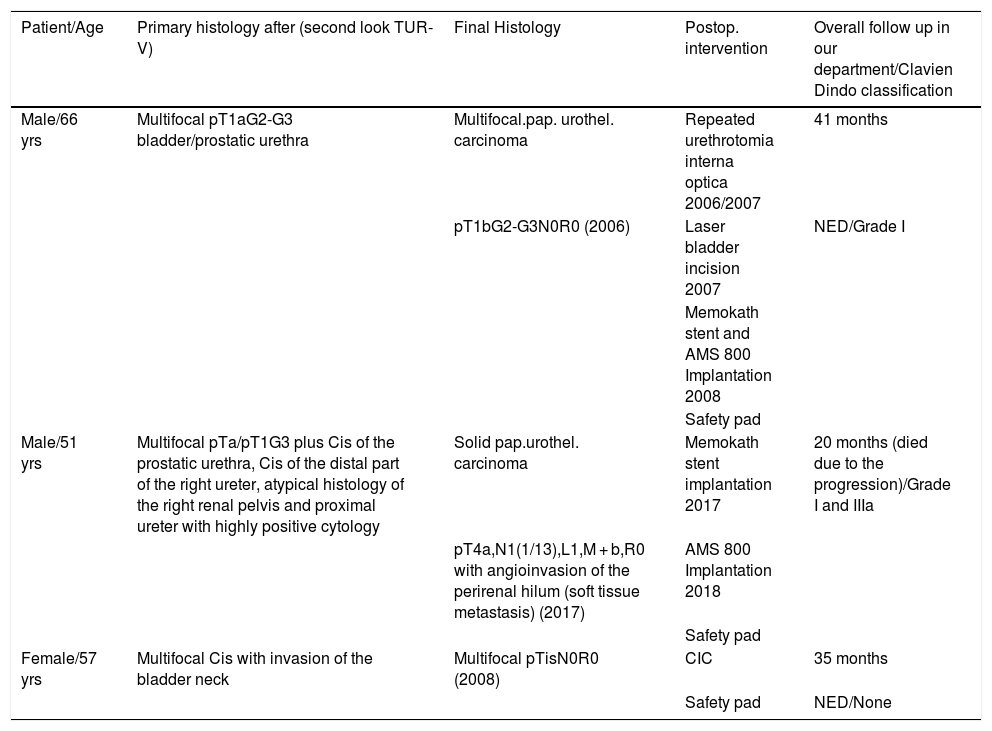
Material and methodsIn a small cohort of 5 patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with tumor involvement of the bladder neck or proximal urethra (2 males/3 females) we performed the following reconstruction. A low pressure reservoir was achieved by antimesenteric longitudinal transection of terminal ileum and cecum/colon ascendens and formation of a pouch. To develop the neourethra, the appendix together with it is accompanying mesentery was drawn through the pelvic floor and sutured to the bulbar urethra in males or formed as a complete neourethra in female patients respectively.
ResultsThere were no intraoperative nor early postoperative unwanted sequelae. Both male patients experienced recurrent anastomotic urethral stricture, consequently a Memokath stent and artificial urinary sphincter was implanted resulting in normal voluntary micturition. All female patients remained socially continent during the follow up period, one of them performing (clean intermittent catheterization) CIC.
ConclusionThe technique described offers the possibility of orthotopic bladder replacement even in traditionally unsuitable, but highly motivated patients, who are requesting orthotopic bladder replacement for improved body image. It allows extension of urethral resection and provides additional continence support. However, additional measures such as urethral stenting, CIC or artificial urinary sphincter implantation may be necessary for long lasting success. Although, not being a routine method for urinary diversion this technique may be used in select patients.
Los autores describen la técnica de sustitución vesical ortotópica mediante bolsa ileocecal y apéndice inalterado como sustituto ortotópico de la uretra. Se describirán procedimientos adicionales con respecto a las molestias por síntomas de vaciado.
Material y métodosEn una pequeña cohorte de 5 pacientes con cáncer de vejiga musculo-invasivo con afectación tumoral del cuello vesical o de la uretra proximal (2 hombres/3 mujeres) realizamos la siguiente reconstrucción. Se obtuvo un reservorio de baja presión mediante la incisión longitudinal antimesentérica del íleon terminal y el ciego/colón ascendente y la formación de una bolsa. Para desarrollar la neouretra, el apéndice y su mesenterio se extrajeron a través del suelo pélvico y se suturó a la uretra bulbar en los hombres o se formó como una neouretra completa en las mujeres respectivamente.
ResultadosNo hubo secuelas indeseables intraoperatorias ni postoperatorias tempranas. Ambos pacientes masculinos experimentaron una estenosis de la anastomosis uretral recurrente, por lo que se realizó un implante de stent Memokath y un esfínter urinario artificial, resultando en una micción voluntaria normal. Todas las pacientes femeninas permanecieron socialmente continentes durante el período de seguimiento, una de ellas realizando cateterismo intermitente limpio (CIL).
ConclusiónLa técnica descrita ofrece la posibilidad la sustitución vesical ortotópica incluso en pacientes tradicionalmente considerados como no aptos, pero muy motivados, que lo solicitan para mejorar su imagen corporal. Permite ampliar la resección uretral y proporciona un apoyo adicional a la continencia. Sin embargo, pueden ser necesarias medidas adicionales como la colocación de un stent uretral, el CIL o el implante de un esfínter urinario artificial para obtener un éxito duradero. Aunque no es un método rutinario de derivación urinaria, esta técnica puede utilizarse en pacientes seleccionados.