To evaluate the incidence and course of urinary tract infections (UTI) in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) and their relationship to the method of bladder evacuation.
Materials and MethodsPatients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction due to MS (n=111) were enrolled in the study. During one-year follow-up, clinical examination with urine culture was performed every 4 months or whenever symptoms occurred. The control group included patients with symptomatic UTI, without neurological or autoimmune disease. Incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic bacteriuria, the effect of urine drainage on UTI incidence, and the effect of antibiotics were statistically evaluated.
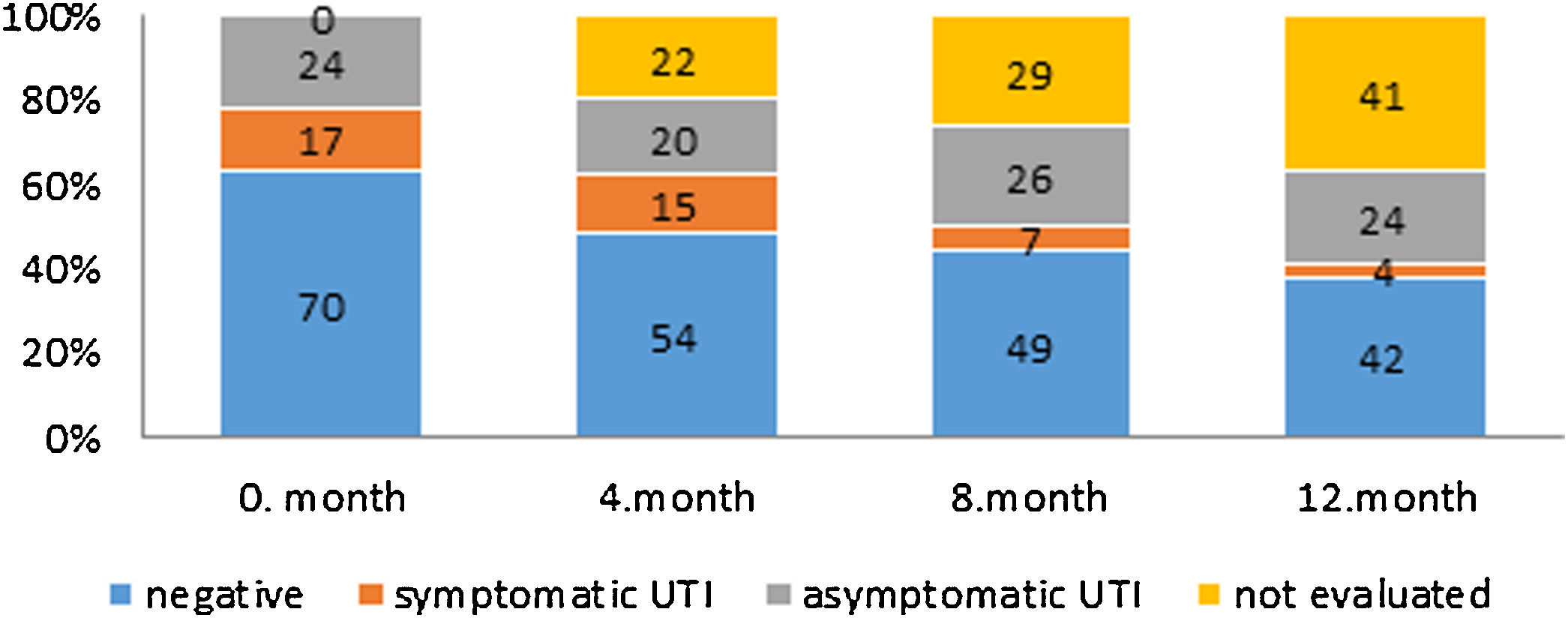
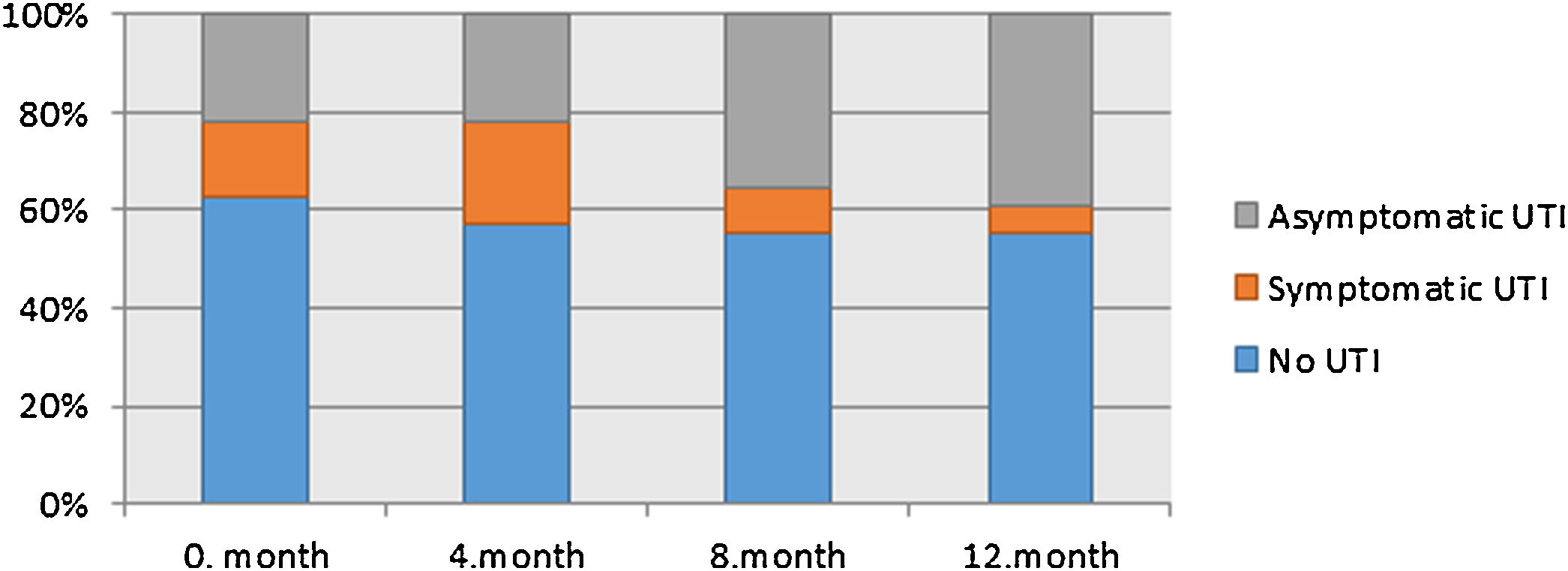
Results54 MS patients completed the protocol. The mean incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic bacteriuria in the MS group was 12.5% and 29.6%, respectively. A decreasing trend in the incidence of symptomatic, and an increasing trend in the incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria was observed. Eradication of UTI in symptomatic MS patients was significantly lower than in controls (37.75% vs. 92.93%, P<0.05). Causative agents significantly differed in both groups (P=0.0005). The hypothesis that the incidence of UTIs in MS patients is independent of the method of bladder evacuation was not rejected (P>0.99 at visit 0, 1 and 3, P=0.078 at visit 2).
ConclusionsThere is a significant difference between the causative agents of UTI in both groups. Eradication of bacteriuria in symptomatic MS patients is difficult when compared to the normal population. We have insufficient evidence to confirm the relationship between the incidence of UTI and the method of bladder evacuation.
