Toothpastes are definitely one of the indispensable elements of oral health care. They are produced to serve multiple purposes and possess complex chemical structures. Slight abrasion, froth, sweetening, bleaching, prevention of plaque, calculus and decay are properties expected from an ideal toothpaste. In recent years, allergic reactions have started to appear more frequently in dental practice. The present case describes the progression of an allergic response to toothpastes, one of the basic agents of oral hygiene.
It has been concluded in many studies that the presence of dental plaque is one of the most significant etiological factors of dental caries and periodontal diseases1–5. Although different methods have been suggested for the removal of dental plaque, there is a general consensus among researchers that mechanical treatment is the most efficient method to serve this purpose1,3,6. Toothpastes are additional elements used in the removal of dental plaque along with toothbrushes. Research so far has indicated that toothpastes having abrasives prevent the accumulation of dental plaque7,8.
The effectiveness of toothpastes significantly increases by the addition of surface-active agents. These surface-active materials not only provide the effervescent action of dental toothpastes and enhance the removal of food particles but they also help in the distribution of the toothpaste in the oral cavity1. In the past, toothpastes were supplied with soap to serve this purpose. Nowadays, synthetic detergents are used instead. Sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) and sodium lauryl sarcosinate are the two most common surface-active agents9. Industrially, SLS is used in hard surface cleansing products, grease cleaners, car washing and detergents, personal hygiene products such as shampoos and shower gels, bath foams, face cleansing soaps, and toothpastes as detergents and foaming agents. The frequent use of this material leads to multiple allergic and toxic reactions10–14. Systemic ingestion of SLS compounds may also exert a carcinogenic effect.
CASE REPORTA 25-year-old male patient presented to our clinic with complaints of dentinal hypersensitivity and gingival bleeding. Intraoral examination revealed a dense accumulation of calculus and dental plaque corresponding to the maxillary left second premolar and molar regions. A periapical radiograph taken from these regions indicated the presence of deep dentinal caries lesions. Prior to restorative treatment, a periodontal scaling was carried out. The patient was instructed about brushing methods and the utilisation of dental floss and mouth rinse. He indicated that he had been well informed about these methods previously, but he was unable to practice any due to abdominal gases, bloating, cramps, and diarrhoea, which occurred after brushing using toothpaste.
The medical history showed that the first symptoms had started seven years before, which led the patient to consult a physician. He was informed that his complaints may be due to appendicitis and he underwent an appendectomy. The symptoms did not subside following surgery and, after an examination by a gastroenterologist, it was concluded that there may be psychological implications. Although the patient used different brands of toothpastes in the market, symptoms such as nausea, abdominal gases, bloating, and diarrhoea persisted. The patient added that he experienced no problems while using mouth rinses.
Clinical EvaluationThe patient's complaints raised suspicion about the ingredients of toothpastes. A thorough review of the literature also indicated that contact allergy of toothpastes containing SLS may cause repetitive aphthous ulcerations, and oral lesions12–14.
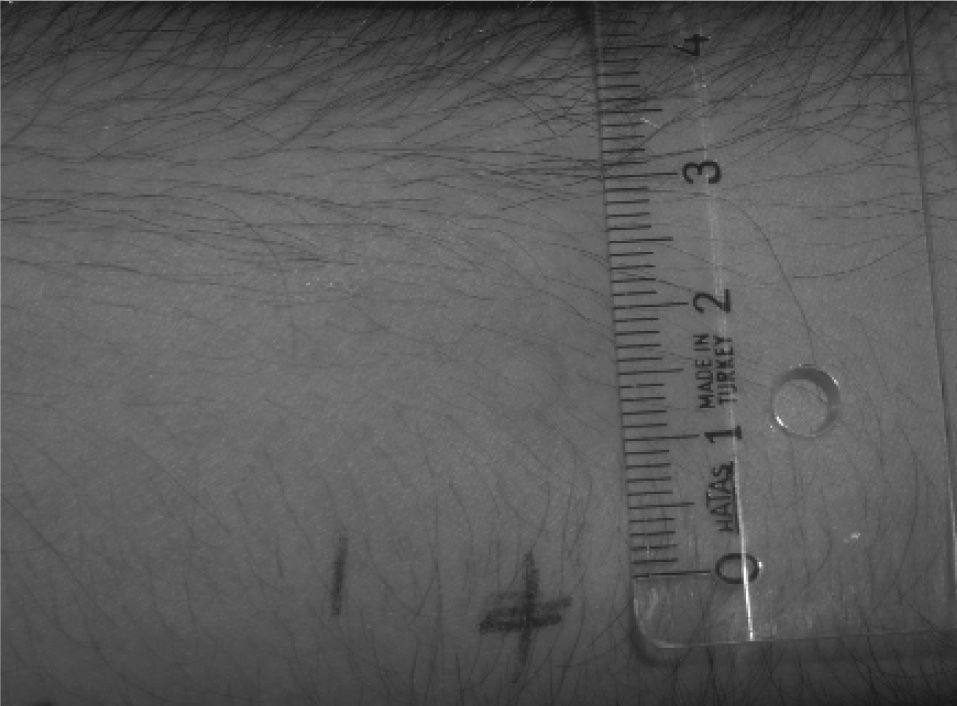
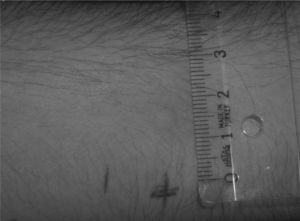
Three samples of toothpaste were prepared in the laboratory; only one of which did not contain SLS. The patient was blind to the toothpastes. Each of them was used on consecutive days. The symptoms occurred with two of them but not with the one which did not contain SLS. To evaluate SLS's allergenicity, skin prick testing was performed. The sterile SLS stock solution containing 1mg/ml SLS was obtained with the help of the Pharmacy Faculty. The stock solution was diluted to 10-4, 10-3, 10-2, 10-1 dilutions with buffered distilled water, as based on a protocol previously described for drug allergy testing15. Prick test was applied to the patient's forearm beginning with the 10-4 dilution. The wheal and flare reaction were compared to the histamine 10mg/ml prick test reaction as a positive control. At least the half size of histamine reaction or 3mm or more wheal diameter was accepted as positive16. The patient was reacted at 10-3 dilution test with 6mm wheal and 30mm flare; and the procedure was stopped. The prick test confirmed that the patient was allergic to SLS (Fig. 1 and 2). The patient has been using SLS free toothpaste for nearly one year without any adverse reactions.
Sodium lauryl sulphate, one of the chemical additives in the composition of toothpastes, is one of the leading products that cause local and systemic reactions17.
It has been reported in some studies that the utilisation of toothpastes may cause acute toxic reactions such as oral lesions, aphthous ulcerations, and xerostomia12–14,18,19. Although the chronic toxic effects of SLS are observed mainly in lungs, there has not been sufficient research to confirm this finding.
The patient's complaints such as abdominal gas and cramps, bloatedness and diarrhoea support our hypothesis that SLS may be an allergic material. Similarly, the fact that no symptoms occurred following brushing with the SLS free laboratory product and the positive result of the prick test confirms our result16.
Researchers have concluded that the local application of toothpastes containing SLS may cause oral lesions whereas carcinogenic effects may ensue with systemic usage10,12–14,19–21.
The initiation of reactions immediately after the utilisation of the toothpaste containing SLS suggests that they may result from the absorption of the material sublingually or from the oral mucosa.
Nowadays, allergic reactions may occur due to many chemical products. Synthetic materials added in the composition of toothpastes may lead to allergic reactions of varying severity.
CONCLUSIONToothpastes are one of the indispensable elements of oral healthcare. It is also a fact that they may contain allergenic synthetic products. Dental practitioners as well as health care providers must be aware of the possibility of allergic reactions and should take all necessary precautions. Furthermore, the selection of natural additives instead of artificial products in toothpastes may exert a positive influence on the prevention of allergic reactions.