Evaluar la incidencia y la evolución de las infecciones del tracto urinario (ITU) en pacientes con esclerosis múltiple (EM) y su relación con el sistema de vaciado vesical.
Materiales y métodosSe incluyeron en el estudio pacientes con disfunciones miccionales neurógenas debido a la EM (n=111). Durante un año de seguimiento, se realizó una evaluación clínica con cultivo de orina cada 4 meses o ante la presencia de síntomas. El grupo de control incluyó a pacientes con ITU sintomática sin enfermedad neurológica o autoinmune. Se evaluó estadísticamente la incidencia de bacteriuria sintomática y asintomática, el efecto del drenaje urinario en la incidencia de ITU y el efecto del tratamiento antibiótico.
Resultados54 pacientes con EM completaron el protocolo. La incidencia media de bacteriuria sintomática y asintomática en el grupo de EM fue del 12,5% y del 29,6%, respectivamente. Se observó una tendencia decreciente en la incidencia de la bacteriuria sintomática y una tendencia creciente en la incidencia de la asintomática. La erradicación de la ITU en los pacientes sintomáticos con EM fue significativamente menor que en los controles (37,75% frente a 92,93%, P<0,05). Los agentes causales fueron significativamente diferentes en ambos grupos (P=0,0005). No se rechazó la hipótesis de que la incidencia de ITU en los pacientes con EM es independiente del sistema de evacuación vesical (P>0,99 en las visitas 0, 1 y 3, P=0,078 en la visita 2).
ConclusionesExiste una diferencia significativa entre los agentes causales de la ITU en ambos grupos. La erradicación de la bacteriuria en los pacientes sintomáticos con EM es difícil en comparación con la población normal. No disponemos de pruebas suficientes para confirmar la relación entre la incidencia de ITU y el sistema de evacuación vesical.